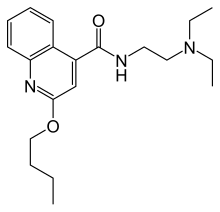
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | topical, intravenous (for animal euthanasia) |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.484 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C20H29N3O2 |
| Molar mass | 343.471 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| (verify) | |
Cinchocaine (INN/BAN) or dibucaine (USAN) is an amide local anesthetic. Among the most potent and toxic of the long-acting local anesthetics, current use of cinchocaine is generally restricted to spinal and topical anesthesia.[1][2] It is sold under the brand names Cincain, Nupercainal, Nupercaine and Sovcaine.
Medical use
[edit]Cinchocaine is the active ingredient in some topical hemorrhoid creams such as Proctosedyl.[3] It is also a component of the veterinary drug Somulose, used for euthanasia of horses and cattle.
Physical properties
[edit]Cinchocaine is relatively insoluble in alkaline aqueous solutions.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Martindale, The Extra Pharmacopoeia, 30th ed, p1006
- ^ "Dibucaine". MeSH Browser. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Henderson R (29 November 2020). "Proctosedyl ointment/suppositories (cinchocaine, hydrocortisone)". Netdoctor. Retrieved 25 December 2019.
Further reading
[edit]- Abdel-Ghani NT, Youssef AF, Awady MA (May 2005). "Cinchocaine hydrochloride determination by atomic absorption spectrometry and spectrophotometry". Farmaco. 60 (5): 419–424. doi:10.1016/j.farmac.2005.03.001. PMID 15910814.
- Souto-Padrón T, Lima AP, Ribeiro Rd (September 2006). "Effects of dibucaine on the endocytic/exocytic pathways in Trypanosoma cruzi". Parasitology Research. 99 (4): 317–320. doi:10.1007/s00436-006-0192-1. PMID 16612626. S2CID 5933459.
- Nounou MM, El-Khordagui LK, Khalafallah N (2005). "Effect of various formulation variables on the encapsulation and stability of dibucaine base in multilamellar vesicles". Acta Poloniae Pharmaceutica. 62 (5): 369–379. PMID 16459486.
- Aroti A, Leontidis E (2001). "Simultaneous Determination of the Ionization Constant and the Solubility of Sparingly Soluble Drug Substances. A Physical Chemistry Experiment". Journal of Chemical Education. 78 (6): 786–788. Bibcode:2001JChEd..78..786A. doi:10.1021/ed078p786.