| Millennium: | 2nd millennium |
|---|---|
| Centuries: | |
| Decades: | |
| Years: |
| 1205 by topic |
|---|
| Leaders |
| Birth and death categories |
| Births – Deaths |
| Establishments and disestablishments categories |
| Establishments – Disestablishments |
| Art and literature |
| 1205 in poetry |
| Gregorian calendar | 1205 MCCV |
| Ab urbe condita | 1958 |
| Armenian calendar | 654 ԹՎ ՈԾԴ |
| Assyrian calendar | 5955 |
| Balinese saka calendar | 1126–1127 |
| Bengali calendar | 611–612 |
| Berber calendar | 2155 |
| English Regnal year | 6 Joh. 1 – 7 Joh. 1 |
| Buddhist calendar | 1749 |
| Burmese calendar | 567 |
| Byzantine calendar | 6713–6714 |
| Chinese calendar | 甲子年 (Wood Rat) 3902 or 3695 — to — 乙丑年 (Wood Ox) 3903 or 3696 |
| Coptic calendar | 921–922 |
| Discordian calendar | 2371 |
| Ethiopian calendar | 1197–1198 |
| Hebrew calendar | 4965–4966 |
| Hindu calendars | |
| - Vikram Samvat | 1261–1262 |
| - Shaka Samvat | 1126–1127 |
| - Kali Yuga | 4305–4306 |
| Holocene calendar | 11205 |
| Igbo calendar | 205–206 |
| Iranian calendar | 583–584 |
| Islamic calendar | 601–602 |
| Japanese calendar | Genkyū 2 (元久2年) |
| Javanese calendar | 1113–1114 |
| Julian calendar | 1205 MCCV |
| Korean calendar | 3538 |
| Minguo calendar | 707 before ROC 民前707年 |
| Nanakshahi calendar | −263 |
| Thai solar calendar | 1747–1748 |
| Tibetan calendar | 阳木鼠年 (male Wood-Rat) 1331 or 950 or 178 — to — 阴木牛年 (female Wood-Ox) 1332 or 951 or 179 |
Year 1205 (MCCV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar.
Events
[edit]By place
[edit]Byzantine Empire
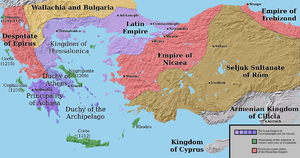
[edit]- Spring – Theodore I Laskaris is proclaimed Byzantine emperor (or basileus), formally founding the Empire of Nicaea, after repelling the invasions of rivals David Komnenos and Manuel Maurozomes into his domains. His appointment is an open challenge to the legitimacy of the Latin emperor Baldwin I, who rules over large parts of the former Byzantine Empire and regards Theodore as a usurper.[1]
- March 19 – Battle of Adramyttion: The Byzantine army, under Constantine Laskaris (brother of Theodore I), appears before the walls of Adramyttium – surprising the Latin garrison. Meanwhile, Henry of Flanders, not wanting to remain trapped within the city, opens the gates and charges out with his heavy cavalry. He and his knights defeat the Byzantine forces, who are scattered and forced to retreat.[2]
- March – Byzantine officials in Adrianople revolt and expel Latin administrators, requesting Bulgarian support from Kaloyan, ruler (tsar) of the Bulgarian Empire, against Baldwin I who assembles an army (some 40,000 men) and marches to aid the Byzantines. Meanwhile, Baldwin sets out from Constantinople in force, he arrives at Adrianople and promptly begins to siege the city by the end of March.
- April 14 – Battle of Adrianople: Latin forces under Baldwin I are defeated and eliminated in a successful ambush by Bulgarians, Vlachs and Cumans. Baldwin is captured and taken as prisoner to Veliko Tarnovo – where he is locked up at the top of a tower in the Tsarevets fortress. Later, Baldwin is possibly executed by orders of Kaloyan (this according to the Byzantine historian George Akropolites).[3]
- Summer – Battle of Koundouros: Byzantine forces (some 5,000 men) under Michael Doukas, governor of the Theme of the Peloponnese (and later Despot of Epirus), tries to stop the Latin army (some 700 knights and foot soldiers) at the Olive Grove of Koundouros. The Byzantines are defeated by William of Champlitte, who later founds the Principality of Achaea (a vassal state of the Latin Empire).
- Othon de la Roche, a Burgundian nobleman, founds the Duchy of Athens (one of the Crusader states set up in Greece) and takes the title of "Grand Lord" (Megaskyr) in Athens.[4]
Europe
[edit]- January 6 – Philip of Swabia becomes King of the Romans and is crowned again with great ceremony at Aachen by Archbishop Adolf of Cologne. After several threats, Adolf is removed from office by Pope Innocent III and excommunicated, on July 19. Philip is able to increasingly assert his kingship against Otto of Brunswick (who is also crowned king of Germany) in the northern parts of the Alps.[5]
- May 29 – Andrew II, brother of the late King Emeric, is crowned ruler of Hungary and Croatia at Székesfehérvár, after his 5-year-old nephew, Ladislaus III, suddenly dies in Vienna. Andrew introduces a new policy for royal grants, which he calls "new institutions". He distributes large portions of his domain–such as royal castles and all estates attached to them–to supporters and Hungarian nobles.[6]
- June 19 – Battle of Zawichost: Polish forces under High Duke Leszek the White defeat the Kievan army at Zawichost. During the ambush, Roman Mstislavich, Grand Prince of Kiev, is killed. He is succeeded by his two infant sons, Daniel and Vasilko. Their principalities are ruled by their mother Anna of Byzantium, but the boyars of Galicia–Volhynia forces her and the young princes into exile.[7]
- Summer – King Philip II ("Augustus") conquers most of the Angevin lands, including much of Aquitaine. Fearing a French invasion of England itself, John, King of England ("Lackland") requires every English male over 12 years to enter a mobilization "for the general defense of the realm and the preservation of peace". John prepares an expedition force of his own, but the barons refuse to cross the Channel.[8]
England
[edit]- William of Wrotham, Lord Warden of the Stannaries, oversees a reform of English currency. In keeping with other high-ranking bureaucrats of his time, this is just one of Wrotham's many offices. He is also "keeper of ports", the forerunner of the First Lord of the Admiralty, supervisor of the mints of Canterbury and London, ward of the vacant Diocese of Bath and Wells and archdeacon of Taunton.[8]
Levant
[edit]- April 1 – Aimery of Cyprus, king of Jerusalem, dies of food poisoning caused by white mullet. He is succeeded by his 9-year-old son Hugh I as ruler of Cyprus. His mother, Queen Isabella I becomes regent over the young boy, but she dies suddenly four days after her husband. The High Court of Cyprus appoints Walter of Montbéliard (brother-in-law of Aimery) as regent and Hugh's guardian.[9]
Africa
[edit]- Caliph Muhammad al-Nasir establishes Almohad domination over the eastern parts of Ifriqiya (modern Tunisia). He appoints General Abu Mohammed ibn Abi Hafs as governor of Ifriqiya.[10]
By topic
[edit]Religion
[edit]- July 15 – Pope Innocent III lays down the principle that Jews are doomed to perpetual servitude, because they had crucified Jesus.
Births
[edit]- January 26 – Emperor Lizong of Song (or Zhao Yun), Chinese emperor (d. 1264)
- March (or May) – Elisabeth of Swabia, queen of Castile and León (d. 1235)[11]
- July 10 – Hōjō Masamura, Japanese nobleman (d. 1273)
- November 5 – As-Salih Ayyub, Ayyubid ruler (d. 1249)
- unknown dates
- Bruno von Schauenburg, Bohemian bishop (d. 1281)[12]
- Wenceslaus I ("the One-Eyed"), king of Bohemia (d. 1253)[13]
- probable
- Azzo VII d'Este, Italian nobleman and knight (d. 1264)[14]
- Batu Khan, Mongol ruler of the Golden Horde (d. 1255)[15]
- Walter IV ("the Great"), French nobleman (d. 1246)[16]
Deaths
[edit]- January 2 – Baldwin II, Count of Guînes, French nobleman and knight
- April 1 – Aimery of Cyprus (or Amaury), king of Jerusalem
- April 5 – Isabella I, queen and regent of Jerusalem (b. 1172)
- April 14
- Garnier de Traînel (or Traisnel), French bishop
- Louis I, French nobleman and knight (b. 1172)
- May 7 – Ladislaus III, king of Hungary and Croatia (b. 1200)
- May/June – Enrico Dandolo (or Henry), doge of Venice (b. 1107)[17]
- June 14 – Walter III, Count of Brienne (or Gautier), French nobleman
- June 19 – Roman Mstislavich, Kievan prince (b. 1152)
- July 4 – Otto II, Margrave of Brandenburg ("the Generous"), German nobleman
- July 10 – Hatakeyama Shigeyasu, Japanese samurai
- July 13 – Hubert Walter, archbishop of Canterbury
- August 8 – Savaric FitzGeldewin, English bishop
- unknown dates"
- probable – Baldwin I, emperor of the Latin Empire (b. 1172)
References
[edit]- ^ Van Tricht, Filip (2011). The Latin Renovatio of Byzantium: The Empire of Constantinople (1204–1228), p. 352. Leiden: Brill. ISBN 978-90-04-20323-5.
- ^ Geoffrey of Villehardouin. Memoirs or Chronicle of the Fourth Crusade and the conquest of Constantinople, p. 63. Echo Library, 2007.
- ^ Steven Runciman (1952). A History of The Crusades. Vol III: The Kingdom of Acre, p. 107. ISBN 978-0-241-29877-0.
- ^ Setton, Kenneth M. (1976). "A Note on Michael Choniates, Archbishop of Athens (1182–1204)", p. 235.
- ^ Wihoda, Martin (2015). Vladislaus Henry: The Formation of the Moravian Identity, p. 93. Brill.
- ^ Engel, Pál (2001). The Realm of St. Stephen: A History of Medieval Hungary (895–1526), pp. 91–92. I.B. Tauris Publishers. ISBN 1-86064-061-3.
- ^ David Nicolle & Viacheslav Shpakovsky (2001). Osprey: Campaign Nr. 98: Kalka River 1223. Genghis Khan's Mongols invade Russia, p. 19. ISBN 1-84176-233-4.
- ^ a b Warren, W. L. (1961). King John. University of California Press. pp. 111, 130.
- ^ Lock, Peter (2006). The Routledge Companion to the Crusades, p. 103. Routledge. ISBN 978-0-415-39312-6.
- ^ Picard, Christophe (1997). La mer et les musulmans d'Occident VIIIe-XIIIe siècle. Paris: Presses Universitaires de France.
- ^ Luis Suárez Fernández, Historia de Espana antigua y media, (Ediciones Rialp, S.A., 1976), 29.
- ^ Biographical Index of the Middle Ages. Walter de Gruyter. 2011. p. 201. ISBN 9783110914160.
- ^ Joseph Thomas (2010). The Universal Dictionary of Biography and Mythology: Pro - Zyp. Cosimo, Incorporated. p. 2253. ISBN 9781616400743.
- ^ Marcellinus Verardus; Antonio Loschi; Gregorio Corraro, eds. (2011). Humanist Tragedies. Harvard University Press. p. 302. ISBN 9780674057258.
- ^ "Batu, Khan of the Golden Horde: The Mongol Khans Conquer Russia (The Silk Road Series)". Association for Asian Studies. Retrieved December 26, 2023.
- ^ Martin Shaw Briggs (1911). In the Heel of Italy: A Study of an Unknown City. Duffield & Company. p. 109.
- ^ Okey. Venice and its Story. p. 167.
- ^ Kazhdan, Alexander (1991). "Aspietes". In Kazhdan, Alexander (ed.). The Oxford Dictionary of Byzantium. Oxford and New York: Oxford University Press. pp. 211–212. ISBN 0-19-504652-8.