AICD (activation-induced cell death) is programmed cell death caused by the interaction of Fas receptors (Fas, CD95) and Fas ligands (FasL, CD95 ligand).[1] AICD is a negative regulator of activated T lymphocytes that results from repeated stimulation of their T-cell receptors (TCR) and helps to maintain peripheral immune tolerance.[2] Alteration of the process may lead to autoimmune diseases.[1]
The AICD effector cell is one that expresses FasL, and apoptosis is induced in the cell expressing the Fas receptor. Both activated T cells and B cells express Fas and undergo clonal deletion by the AICD mechanism.[3][4] Activated T cells that express both Fas and FasL may be killed by themselves or by each other.[1]
Signaling
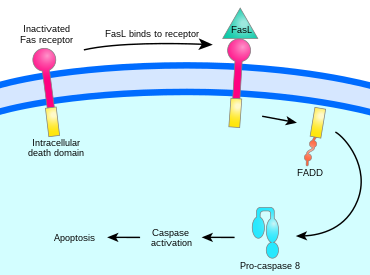
[edit]The binding of Fas ligand to Fas receptor triggers trimerization of Fas, whose cytoplasmic domain is then able to bind the death domain of the adaptor protein FADD (Fas-associated protein with death domain). Procaspase 8 binds to FADD's death effector domain (DED) and proteolytically self-activates as caspase 8. Fas, FADD, and procaspase 8 together form a death-inducing signaling complex (DISC). Activated caspase 8 is released into the cytosol, where it activates the caspase cascade that initiates apoptosis.[5][1]
Regulation of Fas-FasL and AICD
[edit]FasL is primarily regulated at the transcriptional level. (The other option is regulation of the signal emanating from the death receptor itself, controlling sensitivity to the induction of apoptosis.)[3] NFAT activated by TCR stimulation activates FasL transcription, possibly indirectly by upregulating early growth response proteins.[1] T cell activation-induced transcription of FasL is further regulated by c-Myc–MAX heterodimers, and can be blocked by c-Myc downregulation.[1] Interferon regulatory factors IRF1 and IRF2 also upregulate FasL transcription by directly binding to the FasL promoter.[1]
Not much is known about the regulation of Fas and other death receptors. However, overexpression of the protein CFLAR (caspase and FADD-like apoptosis regulator) inhibits Fas-mediated apoptosis.[6]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f g Zhang J, Xu X, Liu Y. (2004), Activation-Induced Cell Death in T Cells and Autoimmunity. Cell Mol Immunol. 1(3):186-92
- ^ Kabelitz D, Janssen O. (1997), Antigen-induced death of T-lymphocytes. Front Biosci. 2:d61-77
- ^ a b Green DR, Droin N, Pinkoski M. (2003), Activation-induced cell death in T cells. Immunol Rev. 193:70-81
- ^ Donjerković D, Scott DW. (2000), Activation-induced cell death in B lymphocytes. Cell Res. 10(3):179-92
- ^ Nagata S. (1997), Apoptosis by death factor. Cell. 88(3):355-65
- ^ Scaffidi C, Schmitz I, Krammer PH, Peter ME. (1999é, The role of c-FLIP in modulation of CD95-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 274:1541–1548