| Total population | |
|---|---|
| 1,593,418 (2021) 4% of the population of Afghanistan[a][2][3][4] | |
| Languages | |
| Aimaq dialect of Persian[5] | |
| Religion | |
| Predominantly Sunni Islam[6] | |
| Related ethnic groups | |
| Hazaras, Tajiks, Pashtuns[5] |
The Aimaq, Aimaq Persians[7][8] (Persian: ایماق, romanized: Aimāq), or Chahar Aimaq (چهار ایماق), also transliterated as Aymaq, Aimagh, Aimak, and Aymak, are a collection of Sunni and mostly Persian[9] nomadic and semi-nomadic tribes.[10] They live mainly in the central and western highlands of Afghanistan, especially in Ghor and Badghis. Aimaqs were originally known as chahar ("four") Aymaqs: Jamshidi, Aimaq Hazara, Firozkohi, and Taymani.[11] The Timuri, which is a separate tribe but is sometimes included among Aimaqs, which is known as Aimaq-e digar ("other Aimaq").[12]
The Aimaq speak several subdialects of the Aimaq dialect of the Persian language, but some southern groups of Taymani, Firozkohi, and northeastern Timuri Aimaqs have adopted the Pashto language.[13]
Etymology
[edit]The word "Aimaq" is derived from the Turkic-Mongolic word "Oymaq" that means "tribe" and "group of tribes".[9][11]
Origin
[edit]The Aimaqs claim different origins based on their tribal background. Some claim to be descended from the troops of Genghis Khan.[14] The Taymani and Firozkohi claim descent from Pashtun tribes.[15]
Culture and society
[edit]The Aimaq are largely nomadic to semi-nomadic goat and sheep herders. They also trade with villages and farmers during migrations for pastures for their livestock. The material culture and foodstuffs of the Aimaq include skins, carpets, milk, dairy products and more. They trade these products to settled peoples in return for vegetables, grains, fruits, nuts, and other types of foods and goods.[14]
Religion
[edit]Aimaqs are largely Sunni Muslims except for the Jamshidi who are mainly Isma'ili Shia Muslims, in contrast to the ethnic Hazaras, who are mainly Twelver Shia Muslims.[16]
Demographics
[edit]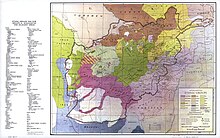
Estimates of the Aimaq population vary between 250,000 and 500,000.[citation needed]
See also
[edit]Notes
[edit]- ^ The last census in Afghanistan was conducted in 1979, and was itself incomplete. Due to the ongoing conflict in the country, no official census has been conducted since.[1]
References
[edit]- ^ "Population Matters". 3 March 2016.
- ^ World Population Review (19 September 2021). ""Afghanistan Population 2021"".
- ^ "Distribution of Afghan population by ethnic group 2020". statista.com. 20 August 2021.
- ^ "Afghan Ethnic Groups: A Brief Investigation". reliefweb.int. 14 August 2011.
- ^ a b Janata, A. "AYMĀQ". In Yarshater, Ehsan (ed.). Encyclopædia Iranica (Online ed.). United States: Columbia University.
- ^ "Aimaq". Minority Rights Group. Retrieved 28 July 2021.
- ^ "Aimaq | Encyclopedia.com". www.encyclopedia.com. Retrieved 2024-06-11.
- ^ PeopleGroups.org. "PeopleGroups.org - Aimaq of Afghanistan". peoplegroups.org. Retrieved 2024-06-11.
- ^ a b "AYMĀQ – Encyclopaedia Iranica". iranicaonline.org. Retrieved 1 February 2021.
- ^ Tom Lansford -A bitter harvest: US foreign policy and Afghanistan 2003 Page 25 "The term Aimaq means "tribe" but the Aimaq people actually include several different ethnic groups. The classification has come to be used for a variety of nonaligned nomadic tribes"
- ^ a b Spuler, B. (2012-04-24), "Aymak", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition, Brill, retrieved 2023-07-14
- ^ Vogelsang, Willem (2002). The Afghans. Wiley-Blackwell. pp. 37–. ISBN 9780631198413. Retrieved 1 April 2011.
- ^ Vogelsang, Willem (2002). The Afghans. Wiley-Blackwell. p. 18. ISBN 0631198415. Retrieved 23 January 2012.
- ^ a b Winston, Robert, ed. (2004). Human: The Definitive Visual Guide. New York: Dorling Kindersley. p. 432. ISBN 0-7566-0520-2.
- ^ Janata, A. "Aymāq". iranicaonline.org. Archived from the original on 29 April 2011. Retrieved 4 April 2021.
A Kākaṛ Pashtun from Baluchistan, Tayman, formed a coalition in Ḡūr around 1650. The traditional chiefs of the northern Fīrūzkūhī, Zay Ḥākem, claim descent from Ačakzay Pashtun ancestors.
- ^ "Afghanistan". Encyclopædia Britannica. Ultimate Reference Suite. Chicago: Encyclopædia Britannica, 2008.
Further reading
[edit]- Macgregor, Central Asia, (Calcutta, 1871)
- Spuler, B. (2012-04-24), "Aymak", Encyclopaedia of Islam, Second Edition, Brill
External links
[edit]- Aimaq Man with Children, Pal-Kotal-I-Guk, Ghor Province
- Aimaq Nomad Camp Pal-Kotal-I-Guk Between Chakhcharan and Jam Afghanistan Archived 2018-09-09 at the Wayback Machine