Bantigue shore (low tide) | |
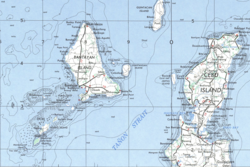
 Location of Bantayan off Cebu | |
| Geography | |
|---|---|
| Location | Tañon Strait |
| Archipelago | Bantayan |
| Adjacent to | |
| Area | 108.77 km2 (42.00 sq mi) |
| Length | 16 km (9.9 mi) |
| Width | 11 km (6.8 mi) |
| Highest elevation | 26 m (85 ft) |
| Administration | |
Bantayan island only | |
| Region | Central Visayas |
| Province | Cebu |
Islands except Bantayan | |
Combined | |
| Demographics | |
| Demonym | Bantayanon |
| Population |
|
| Pop. density | 1,200/km2 (3100/sq mi) |
| Additional information | |
| Time zone | |
 | |
Bantayan Island is an island located in the Visayan Sea, Philippines. It is situated to the west of the northern end of Cebu, across the Tañon Strait. According to the 2015 census, it has a population of 145,436.[1]
The island is administratively divided into three municipalities:
- Bantayan (the largest municipality, covering the central part)
- Madridejos (covering the northern portion)
- Santa Fe (center of tourism in Bantayan Island, covering the southeastern portion)
The island area is 108.77 square kilometers (42.00 sq mi). The island is mostly covered with coconut palms; the elevation is mostly below 10 meters (30 ft), with only one taller hill, at 26 meters (90 ft), in barangay Atop-atop.
Geography
[edit]Island group
[edit]
Bantayan is the main and largest island of the Bantayan island group that lies close to the geographical center of the Philippine archipelago.
The island group includes numerous smaller islands (some uninhabited or uninhabitable), mostly around the southwest corner of the island. About 20 of these islets stretch for about 8 kilometers (5 miles) southwest from Bantayan municipality port area, with some nearer ones being accessible on foot from the main island at low tide. The islands are beside the busy shipping lanes for ships and ferries coming from Mindanao or Cebu City on their way to Manila. The islands are all small and green and low, virtually indistinguishable one from another.
Some of the more notable are:[a]
- Botique (or Botigues, Batquis)
- Botong
- Byagayag Islands (Daku and Diot)
- Doong
- Hilantagaan (or Jicantangan, Jilantagaan, Cabalauan)
- Hilantagaan Diot (or Silion, Pulo Diyot ('little island')
- Hilutungan (or Hilotongan, Lutungan)[b]
- Lipayran
- Mambacayao (or Mambacayao Daku)
- Moambuc (or Maamboc, Moamboc, Kangka Abong, Cangcabong)
- Panangatan (or Pintagan)
- Panitugan (or Banitugan)
- Patao (or Polopolo)
- Sagasay (or Sagasa, Tagasa)
- Silagon
- Yao Islet (or Mambacayao Diot)
In addition, Guintacan Island (or Kinatarkan, Batbatan) to the northeast is part of Santa Fe municipality although it is not part of the Bantayan islands group archipelago.
- 'These Bantayan islets are numerous, and are all low and very small.' —Juan de Medina (1630)
-
Hilantagaan Island seen from the Santa Fe–Hagnaya ferry (S)
-
Hilantagaan Dyot, brgy Hilantagaan, Santa Fe, seen from W.
-
Sunset over Hilutungan, seen from E.
-
Patao island (or Polopolo) off Patao, Bantayan
Demographics
[edit]
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[6][7][8] | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Language
[edit]The Bantayanon language is mostly a mixture of different neighbouring Visayan languages: The principally native Cebuano (from Cebu and Eastern Negros) and Hiligaynon (from Western Negros and Iloilo), Boholano (from Bohol), Masbateño (from Masbate) and Waray-Waray (from Leyte and Samar). However it has its own words such as "kakyop" (yesterday), "sara" (today) and "buwas" (tomorrow).
Climate
[edit]| Bantayan Island Average temperature in Bantayan island is 28.0 °C Humidity 75–85% | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climate chart (explanation) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The climate is typically equatorial – temperature range over the year is less than three degrees Celsius (5.4 deg F), and annual rainfall exceeds 1,500 millimeters (59 in). January to April inclusive are less wet than the other months. This supports at least two rice crops per year. The climate in Bantayan falls within Coronas climate type IV, characterised by not very pronounced maximum rainfall with a short dry season from one to three months and a wet season of nine to ten months. The dry season starts in February and lasts through April sometimes extending to mid‑May.
Bantayan has a tropical climate. Most months of the year are marked by significant rainfall. The short dry season has little impact. This location is classified as Am (Tropical monsoon climate) by Köppen–Geiger climate classification system.
Geology
[edit]Like most of Cebu province,[9] the lithology of the island consists of two unit types:
- the Plio-Pleistocene Carcar Formation
Carcar formation is typically a porous coralline limestone characterized by small sinkholes, pitted grooves, and branching pinnacles.[10] This suggests in situ deposition. Its dominant composition are shell, algae, and other carbonate materials, while macro and micro fossils are found abundant in its formation. - quaternary alluvium (the youngest lithologic unit)
Alluvium is mostly found in coastal areas. Calcareous sand derived from the weathering of limestone mostly makes up the tidal flat. This appears as fine to coarse-grained sand mixed with shell fragments.
As a consequence of the geology, water supplies are hard.
National protected areas
[edit]
Uncultivated Vanda coerulea
Bantayan and its surrounding islands have been included in several pieces of legislation giving protected status.
Wilderness area
[edit]In 1981 President Marcos signed proclamation no. 2151 giving certain parts of the country protected status.[2] This included Bantayan Island with the status of a "Wilderness Area",[c] although its physical extent was undefined, albeit the proclamation described all the areas named as "containing an aggregate area of 4,326 hectares [10,690 acres], more or less". Eleven years later the Philippine Congress passed Republic Act 7586 – the National Integrated Protected Areas System (NIPAS) Act of 1992, managed by the Department of Environment and Natural Resources (DENR) – which reaffirmed the protected status.[3] However it too did not specify the extent of Bantayan Island Wilderness Area (BIWA), which is therefore taken to include the whole island group, more than 11,000 hectares (27,000 acres).[d]
After 2013's Typhoon Yolanda, there has naturally been a need and desire for reconstruction, however one major problem is that because of the designation, there is little land titling, and international relief organizations (and others) are reluctant to fund construction on land where title does not exist.[11] 2014 has seen[update] the start of initiatives to define the area, and to devise a general plan for its management (BIWA-GMP). That plan recommends retaining only 596.41 ha (1,473.8 acres) as strictly protected wildlife reserves, or 5.3% of the original BIWA, and allowing multi-use zoning of 10,648.27 ha (26,312.4 acres).[d] From that has arisen a more concrete proposal regarding reclassification.[12] Now[update] the plan is to be recommended to Congress.[13]
Tourist zone and marine reserve
[edit]Presidential proclamation no. 1801 of 1978 established Tourist zones and marine reserves, and placed the island of Hilutungan within its scope.[5]
Protected seascape
[edit]The Tañon Strait protected seascape was established by President Ramos under proclamation no. 1234 of 1998.[14] This includes more than 29,187 m (29 km; 18 mi) of the eastern shoreline of Bantayan island. In February 2015[update], 17 years after its declaration, the first summit on the Tañon Strait protected seascape is to be held.[15]
Agriculture
[edit]The dominant uncultivated vegetation is ipil-ipil (Leucaena leucocephala). Cultivated crops include coconut, cassava, banana, sugarcane, corn and mango.
The principal cash crops are:[e]
| Plant | Area (ha) | Yield |  |
|---|---|---|---|
| Corn | 400 | 775 tonnes (763 tons) | |
| Mango | 47.53 (1214 trees) | 455 tonnes (448 tons) | |
| Chico | 23 | n/a | |
| Coconut | 713 | n/a |
Fauna
[edit]

The common wolf snake can occasionally be found on the island.
The following list shows birds whose presence has been verified:[17][18]
- Eastern reef-egret (Pacific reef-egret) - Egretta sacra
- Chinese egret - Egretta eulophotes
- Little heron (striated heron) - Butorides striata
- Grey plover - Pluvialis squatarola
- Greater sand-plover - Charadrius leschenaultii
- Eurasian whimbrel - Numenius phaeopus
- Ruddy turnstone - Arenaria interpres
- Godwit sp - Limosa sp
- Lesser frigatebird - Fregata ariel
- Pied harrier - Circus melanoleucos
- Black-chinned fruit dove - Ptilinopus leclancheri
- Philippine collared dove - Streptopelia dusumieri
- Island swiftlet - Collocalia vanikorensis
- White-collared kingfisher - Halcyon chloris
In a survey conducted on Carnaza Island on July 16–20, 1990, a total of 18 species of birds representing 7 orders and 15 families were identified and reported. The most common species observed were Glossy Swiftlets (Collocalia esculenta), White-collared Kingfishers (Halcyon chloris), Pied Trillers (Lalage nigra), Black-naped Orioles (Oriolus chinensis), Philippine mapgie robins (Copsychus saularis), Malaysia fantails (Rhipidura javanica), White-breasted Woodswallows (Artamus leucorhynchus), glossy starlings (Aplonis panayensis), yellow-breasted sunbirds (Nectarinia jugularis) and Eurasian tree sparrows (Passer montanus). For the rest of the species either only one or two individuals were seen or only either calls were heard.[19]
The islanders revealed that the Tabon bird (Megapodius freycinet) used to be numerous in Carnaza Island.
Also listed on the survey are the orders Cephalopoda, Gastropoda and Pelecypoda. Two genera of Cephalopods were identified, namely; Sepia and Sepioteuthis.
A total of 36 species belonging to 19 families of gastropods have been listed. However, further study is needed to get a complete listing of the gastropods in the area.[19]
The sea
[edit]

The coast of Bantayan and its islands mostly alternates between mangal and palm trees. Because of the shallow slope on the shelf, the intertidal area can be quite extended, leading to rocky and muddy shallows at low tide. This means that places with a sandy shore – a beach – are infrequent. Good beaches can be found in the southeast around Santa Fe, and in the northwest at Patao and Madridejos. Even these though are not cleaned, and depending on the currents there can be considerable amounts of flotsam and jetsam on the beach and in the sea.
Coral
[edit]Of the approximately 500 varieties of coral known worldwide, about 400 are found in the Philippines.[20] However their future is seriously threatened – mainly due to destructive fishing techniques, such as blast fishing and cyanide fishing, which indiscriminately destroy much of the ecosystem, including the coral reefs. In addition, global warming and ocean acidification also contribute significantly to worldwide loss. Globally coral sees 50%–70% threatened or lost; southeast Asian coral reefs are in even worse condition, and it is estimated in the Philippines the figure under threat is greater than 90%, with less than 1% in good condition. Until now proper compliance of international laws has been poor,[21] although it is starting to be taken seriously. Meanwhile, other efforts are under way in Bantayan to accelerate the regrowth, using coral farms.[22]
Starfish
[edit]

There are many starfish to be seen in the intertidal area. Their detrivorous diet helps keep the water clean. Further out though, the crown-of-thorns starfish is a considerable threat to the coral reef, because of its voracious hunger for the coral.

Mangal
[edit]Mangroves are salt-tolerant, woody, seed-bearing plants that are found in tropical and subtropical areas where they are subject to periodic tidal inundation.[23] The Philippines has over 40 species of mangroves and is one of the most biodiverse regions in the world as there are only about 70 species of mangroves worldwide. The mangrove ecosystem is a very diverse one and is home to many birds, fish, mammals, crustaceans and other animals.
Mangroves provide an important nursery for fish, shellfish and other organisms. It is estimated that each hectare of mangrove can provide food for 1,000 kg of marine organisms (890 lb/acre). With this abundance of food for fish present in the mangroves, each hectare of mangal yields 283.5 metric tons of fish per year (112.9 long ton/acre). Mangroves also provide other important functions such as preventing soil erosion and protecting shoreline from typhoons and strong waves. Mangroves provide many other products and services such as medicines, alcohol, housing materials and are an area for research and tourism.
However even with all of these known benefits the state of mangroves within the Philippines is very dim. In the early 1900s there were approximately 5,000 km2 (1,900 sq mi) of mangroves but today there are only about 1,200 km2 (460 sq mi). Many of the mangrove areas were destroyed to make way for fishponds and reclamation areas. They were used indiscriminately for housing – both building materials and reclamation – and were disturbed by siltation and pollution.
Now that the true benefit of these ecosystems is known there is protection and rehabilitation of these important ecosystems. It is now illegal to cut down mangroves for any purpose and local governments and community organizations have taken active roles in planting and managing mangrove plantations. There is hope that in the future mangroves will return to the healthy status that they once held.
History
[edit]Early origins
[edit]There are almost no physical records nor evidence to indicate when the first people came to Bantayan, nor their places of origin. Some believe they can be traced back to Panay, others believe that the bulk of them were of Cebuano origin, and still others say they came from Leyte and Bohol.
Connections between Bantayan and other places can be deduced from the mixed dialects spoken by the people, and their ancient culture such as cloth‑weaving, dance, and architecture. In addition certain old-established Hispanic family names are associated with certain locations:
- Panay
- Rubio
- Arcenaz
- Alvarez
- Sevilleno
- Cebu
- Rodriguez
- Ancaja
- Mansueto
- Villacrucis
- Leyte
- Villacin
- Villaflor
- Ortega
- Carabio
- Bohol
- Hubahib
- Garcia
- Caquilla
- Paraguay
- Nepanggus
- Nepangue
- Panay
There is little documentary evidence of life and culture before the arrival of the Spanish conquistadores. What we know of them is gathered from handed-down accounts and folklore.
The early people were said to be timid. They did not travel and knew little of places away from their homes. They wore little clothing because the climate did not need it. The abundance of fish, wild game, wild fruits and tuber, such as ba-ay, hagmang,[f] bailacog, and kiot, made the people do little more than make clearings on which to plant corn, camote (sweet potato) and other vegetables. Large and small trees grew and spread, shading the ground all year round with their heavy foliage. Vines and creepers climbed the trees hanging from bough to bough; cultivation of open land was difficult.
The Spanish period
[edit]Early years
[edit]During the period 1565–1898 the Philippines was a Spanish colony, part of the Spanish East Indies.
The parish church was established in 1580 – as an encomienda of the heir of Don Pedro de Gamboa.
Writing in 1582, Miguel de Loarca stated:[24]
He also wrote:[25]
Writing in 1588, Domingo de Salazar reported:[26] "The island of Bantayan is small and densely populated. It has more than eight hundred tributarios, most of them Christians. The Augustinians who had them in charge have abandoned them also, and they are now without instruction. This island is twenty leagues from Zubu."
Some time in 1591, Bantayan's population totalled 683 tributes representing 6732 persons.[27]
Writing in 1630, Fray Juan de Medina noted:[j]
Religious were established in the island of Bantayan, located between the island of Panay and that of Sugbú,[k] but farther from that of Panay. However, if one wishes to go to the island of Sugbú without sailing in the open sea, he may coast from islet to islet, although the distance across is not greater than one or one and one-half leguas.[h] These Bantayan islets are numerous, and are all low and very small. The largest is the above-named one. When Ours acquired it, it had many inhabitants, all of very pleasing appearance, and tall and well-built. But now it is almost depopulated by the ceaseless invasions from Mindanao and Jológ.
He goes on to say: "This island has a village called Hilingigay, which it is said was the source of all the Bisayan Indians who have peopled these shores, and whose language resembles that of Hilingigay."
Derivation of name
[edit]During the time of 22nd Governor-General Sebastián Hurtado de Corcuera,[l] the Visayans were continually harassed by Moro pirates who came on raids to capture slaves. Consequently, tall stone walls and watchtowers were built in different parts of the archipelago, for refuge and protection from Moro aggression.
Popular folklore says that these watchtowers were known locally as "Bantayan sa Hari", meaning "Watchtowers of the King", and they served as lookout towers for incoming vintas (Moro pirate vessels). In the course of their vigil, it became common to say, "Bantayan! Bantayan!", meaning, "Keep watch! Keep watch!", and that was how this island-group got its name.
However Madridejos history scholar Eng'r. Brient Mangubat who has studied Bantayan Island History and the Lawis Old Fort foundation in Madridejos claimed that the origin of the Island's name Bantayan has nothing to do with the Muslim raiders. According to him the Island got its name Bantayan way back in the year 1574, when the Island's northern side (LAWIS), was used as a "Lookout post" to monitor the Visayan Sea against Chinese attacks. The residents of Bantayan Island decided to do this precautionary act as Manila, the country's capital city was under attack by the forces led by Limahong. The Island's name (Bantayan) was already in use 25 years earlier, before the (first) Muslim raid took place on Bantayan Island in year 1600.

In all there were 18 watchtowers built on the Bantayan islands. Most have not survived, although relics can be seen to this day. That at Madridejos is in fair condition, that at Santa Fe less so. There is a particularly fine example on Doong island [28]
Construction of watchtowers was not limited to Bantayan. Watchtowers were built in many locations in Cebu vulnerable to Moro raids, as well as in other parts of the Visayas, such as Southern Leyte, Northern Samar and Bohol.
In his "Statement of the Annual Incomes and Sources of Profit of His Majesty in These Philipinas Islands" for the year 1608, Pedro de Caldierva de Mariaca declares the tributes (tax) from Bantayan and Bohol combined amount to 2400 gold pesos.[29][m]
Industry
[edit]Don José Basco y Vargas was Governor-General of the Philippines from July 1778 until September 1787. During his period in office, he pioneered many projects for the encouragement of agriculture and industries. However many small industries in the islands were completely abandoned because the people were forced to work on building roads, public buildings and churches. Those enforcing were called politas.[n]
The abundance of fish, favourable climate and virgin soil then greatly determined the occupation of the people. These geographical factors became strong stimuli for the people to be fishermen, farmers and sailors. Much later, the small clearings were expanded to fields.
The old Spanish roads connecting Santa Fe, Bantayan, and Madridejos were constructed chiefly through the services of labour and partly supported by the tribute funds.
Religion
[edit]When the Spaniards came to Bantayan, the people already had some form of religious convictions and worship, such as animism, shamanism, evocation and magic. They easily conceived the idea of evil spirits, good spirits, witches and ghosts. In order to please these imaginary creatures people often resorted to charms, vows, sacrifices and self-harm. It was a common belief among the illiterate people of the past that cholera and other fatal diseases were caused by poison which an evil spirit had put into the wells and that the people could be saved from the dreaded disease only by chanting prayer and holding processions.[30][31]
The cooperation between the church and the state did not last very long. Quarrels between the church and the state ensued. There was struggle for political power, from the Governor-General down to the alcalde mayors on one hand and from the archbishop to the friars on the other. Because of this, projects for improvements were all paralysed.
The American period
[edit]On January 4, 1899, following the defeat of Spain in the Spanish–American War, a new government was born to the Philippines. With instructions from President McKinley, General Otis, who commanded the US Army in the Philippines, declared that the American sovereignty must be recognized without condition. This was the beginning of the American period.
This island-group did not take any active part in the revolution against Spain or America. However, after the Filipino–American War,[32] a reactionary group was organized, headed by Patorete of Santa Fe, then still a barrio of Bantayan. Their announced purpose was to resist the invaders, but the armed goons carried a campaign of terror burning the northern part of Santa Fe, plundering and forcing Capitan Miroy and Aguido Batabalonos to join them. This resulted in great fear and tension among the inhabitants.
The condition of the barrios, after the overthrow and immediately preceding the arrival of the Americans, in general, was very far from satisfactory. Sanitation was entirely a stranger; barrio life was dreadful. There were few signs of improvement among the people since their primitive ancestors.
The subdivision of the province of Cebu was developed utilizing the method introduced by Spain. A new provincial law had been enacted in 1895 and necessary appointments were then made. At that time, Bantayan was already organized as pueblo. Santa Fe was organized as such in 1911 and Madridejos in 1917. These pueblos were given a new corporate form under the Municipal Council chosen by a limited native electorate. For the local head of the administration, the title Presidente took the place of the former Gobernadorcillo or Capitan[o]
Committed to the task of administering the newly organized municipal governments were the first presidentes of the three towns comprising the island-group namely: Gregorio Escario for Bantayan, Vicente Bacolod for Madridejos and Casimiro Batiancila for Santa Fe. Political parties were formally organized since the early days of the American regime. Partido Liberal came towards the end of 1900. Pascual Poblete founded the Partido Independista in 1902.
During the administration of Governor-General Luke E. Wright (1904–1906), the public road policy was inaugurated. Little by little the stage trails were changed to roads of more durable construction. Late in 1913 the construction of Santa Fe—Bantayan road began and in 1918 the Bantayan—Madridejos road followed; both were completed in 1924.
Then and now, fishing and farming were important industries of the people, but from the year 1903 to 1925, weaving of piña cloth and the gathering of maguey fibre were very lucrative pursuits of the people. Over the years demand for these products weakened and died out. At about the same, hand embroidery termed as "spare time industry" came in. A good number of women adopted it and were actively engaged in it for some years. The local output was quite significant. In 1923, because of weak and unsettled market conditions, particularly in Manila, the business gradually disappeared.

Independent Philippines
[edit]Gregorio Zaide described the Philippine national characteristic as "pliant, like bamboo, bending in the wind without breaking".[33] This might explain the war-time actions of the then mayor Isidro Escario, who had himself rowed out to meet a fleet of Japanese warships where he treated with them: Bantayan was not invaded and the war basically passed it by.[p]
Economy
[edit]Commerce
[edit]
Bantayan islands are considered Cebu's fishing ground from where boatloads of fish – guinamos (salted fish) and buwad (dried fish) – are transported daily to Cebu and Negros for consumption and further distribution to as far as Manila and Mindanao. Equally important is the thriving poultry industry with hundreds of thousands of chicken eggs produced daily.
Years ago, poultry raising was mainly a backyard affair. Today it has grown into a large scale and highly specialized industry. Big poultry farms are located near the national and feeder roads. Over one million chickens are kept in yards and specially constructed barns with more than half a million eggs gathered every day. These eggs are exported to Cebu, Manila, and Mindanao and other towns and cities in the Visayas. This industry, along with copra making, tubâ gathering and fishing, has helped Bantayan solve its unemployment problem.
Transport
[edit]The island can be reached via ferry services from Hagnaya (San Remigio) to Santa Fe, and from Estancia, Iloilo and Sagay to Bantayan municipal port. Bantayan Airport handles infrequent flights from chartered planes usually arriving from Mactan–Cebu International Airport.
Goods are shipped through Bantayan municipal port. There is also a small dock in Baigad capable of handling small pumpboats. However it is in a very poor state of repair, and has not handled any vessel since 2007.
There are three lightstations around the islands:
| ⛯ | LS Bantayan on the beach at Bantigue |
| ⛯ | LS Buntay offshore of the Kota promontory, Madridejos |
| ⛯ | LS Guintacan at the southeast end of Guintacan island |
Society
[edit]Health care
[edit]In view of the relatively high population of the island, and its growing popularity as a tourist spot, a bill has already been presented in Congress for the establishment of a 100‑bed tertiary‑level hospital.[35][36] The nearest available tertiary care is in Cebu City, four hours travel by land and sea. The level‑1 facility available in Bogo takes at least 1+1⁄2 hours travel.[citation needed]
Education
[edit]

The first school in Bantayan, called the "Gabaldon School", opened in 1915.[37][38][39][40]
Public high schools on Bantayan are located in the municipalities of Bantayan, Santa Fe and Madridejos as well as on Doong island. There are also private high schools and tertiary colleges such as Bantayan Southern Institute and Salazar College. St Paul Academy (SPA) is a private high school in Bantayan municipality.[citation needed]

Sport
[edit]As is common through the Philippines, 'sport' is synonymous with cockfighting. It is an unusual sport in that the winner dies as well as the loser. Large sums are bet on the outcome of a fight, which usually lasts little more than one minute. There are several sports centers (cockpits) on the island. Smaller puroks just have an open-air arena.[citation needed]
Notable events
[edit]- 1580 – The Augustinians established the Parish of Bantayan as a convent under the patronage of La Asuncion de Nuestra Señora (The Ascension of Our Lady), a mission-station of the friars in the Visayas and thus the first parish in Cebu province and one of the few parishes still in existence outside Mexico which were once a part of the Archdiocese of Mexico.[citation needed]
- 1603 – The Augustinians relinquished the administration of the church to the secular clergy. During the time of Bishop Pedro de Arce, Daan Bantayan (also Daanbantayan) and the nearby villages located in northern Cebu were placed under the administration of the parish,[q] followed by the island of Maripipi.[citation needed]
- 1628 – The biggest Moro attack took place when a fleet of vintas attacked, killing or abducting more than 800 natives mostly from the village of Hilingigay, now barangay Suba, and burning down the church.[r] Juan de Medina wrote that the priest and a few Spanish residents tried to defend but had to run and hide after running out of ammunition.[42]
- 1754 – Moro raid left the church and community in ashes.[citation needed]
- 1778 – The old Spanish roads linking Santa Fe, Bantayan and Madridejos were constructed through forced labour.[n]
- 1790–1796 – Severe famine after crop failure. Not even a grain of corn could be had but the people subsisted upon amorseko (crab grass) which continuously grew on the walls of their nipa huts.[43][44]
- 1860 – The first casa real was constructed (now Municipal Hall).[citation needed]
- 1864 – Following the Education Decree of 1863,[45] the first Spanish school (for boys) was established under the direct supervision of the curate where religious instruction was instilled.[46][47]
- 1880–1890 – Smallpox epidemic devastated the island.[citation needed]
- 1894 – The entire barrio of Ticad was razed to the ground by fire. Only the stumps of the posts could be seen above the ground.
- 1902–1903 – Cholera epidemic.[s]
- 1905 – Typhoon.[citation needed]
- 1905 – First local election in Bantayan. Gregorio Escario, who had been appointed as first "Presidente", now won the election by a small margin over his rival.[citation needed]
- 1906 – The first bicycle came to Bantayan, owned by Leon Villacrusis. It was imported from Manila. The first bicycle imported from Japan was owned by Dr. Mabugat.[t][citation needed]
- 1908 – Smallpox epidemic, eventually controlled by complete vaccination.[citation needed]
- 1910 – The first motorized boat, MV Carmela, was owned by Yap Tico.[u] It served the Bantayan–Cebu route. It also brought merchandise to and from Bantayan until it was destroyed by the typhoon of 1912.[citation needed]
- 1912 – Typhoon, which took hundreds of lives in addition to work animals and agricultural crops that were destroyed.[50]
- 1913 – Construction of the present Bantayan–Santa Fe road began.[citation needed]
- 1915 – As a result of Public Act 1801, [v] the main building of Bantayan Central School was built.[52]
- 1918 – Construction of the Bantayan–Madridejos road began.[citation needed]
- 1923 – The first car came to Bantayan island – a second-hand Dodge owned by Kapitan Casimiro Batiancila of Santa Fe.[citation needed]
- 1924 – The whole road construction project linking Santa Fe, Bantayan and Madridejos ended.[citation needed]
- 1927 – Bantayan Postal Office was opened within the municipal building.[citation needed]
- 1930 – Cholera epidemic.[citation needed]
- 1935 – Beer was first distributed in Bantayan.[citation needed]
- 1961 – Oil explorers came to Bantayan to dig the first oil well somewhere within Patao and Kabac.[53]
- 1968 – A storm washed away the historic watchtower in Baluarte, Suba.[w]
- 1968 – A fire that started in San Pedro Bakery gutted 17 houses and claimed the life of one person.[citation needed]
- 1973 – Fire broke out which destroyed almost the whole section of Suba, razed the entire public market and rendered more than 700 families homeless.[citation needed]
- 1978 –Death of Isidro R. Escario, who had been mayor of Bantayan since 1937 apart from the war. His funeral procession and wake drew thousands: people were seen queueing one kilometer away from the wake.[citation needed]
- 1981 – Presidential decree nominates Bantayan as a National Protected Area: Wilderness area.[2]
- 1997 – Death of Antonio Ilustrisimo (born Bantayan 1904). He was a Master of Kali Ilustrisimo – his own development of the eskrima he learned from his father.[55][56]
- 1999 – Overloaded ferry MV Asia South Korea en route Cebu–Iloilo City strikes submerged rocks about 8 nautical miles (15 km; 9 mi) west of Bantayan island and sinks in heavy seas with loss of 56 lives.[57][x]
- 2010 – Lipayran island hit by tornado – 15 shanties destroyed and seven damaged.[58]
- 2013 – Class‑5 Super Typhoon Haiyan, within Philippines known as Yolanda, caused considerable damage to the entire island, but with relatively little loss of life.[y]
Notes
[edit]- ^ Islands have several names, according to speaker's language. First name shown is as it appears on the NAMRIA topographical map.[4] Some of the smallest islands are not named on map.
- ^ Declared a "Tourist Zone and Marine Reserve under the administration and control of the Philippine Tourism Authority" by Presidential Proclamation 1801 of 1978 [5]
- ^ Wilderness area is a protected area that is created and managed mainly for purposes of research or for the protection of large, unspoiled areas of wilderness, whose primary purpose is the preservation of biodiversity and as essential reference areas for scientific work and environmental monitoring.
- ^ a b The total area of BIWA [11,244.5 ha (27,785.8 acres)] includes coastal areas below the high water mark, as well as other islands.
- ^ 2001 data [16]
- ^ wild yam having long edible tubers and thorny vines
- ^ a b Bohol
- ^ a b The league (legua) was not well defined, but was about 4 nautical miles (4.6 miles; 7.4 kilometers) ± 5%
- ^ barangay here in its original meaning, a large boat
- ^ de Medina 1630 full translation into English in Blair & Robertson (1905w, pp. 259–260) (and Blair & Robertson (1905x), which does not mention Bantayan.)
- ^ Sugbú = Cebu
- ^ In office June 1635 – August 1644
- ^ A gold peso weighed 1 Troy ounce (1.1 oz; 31.1 g) so at 2023 prices one oz T gold ≈ $2320 that makes the tribute about $5.6 mn. See also Blair & Robertson 1903c, p. 177
- ^ a b As well as paying tribute, all male Filipinos from 18 to 50 were obliged to render forced labour called polo, for 40 days of the year, reduced in 1884 to 15 days. It took various forms, such as building of roads and bridges; construction of public buildings and churches; cutting timber in forests; working in shipyards; and serving in Spanish military expeditions. A person who rendered polo was called a polista. The members of the principalia were exempt from polo: in addition rich Filipinos could pay a falla to avoid forced labour – about seven pesos annually. Local officials (former and current governadorcillos, cabezas de barangay etc.) and schoolteachers were exempt by law because of their service to the state. Thus the only ones who rendered forced labour were those poor Filipinos lacking social, economic or political prestige in the community. This served to reinforce notions of the indignity of labour in the minds of the Hispanicised Filipinos: labour became the badge of plebeianism.
- ^ During the Spanish administration, each pueblo was under an Administrador Civil styled Gobernadorcillo (later Capitan Municipal), assisted by a Teniente Mayor, a Teniente Segundo, a Teniente Tercero, a Teniente del Barrio and a Cabeza de Barangay
- ^ Similar collaboration by Emilio Aguinaldo saw him imprisoned after the war.
- ^ The town plan of Daanbantayan somewhat echoes the butterfly shape of Bantayan Island itself
- ^ "Accordingly, in the past year of 1600 they came with a fleet of many vessels to the Pintados provinces, which are subject to your Majesty; and in the region known as Bantayan they burned the village and the church, killed many, and took captive more than eight hundred persons"[41]
- ^ The 1902–1904 cholera epidemic claimed 200,000 lives in the Philippines.[48]
- ^ The Mabugat family at that time substantially owned Mambacayao Island
- ^
F. M. Yap Tico & Co. Ltd. Headquarters Manila,PhilippinesKey peopleLim Tuan (manager) Services - Importer of rice
- Insurance agent
Yap Tico was a Chinese-owned trading company based in Manila. Although its nominal principal business was the import of rice, as an insurance company and general financial agency, it featured in many civil lawsuits, most notably throughout the 1910s and 1920s, some of which set case law precedents, Lizarraga Hermanos vs. Yap Tico for example.[49]
- ^ popularly known as the Gabaldon Act after its original author, Assemblyman Isauro Gabaldon.[51]
- ^ The eye of the storm passed directly overhead around 0:00am on November 24, 1968. It did not become a real Class‑1 typhoon until two days later.[54]

Track of Typhoon Nina (Seniang) - ^
- ^ Eye of storm passed overhead around midnight of November 7, 2013. At that time wind speeds were reaching 160 knots (300 km/h; 82 m/s; 180 mph).[59]

Track of Typhoon Yolanda (Haiyan)
References
[edit]- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). Table B - Population and Annual Growth Rates by Province, City, and Municipality - By Region. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ a b c Presidential Proclamation No. 2151 (December 29, 1981), Declaring certain islands and/or parts of the country as Wilderness Areas. (s.1981), Official Gazette, retrieved October 28, 2014
- ^ a b Republic Act No. 7586 (June 1, 1992), An act providing for the establishment and management of National Integrated Protected Areas System, defining its scope and coverage and for other purposes, Official Gazette, retrieved October 28, 2014
- ^ NAMRIA 1995
- ^ a b Presidential Proclamation No. 1801 (November 10, 1978), Declaring certain islands, coves and peninsulas in the Philippines as tourist zones and marine reserve under the administration and control of the Philippine Tourism Authority (s.1978), Official Gazette, retrieved November 13, 2014
- ^ Census of Population (2015). Highlights of the Philippine Population 2015 Census of Population. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ Census of Population and Housing (2010). Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities (PDF). National Statistics Office. Retrieved June 29, 2016.
- ^ Censuses of Population (1903–2007). Table 1. Population Enumerated in Various Censuses by Region: 1903 to 2007. National Statistics Office.
- ^ Del Rosario, Pastor & Malapitan 2005, Figure 2: General Geology of Cebu Province
- ^ Hillmer & Scholz 1986
- ^ The Freeman 2014a
- ^ The Freeman 2014b
- ^ The Freeman 2014c
- ^ Presidential Proclamation No. 1234 (May 27, 1998), Declaring the Tañon Strait situated in the provinces of Cebu, Negros Occidental and Negros Oriental as a protected area pursuant to RA 7586 (NIPAS Act of 1992) and shall be known as Tañon Strait Protected Seascape (s. 1998), Official Gazette, retrieved November 16, 2014
- ^ The Freeman 2015
- ^ "Municipality of Bantayan published figures". Archived from the original on May 5, 2010. Retrieved November 30, 2012.
- ^ Wild Bird Club of the Philippines 2004
- ^ Robson 2011
- ^ a b Mapalo, Amuerfino M. (January–June 1991), "Notes on the Avifauna of Carnaza Island, Cebu, Philippines", Ecosystems Research Digest, 1 (1): 30–34
- ^ Philippine Daily Inquirer 2005
- ^ San Francisco Chronicle 2002
- ^ The Manila Bulletin 2009
- ^ Mangrove Action Project
- ^ Blair & Robertson 1903e, p. 48
- ^ Blair & Robertson 1903e, p. 140
- ^ Blair & Robertson 1905a, p. 41
- ^ Blair & Robertson 1903h, p. 132
- ^ Cabigas 2009
- ^ Blair & Robertson 1904n, p. 246
- ^ Zaide 1937a
- ^ Zaide 1937b
- ^ Grimsley 1996
- ^ Zaide 1968
- ^ Department of Transport and Communications 2016
- ^ The Freeman 2014d
- ^ House Bill No. HB04802 (August 12, 2014), An act establishing the Bantayan Island National Hospital in the municipality of Bantayan, Province of Cebu and appropriating funds therefor (PDF), archived from the original (PDF) on March 4, 2016
- ^ Aldana 1949
- ^ Catapang 1926
- ^ Fresnoza 1950
- ^ Isidro y Santos 1949
- ^ Blair & Robertson 1903h, pp. 235–238
- ^ de Medina 1630
- ^ Clayton et al. 2002
- ^ Galinato, Moody & Piggin 1999
- ^ de la Concha 1863
- ^ Alzona 1932
- ^ Bazaco 1939
- ^ Society of Philippine Health History 2004
- ^ Lizarraga Hermanos vs. Yap Tico, 24 Phil. 504 (1913)
- ^ Adelaide Advertiser 1912
- ^ The Freeman 2010
- ^ Cruz Araneta 2006
- ^ Department of Energy 1961
- ^ Unisys Weather Information Systems 1968
- ^ Wiley 1997
- ^ Diego & Ricketts 2002
- ^ People's Daily 1999
- ^ Philippine Daily Inquirer 2010
- ^ Unisys Weather Information Systems 2013
Sources
[edit]- Adelaide Advertiser (October 21, 1912). "Typhoon in the Philippines – Heavy loss of life". Adelaide, South Australia: National Library of Australia. p. 9. Archived from the original on December 31, 2017
- Aldana, Benigno V (1949). The Educational System of the Philippines. Manila: University Publishing. OCLC 8985344
- Alzona, Encarnacion (1932). A History of Education in the Philippines 1565–1930. Manila: UP Press. OCLC 3149292
- Cruz Araneta, Gemma (August 30, 2006). "Gabaldon Schools and other Heritage School Buildings". Philippine National Heritage Watch. Heritage Conservation Society. Archived from the original on November 14, 2015
- Bazaco, Fr Evergisto (1939). History of Education in the Philippines – Spanish period 1565–1898. Manila: UST Press. OCLC 3961863
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1903c). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1803. Vol. 3 of 55 (1569–1576). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1903e). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1803. Vol. 5 of 55 (1582–1583). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1905a). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1898. Vol. 7 of 55 (1588–1591). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1903h). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1898. Vol. 8 of 55 (1591–1593). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1904n). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1898. Vol. 14 of 55 (1606–1609). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne; additional translations by Henry B. Lathrop, Robert W. Haight. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1905w). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1898. Vol. 23 of 55 (1629–1630). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark
- Blair, Emma Helen & Robertson, James Alexander, eds. (1905x). The Philippine Islands, 1493–1898. Vol. 24 of 55 (1630–1634). Historical introduction and additional notes by Edward Gaylord Bourne; additional translations by Rev T.C. Middleton & Robert W. Haight. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark
- Cabigas, Estan (September 21, 2009), Cebu's lonely sentinels of the sea (Photographic essay), langyaw.com, retrieved February 12, 2015
- Catapang, Rev Vincent R. (1926). The Development of the Present Status of Education in the Philippine Islands. Boston: Stratford. OCLC 2605052
- Clayton, W. Derek; Vorontsova, Maria S.; Harman, Kehan T. & Williamson, H. (2002). "World Grass Species: Descriptions, Identification, and Information Retrieval". GrassBase – The Online World Grass Flora. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. Archived from the original on July 14, 2017.
Dallwitz (1980); Dallwitz, Paine and Zurcher should also be cited
- de la Concha, José (1863). "Decree of 20 December 1863". Archived from the original on September 24, 2002
- de Medina, Fray Juan (1630) [1893]. Historia de los sucesos de la orden de n. gran P. S. Agustin de estas islas Filipinas: desde que se descubrieron y se poblaron por los españoles, con las noticias memorables / compuesta por el venerable Fray Juan de Medina [History of the Augustinian Order in the Filipinas Islands] (scan) (in Spanish). Manila: Chofréy. OCLC 11769618.
Page numbers 487–488 used twice.
- Del Rosario, R. A.; Pastor, M. S. & Malapitan, R. T. (April 2005). Controlled Source Magnetotelluric (CSMT) Survey of Malabuyoc Thermal Prospect, Malabuyoc/Alegria, Cebu, Philippine (PDF). World Geothermal Congress. Antalya, Turkey. Archived (PDF) from the original on November 12, 2014
- Department of Energy (1961). "List of drilled wells in basins for petroleum areas on offer". rows 207ff. Archived from the original (Tabular text data) on January 25, 2010
- Department of Transport and Communication, Maritime Safety Services Command (2016). "Coast Guard District Central Visayas". Archived from the original on March 23, 2016.
- Diego, Antonio & Ricketts, Christopher (2002). The secrets of kalis Ilustrisimo. Boston: Tuttle Publishing. ISBN 978-0804831451. OCLC 48449942
- Fresnoza, Florencio P. (1950). Essentials of the Philippine Educational System. Manila: Abiva Publishing House. OCLC 80529874
- Galinato, Marita Ignacio; Moody, Keith & Piggin, Colin M. (1999). Upland Rice Weeds of South and Southeast Asia (PDF). Manila: IRRI. Chrysopogon aciculatus. ISBN 978-9712201301. Archived (PDF) from the original on December 31, 2017.
- Grimsley, Mark (1996). "Filipino–American War 1899–1902". Archived from the original on October 9, 2012
- Hillmer, Gero & Scholz, Joachim (1986). "Dependence of Quaternary Reef Terrace formation on tectonic and eustatic effects". The Philippine Scientist. 23: 58–64
- Isidro y Santos, Antonio (1949). The Philippines Educational System. Manila: Bookman. OCLC 554406
- NAMRIA (March 1995). NTMS (National Topographic Map Series) (Digitised map) (Map) (1 ed.). 1:50,000. Cartography by SPOT satellite imagery 1990 (Panchromatic) & 1987 (Multispectral) by SSC Satellitbild / S‑117 topographic maps by NAMRIA based on aerial photography. Fort Bonifacio, Manila: National Planning and Resource Information Authority. Retrieved February 24, 2013. 3723‑I Madridejos and 3723‑III Bantayan
- People's Daily (December 25, 1999). "More Than 600 Rescued From Sinking Ferry in Philippines". Archived from the original on September 30, 2011
- "95% of Philippine reefs ruined – Reef Check". Philippine Daily Inquirer. Manila. November 15, 2005. Archived from the original on December 4, 2007
- Philippine Daily Inquirer, Doris C. Bongcac (August 21, 2010). "Twister victims fall ill". Archived from the original on May 18, 2015
- Robson, Craig (2011). A Field Guide to the Birds of Southeast Asia. New Holland Publishers Ltd. ISBN 978-1780090498
- San Francisco Chronicle, Glen Martin (May 30, 2002). "The depths of destruction / Dynamite fishing ravages Philippines' precious coral reefs". Archived from the original on November 6, 2014
- Society of Philippine Health History (2004). "1900s : The Epidemic years". Archived from the original on April 20, 2005
- The Freeman, Ria Mae Y. Booc (August 21, 2010). "Historical Structures: Gabaldon school buildings to be preserved". The Philippine STAR. Archived from the original on May 18, 2015
- The Freeman, Jessica J. Agua (July 25, 2014a). "DENR starts Bantayan Island survey to come up with management plan". The Philippine STAR. Archived from the original on November 9, 2014
- The Freeman, Jessica J. Agua (September 14, 2014b). "DENR forms TWG to review town's management plan for protected area". Archived from the original on November 8, 2014
- The Freeman, Gregg M. Rubio (October 10, 2014c). "RDC-7: Reclassify Bantayan Island". The Philippine STAR. Archived from the original on December 6, 2014
- The Freeman, Gregg M. Rubio (November 1, 2014d). "Solon pushes for "tertiary hospital" in Bantayan". p. 7. Archived from the original on December 17, 2014
- The Freeman, Gregg M. Rubio (February 4, 2015). "First Tañon Strait summit set". Archived from the original on July 21, 2015
- The Manila Bulletin, Ellalyn de Vera (December 11, 2009). "Environmental group moves to protect Cebu's coral reefs". Archived from the original on December 14, 2009
- Unisys Weather Information Systems (November 18–28, 1968), Unisys Western Pacific Hurricane Tracking Data by Year, archived from the original (Tabular text data) on March 4, 2016, retrieved December 2, 2012
- Unisys Weather Information Systems (November 3–11, 2013), Unisys Western Pacific Hurricane Tracking Data by Year, archived from the original (Tabular text data) on February 21, 2016, retrieved October 17, 2014
- Wild Bird Club of the Philippines (January 21, 2004), Taxonomic list of confirmed sightings (spreadsheet (XL))
- Wiley, Mark V. (1997). Filipino Martial Culture: A Sourcebook. Boston: Tuttle Publishing. ISBN 978-0804820882
- Zaide, Gregorio F. (1937a). Catholicism in the Philippines. Manila: UST Press
- Zaide, Gregorio F. (1937b). Early Philippine History and Culture. Manila: Oriental Printing
- Zaide, Gregorio F. (1968). The United Nations and our Republic (revised ed.). Quezon City: Bede's Publishing House