 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Biogest, Sterolibrin, Antigest B, Agelin |
| Other names | SCH-12600; 6-Chloromethylenedehydroacetoxyprogesterone; 17α-Acetoxy-6-chloro-16-methylene-6-dehydroprogesterone; 16-Methylenechlormadinone acetate; 17α-Acetoxy-6-chloro-16-methylenepregna-4,6-diene-3,20-dione |
| Drug class | Progestogen; Progestin; Progestogen ester |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
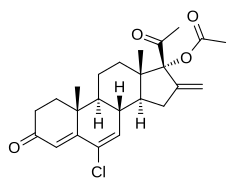
| Formula | C24H29ClO4 |
| Molar mass | 416.94 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Chlormethenmadinone acetate (CMMA), also known as chlorsuperlutin, is a progestin medication which was developed in Czechoslovakia in the 1960s.[1] It has been used in combination with mestranol in birth control pills under the brand names Biogest, Sterolibrin, and Antigest B,[2][3] and in veterinary medicine under the brand name Agelin.[4] Analogues of CMMA include bromethenmadinone acetate (bromsuperlutin), which was assessed but was never marketed,[3][5] and melengestrol acetate (methylsuperlutin), which is used in veterinary medicine.[6]
See also
[edit]- List of progestogen esters § Esters of 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivatives
- 16-Methylene-17α-hydroxyprogesterone acetate
References
[edit]- ^ Sterba R (1968). "New biological application of contraceptive steroids". Endocrinologia Experimentalis. 2 (2): 101–110. Archived from the original on 16 September 2018.
- ^ Melich H (July 1972). "[Biogest]". Casopis Lekaru Ceskych (in Czech). 111 (30): 694–695. PMID 5079918. Archived from the original on 2018-09-16. Retrieved 2018-09-16.
- ^ a b Stĕrba R (March 1970). "[Towards a more physiological hormonal contraception]". Zentralblatt Fur Gynakologie (in German). 92 (10): 303–312. PMID 4096927. Archived from the original on 2018-09-16. Retrieved 2018-09-16.
- ^ Bekeová E, Krajnicáková M, Hendrichovský V, Maracek I (November 1995). "[Thyroid and ovarian hormones in ewes treated with gestagens and PMSG in the spring season]". Veterinarni Medicina (in Slovak). 40 (11): 345–352. PMID 8659087. Archived from the original on 2018-09-16. Retrieved 2018-09-16.
- ^ Štěrba, R. (1971). "On the Way to a More Physiological Hormonal Contraception". Current Problems in Fertility. pp. 154–158. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-8651-7_28. ISBN 978-1-4615-8653-1. Archived from the original on 2018-09-16. Retrieved 2018-09-16.
- ^ von Kunz W (8 March 2013). "Über neue Arzneimittel". In Denkewalter RG, Tishler M, Ehrhart G, Biel JH, Lum BK, Büchi J, Winter CA, Münzel K, Kunz W, Ariëns EJ, Labhardt F (eds.). Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung / Progress in Drug Research / Progrès des recherches pharmaceutiques. Birkhäuser. pp. 407–. ISBN 978-3-0348-7059-7.