 | |
 | |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Systematic IUPAC name
[(2R,3S,4R,5R)-5-(6-Amino-9H-purin-9-yl)-4-hydroxy-3-(phosphonooxy)tetrahydro-2-furanyl]methyl (3R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-oxo-4-({3-oxo-3-[(2-sulfanylethyl)amino]propyl}amino)butyl dihydrogen diphosphate | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| DrugBank | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.472 |
| KEGG | |
| MeSH | Coenzyme+A |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C21H36N7O16P3S | |
| Molar mass | 767.535 |
| UV-vis (λmax) | 259.5 nm[1] |
| Absorbance | ε259 = 16.8 mM−1 cm−1[1] |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Coenzyme A (CoA, SHCoA, CoASH) is a coenzyme, notable for its role in the synthesis and oxidation of fatty acids, and the oxidation of pyruvate in the citric acid cycle. All genomes sequenced to date encode enzymes that use coenzyme A as a substrate, and around 4% of cellular enzymes use it (or a thioester) as a substrate. In humans, CoA biosynthesis requires cysteine, pantothenate (vitamin B5), and adenosine triphosphate (ATP).[2]
In its acetyl form, coenzyme A is a highly versatile molecule, serving metabolic functions in both the anabolic and catabolic pathways. Acetyl-CoA is utilised in the post-translational regulation and allosteric regulation of pyruvate dehydrogenase and carboxylase to maintain and support the partition of pyruvate synthesis and degradation.[3]
Discovery of structure
[edit]
Coenzyme A was identified by Fritz Lipmann in 1946,[4] who also later gave it its name. Its structure was determined during the early 1950s at the Lister Institute, London, together by Lipmann and other workers at Harvard Medical School and Massachusetts General Hospital.[5] Lipmann initially intended to study acetyl transfer in animals, and from these experiments he noticed a unique factor that was not present in enzyme extracts but was evident in all organs of the animals. He was able to isolate and purify the factor from pig liver and discovered that its function was related to a coenzyme that was active in choline acetylation.[6] Work with Beverly Guirard, Nathan Kaplan, and others determined that pantothenic acid was a central component of coenzyme A.[7][8] The coenzyme was named coenzyme A to stand for "activation of acetate". In 1953, Fritz Lipmann won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine "for his discovery of co-enzyme A and its importance for intermediary metabolism".[6][9]
Biosynthesis
[edit]Coenzyme A is naturally synthesized from pantothenate (vitamin B5), which is found in food such as meat, vegetables, cereal grains, legumes, eggs, and milk.[10] In humans and most living organisms, pantothenate is an essential vitamin that has a variety of functions.[11] In some plants and bacteria, including Escherichia coli, pantothenate can be synthesised de novo and is therefore not considered essential. These bacteria synthesize pantothenate from the amino acid aspartate and a metabolite in valine biosynthesis.[12]
In all living organisms, coenzyme A is synthesized in a five-step process that requires four molecules of ATP, pantothenate and cysteine[13] (see figure):

- Pantothenate (vitamin B5) is phosphorylated to 4′-phosphopantothenate by the enzyme pantothenate kinase (PanK; CoaA; CoaX). This is the committed step in CoA biosynthesis and requires ATP.[12]
- A cysteine is added to 4′-phosphopantothenate by the enzyme phosphopantothenoylcysteine synthetase (PPCS; CoaB) to form 4'-phospho-N-pantothenoylcysteine (PPC). This step is coupled with ATP hydrolysis.[12]
- PPC is decarboxylated to 4′-phosphopantetheine by phosphopantothenoylcysteine decarboxylase (PPC-DC; CoaC)
- 4′-phosphopantetheine is adenylated (or more properly, AMPylated) to form dephospho-CoA by the enzyme phosphopantetheine adenylyl transferase (COASY; PPAT; CoaD)
- Finally, dephospho-CoA is phosphorylated to coenzyme A by the enzyme dephosphocoenzyme A kinase (COASY, DPCK; CoaE). This final step requires ATP.[12]
Enzyme nomenclature abbreviations in parentheses represent mammalian, other eukaryotic, and prokaryotic enzymes respectively. In mammals steps 4 and 5 are catalyzed by a bifunctional enzyme called COASY.[14] This pathway is regulated by product inhibition. CoA is a competitive inhibitor for Pantothenate Kinase, which normally binds ATP.[12] Coenzyme A, three ADP, one monophosphate, and one diphosphate are harvested from biosynthesis.[13]
Coenzyme A can be synthesized through alternate routes when intracellular coenzyme A level are reduced and the de novo pathway is impaired.[15] In these pathways, coenzyme A needs to be provided from an external source, such as food, in order to produce 4′-phosphopantetheine. Ectonucleotide pyrophosphates (ENPP) degrade coenzyme A to 4′-phosphopantetheine, a stable molecule in organisms. Acyl carrier proteins (ACP) (such as ACP synthase and ACP degradation) are also used to produce 4′-phosphopantetheine. This pathway allows for 4′-phosphopantetheine to be replenished in the cell and allows for the conversion to coenzyme A through enzymes, PPAT and PPCK.[16]
A 2024 article[citation needed] detailed a plausible chemical synthesis mechanism for the pantetheine component (the main functional part) of coenzyme A in a primordial prebiotic world.
Commercial production
[edit]Coenzyme A is produced commercially via extraction from yeast, however this is an inefficient process (yields approximately 25 mg/kg) resulting in an expensive product. Various ways of producing CoA synthetically, or semi-synthetically have been investigated, although none are currently operating at an industrial scale.[17]
Function
[edit]Fatty acid synthesis
[edit]Since coenzyme A is, in chemical terms, a thiol, it can react with carboxylic acids to form thioesters, thus functioning as an acyl group carrier. It assists in transferring fatty acids from the cytoplasm to mitochondria. A molecule of coenzyme A carrying an acyl group is also referred to as acyl-CoA. When it is not attached to an acyl group, it is usually referred to as 'CoASH' or 'HSCoA'. This process facilitates the production of fatty acids in cells, which are essential in cell membrane structure.
Coenzyme A is also the source of the phosphopantetheine group that is added as a prosthetic group to proteins such as acyl carrier protein and formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase.[18][19]
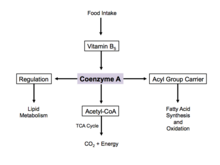
Energy production
[edit]Coenzyme A is one of five crucial coenzymes that are necessary in the reaction mechanism of the citric acid cycle. Its acetyl-coenzyme A form is the primary input in the citric acid cycle and is obtained from glycolysis, amino acid metabolism, and fatty acid beta oxidation. This process is the body's primary catabolic pathway and is essential in breaking down the building blocks of the cell such as carbohydrates, amino acids, and lipids.[20]
Regulation
[edit]When there is excess glucose, coenzyme A is used in the cytosol for synthesis of fatty acids.[21] This process is implemented by regulation of acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which catalyzes the committed step in fatty acid synthesis. Insulin stimulates acetyl-CoA carboxylase, while epinephrine and glucagon inhibit its activity.[22]
During cell starvation, coenzyme A is synthesized and transports fatty acids in the cytosol to the mitochondria. Here, acetyl-CoA is generated for oxidation and energy production.[21] In the citric acid cycle, coenzyme A works as an allosteric regulator in the stimulation of the enzyme pyruvate dehydrogenase.
Antioxidant function and regulation
[edit]Discovery of the novel antioxidant function of coenzyme A highlights its protective role during cellular stress. Mammalian and bacterial cells subjected to oxidative and metabolic stress show significant increase in the covalent modification of protein cysteine residues by coenzyme A.[23][24] This reversible modification is termed protein CoAlation (Protein-S-SCoA), which plays a similar role to protein S-glutathionylation by preventing the irreversible oxidation of the thiol group of cysteine residues.
Using anti-coenzyme A antibody[25] and liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) methodologies, more than 2,000 CoAlated proteins were identified from stressed mammalian and bacterial cells.[26] The majority of these proteins are involved in cellular metabolism and stress response.[26] Different research studies have focused on deciphering the coenzyme A-mediated regulation of proteins. Upon protein CoAlation, inhibition of the catalytic activity of different proteins (e.g., metastasis suppressor NME1, peroxiredoxin 5, GAPDH, among others) is reported.[27][28][24][29] To restore the protein's activity, antioxidant enzymes that reduce the disulfide bond between coenzyme A and the protein cysteine residue play an important role. This process is termed protein deCoAlation. Thioredoxin A and Thioredoxin-like protein (YtpP), two bacterial proteins, are shown to deCoAlate proteins.[30]
Use in biological research
[edit]Coenzyme A is available from various chemical suppliers as the free acid and lithium or sodium salts. The free acid of coenzyme A is detectably unstable, with around 5% degradation observed after 6 months when stored at −20 °C,[1] and near complete degradation after 1 month at 37 °C.[31] The lithium and sodium salts of CoA are more stable, with negligible degradation noted over several months at various temperatures.[32] Aqueous solutions of coenzyme A are unstable above pH 8, with 31% of activity lost after 24 hours at 25 °C and pH 8. CoA stock solutions are relatively stable when frozen at pH 2–6. The major route of CoA activity loss is likely the air oxidation of CoA to CoA disulfides. CoA mixed disulfides, such as CoA-S–S-glutathione, are commonly noted contaminants in commercial preparations of CoA.[1] Free CoA can be regenerated from CoA disulfide and mixed CoA disulfides with reducing agents such as dithiothreitol or 2-mercaptoethanol.
Non-exhaustive list of coenzyme A-activated acyl groups
[edit]- Acetyl-CoA
- fatty acyl-CoA (activated form of all fatty acids; only the CoA esters are substrates for important reactions such as mono-, di-, and triacylglycerol synthesis, carnitine palmitoyl transferase, and cholesterol esterification)
- Propionyl-CoA
- Butyryl-CoA
- Myristoyl-CoA
- Crotonyl-CoA
- Acetoacetyl-CoA
- Coumaroyl-CoA (used in flavonoid and stilbenoid biosynthesis)
- Benzoyl-CoA
- Phenylacetyl-CoA
- Acyl derived from dicarboxylic acids
- Malonyl-CoA (important in chain elongation in fatty acid biosynthesis and polyketide biosynthesis)
- Succinyl-CoA (used in heme biosynthesis)
- Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA (used in isoprenoid biosynthesis)
- Pimelyl-CoA (used in biotin biosynthesis)
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d Dawson RM, Elliott DC, Elliott WH, Jones KM (2002). Data for Biochemical Research (3rd ed.). Clarendon Press. pp. 118–119. ISBN 978-0-19-855299-4.
- ^ Daugherty M, Polanuyer B, Farrell M, Scholle M, Lykidis A, de Crécy-Lagard V, Osterman A (June 2002). "Complete reconstitution of the human coenzyme A biosynthetic pathway via comparative genomics". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 277 (24): 21431–21439. doi:10.1074/jbc.M201708200. PMID 11923312.
- ^ "Coenzyme A: when small is mighty". www.asbmb.org. Archived from the original on 2018-12-20. Retrieved 2018-12-19.
- ^ Lipmann F, Kaplan NO (1946). "A common factor in the enzymatic acetylation of sulfanilamide and of choline". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 162 (3): 743–744. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)41419-0.
- ^ Baddiley J, Thain EM, Novelli GD, Lipmann F (January 1953). "Structure of coenzyme A". Nature. 171 (4341): 76. Bibcode:1953Natur.171...76B. doi:10.1038/171076a0. PMID 13025483. S2CID 630898.
- ^ a b Kresge N, Simoni RD, Hill RL (2005-05-27). "Fritz Lipmann and the Discovery of Coenzyme A". Journal of Biological Chemistry. 280 (21): e18. ISSN 0021-9258. Archived from the original on 2019-04-12. Retrieved 2017-10-24.
- ^ Lipmann F, Kaplan NO (March 1947). "Coenzyme for acetylation, a pantothenic acid derivative". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 167 (3): 869–870. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(17)30973-0. PMID 20287921.
- ^ Lipmann F, Kaplan NO, Novelli GD, Tuttle LC, Guirard BM (September 1950). "Isolation of coenzyme A". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 186 (1): 235–243. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)56309-2. PMID 14778827.
- ^ "Fritz Lipmann – Facts". Nobelprize.org. Nobel Media AB. 2014. Retrieved 8 November 2017.
- ^ "Vitamin B5 (Pantothenic acid)". University of Maryland Medical Center. Archived from the original on 2017-10-18. Retrieved 2017-11-08.
- ^ "Pantothenic Acid (Vitamin B5): MedlinePlus Supplements". medlineplus.gov. Archived from the original on 2017-12-22. Retrieved 2017-12-10.
- ^ a b c d e Leonardi R, Jackowski S (April 2007). "Biosynthesis of Pantothenic Acid and Coenzyme A". EcoSal Plus. 2 (2). doi:10.1128/ecosalplus.3.6.3.4. PMC 4950986. PMID 26443589.
- ^ a b Leonardi R, Zhang YM, Rock CO, Jackowski S (2005). "Coenzyme A: back in action". Progress in Lipid Research. 44 (2–3): 125–153. doi:10.1016/j.plipres.2005.04.001. PMID 15893380.
- ^ Evers C, Seitz A, Assmann B, Opladen T, Karch S, Hinderhofer K, et al. (July 2017). "Diagnosis of CoPAN by whole exome sequencing: Waking up a sleeping tiger's eye". American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A. 173 (7): 1878–1886. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.38252. PMID 28489334. S2CID 27153945.
- ^ de Villiers M, Strauss E (October 2015). "Metabolism: Jump-starting CoA biosynthesis". Nature Chemical Biology. 11 (10): 757–758. doi:10.1038/nchembio.1912. PMID 26379022.
- ^ Sibon OC, Strauss E (October 2016). "Coenzyme A: to make it or uptake it?". Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology. 17 (10): 605–606. doi:10.1038/nrm.2016.110. PMID 27552973. S2CID 10344527.
- ^ Mouterde LM, Stewart JD (19 December 2018). "Isolation and Synthesis of One of the Most Central Cofactors in Metabolism: Coenzyme A" (PDF). Organic Process Research & Development. 23: 19–30. doi:10.1021/acs.oprd.8b00348. S2CID 92802641.
- ^ Elovson J, Vagelos PR (July 1968). "Acyl carrier protein. X. Acyl carrier protein synthetase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 243 (13): 3603–3611. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)34183-3. PMID 4872726.
- ^ Strickland KC, Hoeferlin LA, Oleinik NV, Krupenko NI, Krupenko SA (January 2010). "Acyl carrier protein-specific 4'-phosphopantetheinyl transferase activates 10-formyltetrahydrofolate dehydrogenase". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 285 (3): 1627–1633. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.080556. PMC 2804320. PMID 19933275.
- ^ Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M, Roberts K, Walter P (2002). "Chapter 2: How Cells Obtain Energy from Food". Molecular Biology of the Cell (4th ed.). Garland Science.
- ^ a b Shi L, Tu BP (April 2015). "Acetyl-CoA and the regulation of metabolism: mechanisms and consequences". Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 33: 125–131. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2015.02.003. PMC 4380630. PMID 25703630.
- ^ Berg JM, Tymoczko JL, Stryer L (2002). "Acetyl Coenzyme A Carboxylase Plays a Key Role in Controlling Fatty Acid Metabolism". Biochemistry.
- ^ Tsuchiya Y, Peak-Chew SY, Newell C, Miller-Aidoo S, Mangal S, Zhyvoloup A, et al. (July 2017). "Protein CoAlation: a redox-regulated protein modification by coenzyme A in mammalian cells". The Biochemical Journal. 474 (14): 2489–2508. doi:10.1042/BCJ20170129. PMC 5509381. PMID 28341808.
- ^ a b Tsuchiya Y, Zhyvoloup A, Baković J, Thomas N, Yu BY, Das S, et al. (June 2018). "Protein CoAlation and antioxidant function of coenzyme A in prokaryotic cells". The Biochemical Journal. 475 (11): 1909–1937. doi:10.1042/BCJ20180043. PMC 5989533. PMID 29626155.
- ^ Malanchuk OM, Panasyuk GG, Serbyn NM, Gout IT, Filonenko VV (2015). "Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific to Coenzyme A". Biopolymers and Cell. 31 (3): 187–192. doi:10.7124/bc.0008DF. ISSN 0233-7657.
- ^ a b Tossounian MA, Baczynska M, Dalton W, Newell C, Ma Y, Das S, et al. (July 2022). "Profiling the Site of Protein CoAlation and Coenzyme A Stabilization Interactions". Antioxidants. 11 (7): 1362. doi:10.3390/antiox11071362. PMC 9312308. PMID 35883853.
- ^ Tossounian MA, Zhang B, Gout I (December 2020). "The Writers, Readers, and Erasers in Redox Regulation of GAPDH". Antioxidants. 9 (12): 1288. doi:10.3390/antiox9121288. PMC 7765867. PMID 33339386.
- ^ Yu BY, Tossounian MA, Hristov SD, Lawrence R, Arora P, Tsuchiya Y, et al. (August 2021). "Regulation of metastasis suppressor NME1 by a key metabolic cofactor coenzyme A". Redox Biology. 44: 101978. doi:10.1016/j.redox.2021.101978. PMC 8212152. PMID 33903070.
- ^ Baković J, Yu BY, Silva D, Chew SP, Kim S, Ahn SH, et al. (November 2019). "A key metabolic integrator, coenzyme A, modulates the activity of peroxiredoxin 5 via covalent modification". Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry. 461 (1–2): 91–102. doi:10.1007/s11010-019-03593-w. PMC 6790197. PMID 31375973.
- ^ Tossounian MA, Baczynska M, Dalton W, Peak-Chew SY, Undzenas K, Korza G, et al. (April 2023). "Bacillus subtilis YtpP and Thioredoxin A Are New Players in the Coenzyme-A-Mediated Defense Mechanism against Cellular Stress". Antioxidants. 12 (4): 938. doi:10.3390/antiox12040938. PMC 10136147. PMID 37107313.
- ^ "Datasheet for free acid coenzyme A" (PDF). Oriental Yeast Co., LTD.
- ^ "Datasheet for lithium salt coenzyme A" (PDF). Oriental Yeast Co., LTD.
Bibliography
[edit]- Nelson DL, Cox MM (2005). Lehninger: Principles of Biochemistry (4th ed.). New York: W .H. Freeman. ISBN 978-0-7167-4339-2.