| Observation data Epoch J2000 Equinox J2000 | |
|---|---|
| Constellation | Aries |
| Right ascension | 03h 11m 37.76465s[1] |
| Declination | +19° 43′ 36.0397″[1] |
| Apparent magnitude (V) | 4.349[2] |
| Characteristics | |
| Spectral type | K2 III[3] |
| U−B color index | +0.914[2] |
| B−V color index | +1.035[2] |
| R−I color index | 0.51 |
| Variable type | Suspected[4] |
| Astrometry | |
| Radial velocity (Rv) | 23.05 ± 0.20[3] km/s |
| Proper motion (μ) | RA: +153.33[1] mas/yr Dec.: –8.28[1] mas/yr |
| Parallax (π) | 19.22 ± 0.19 mas[1] |
| Distance | 170 ± 2 ly (52.0 ± 0.5 pc) |
| Absolute magnitude (MV) | +0.77[5] |
| Details | |
| Mass | 1.91[3] M☉ |
| Radius | 10.42 ± 0.97[6] R☉ |
| Luminosity | 45 ± 6[6] L☉ |
| Surface gravity (log g) | 2.93[6] cgs |
| Temperature | 4,810[6] K |
| Metallicity [Fe/H] | –0.03[6] dex |
| Rotational velocity (v sin i) | 4.3[7] km/s |
| Other designations | |
| Database references | |
| SIMBAD | data |
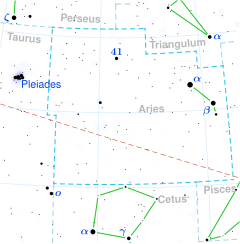
Delta Arietis (δ Arietis, abbreviated Delta Ari, δ Ari), officially named Botein /ˈboʊtiːn/,[9] is a star in the northern constellation of Aries, 1.8 degrees north of the ecliptic. The apparent visual magnitude is 4.35,[2] so it is visible to the naked eye. It has an annual parallax shift of 19.22 mas;[1] corresponding to a distance of about 170 ly (52 pc) from the Sun.
Nomenclature
[edit]δ Arietis (Latinised to Delta Arietis) is the star's Bayer designation.
It bore the traditional name Botein which is derived from Al Bīrūnī's Al Buṭayn (Arabic: البُطَين), the diminutive of Al Baṭn, "the Belly". This is the name of a star association consisting of this star, Epsilon Arietis, Zeta Arietis, Pi Arietis, and Rho3 Arietis[10] According to a 1971 NASA catalogue of stars, Al Buṭain was the title for five stars: Delta Arietis (listed as Botein), Pi Arietis (as Al Buṭain I), Rho3 Arietis (Al Buṭain II), Epsilon Arietis (Al Buṭain III) and Zeta Arietis (Al Buṭain IV).[11] In 2016, the International Astronomical Union organized a Working Group on Star Names (WGSN)[12] to catalogue and standardize proper names for stars. The WGSN approved the name Botein for this star on 12 September 2016 and it is now so included in the List of IAU-approved Star Names.[9]
In the catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Al Achsasi Al Mouakket, this star was designated Nir al Botain, which was translated into Latin as Lucida Ventris, meaning "the brightest of the belly".[13]
In Chinese, 天陰 (Tiān Yīn), meaning Yin Force, refers to an asterism consisting of Delta Arietis, 63 Arietis, Zeta Arietis, Tau Arietis and 65 Arietis.[14] Consequently, the Chinese name for Delta Arietis itself is 天陰四 (Lóu Su sì, English: the Fourth Star of Yin Force.)[15]
Properties
[edit]Delta Arietis is an evolved giant star with a stellar classification of K2 III.[3] It belongs to a population known as red clump giants, which means it is generating energy through the fusion of helium at its core.[16] With close to twice the mass of the Sun,[3] the outer envelope has expanded until it is around ten[6] times the Sun's radius. It shines with 45[6] times the Sun's luminosity at an effective temperature of 4,810 K,[6] giving it the orange-hued glow of a K-type star.[17] It is a suspected variable star that ranges in magnitude from 4.33 to 4.37.[4]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e f van Leeuwen, F. (November 2007), "Validation of the new Hipparcos reduction", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 474 (2): 653–664, arXiv:0708.1752, Bibcode:2007A&A...474..653V, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20078357, S2CID 18759600.
- ^ a b c d Jennens, P. A.; Helfer, H. L. (September 1975), "A new photometric metal abundance and luminosity calibration for field G and K giants.", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 172 (3): 667–679, Bibcode:1975MNRAS.172..667J, doi:10.1093/mnras/172.3.667.
- ^ a b c d e Hekker, S.; et al. (August 2006), "Precise radial velocities of giant stars. I. Stable stars", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 454 (3): 943–949, arXiv:astro-ph/0604502, Bibcode:2006A&A...454..943H, doi:10.1051/0004-6361:20064946, S2CID 119529768.
- ^ a b Samus, N. N.; Durlevich, O. V.; Kazarovets, R. V., "NSV 01066", General Catalogue of Variable Stars, retrieved 2012-08-04.
- ^ Anderson, E.; Francis, Ch. (2012), "XHIP: An extended hipparcos compilation", Astronomy Letters, 38 (5): 331, arXiv:1108.4971, Bibcode:2012AstL...38..331A, doi:10.1134/S1063773712050015, S2CID 119257644.
- ^ a b c d e f g h Piau, L.; et al. (February 2011), "Surface convection and red-giant radius measurements", Astronomy and Astrophysics, 526: A100, arXiv:1010.3649, Bibcode:2011A&A...526A.100P, doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201014442, S2CID 118533297.
- ^ Massarotti, Alessandro; et al. (January 2008), "Rotational and Radial Velocities for a Sample of 761 HIPPARCOS Giants and the Role of Binarity", The Astronomical Journal, 135 (1): 209–231, Bibcode:2008AJ....135..209M, doi:10.1088/0004-6256/135/1/209, S2CID 121883397.
- ^ "del Ari". SIMBAD. Centre de données astronomiques de Strasbourg. Retrieved 2012-08-04.
- ^ a b "Naming Stars". IAU.org. Retrieved 16 December 2017.
- ^ Allen, R. H. (1963), Star Names: Their Lore and Meaning (Reprint ed.), New York: Dover Publications Inc, p. 83, ISBN 0-486-21079-0, retrieved 2010-12-12
- ^ Jack W. Rhoads - Technical Memorandum 33-507-A Reduced Star Catalog Containing 537 Named Stars, Jet Propulsion Laboratory, California Institute of Technology; November 15, 1971
- ^ IAU Working Group on Star Names (WGSN), International Astronomical Union, retrieved 22 May 2016.
- ^ Knobel, E. B. (June 1895). "Al Achsasi Al Mouakket, on a catalogue of stars in the Calendarium of Mohammad Al Achsasi Al Mouakket". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 55: 429–438. Bibcode:1895MNRAS..55..429K. doi:10.1093/mnras/55.8.429.
- ^ (in Chinese) 中國星座神話, written by 陳久金. Published by 台灣書房出版有限公司, 2005, ISBN 978-986-7332-25-7.
- ^ (in Chinese) 香港太空館 - 研究資源 - 亮星中英對照表 Archived 2010-08-11 at the Wayback Machine, Hong Kong Space Museum. Accessed on line November 23, 2010.
- ^ Puzeras, E.; et al. (October 2010), "High-resolution spectroscopic study of red clump stars in the Galaxy: iron-group elements", Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, 408 (2): 1225–1232, arXiv:1006.3857, Bibcode:2010MNRAS.408.1225P, doi:10.1111/j.1365-2966.2010.17195.x, S2CID 44228180.
- ^ "The Colour of Stars", Australia Telescope, Outreach and Education, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, December 21, 2004, archived from the original on 2012-03-18, retrieved 2012-01-16