This section needs additional citations for verification. (October 2012) |
| Part of a series of articles about |
| Calculus |
|---|
In multivariable calculus, the directional derivative measures the rate at which a function changes in a particular direction at a given point.[citation needed]
The directional derivative of a multivariable differentiable (scalar) function along a given vector v at a given point x intuitively represents the instantaneous rate of change of the function, moving through x with a direction specified by v.
The directional derivative of a scalar function f with respect to a vector v at a point (e.g., position) x may be denoted by any of the following:
It therefore generalizes the notion of a partial derivative, in which the rate of change is taken along one of the curvilinear coordinate curves, all other coordinates being constant. The directional derivative is a special case of the Gateaux derivative.
Definition
[edit]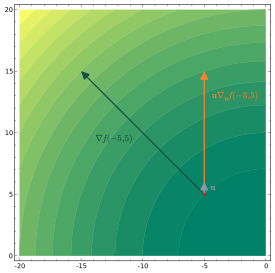
The directional derivative of a scalar function along a vector is the function defined by the limit[1]
This definition is valid in a broad range of contexts, for example where the norm of a vector (and hence a unit vector) is undefined.[2]
For differentiable functions
[edit]If the function f is differentiable at x, then the directional derivative exists along any unit vector v at x, and one has
where the on the right denotes the gradient, is the dot product and v is a unit vector.[3] This follows from defining a path and using the definition of the derivative as a limit which can be calculated along this path to get:
Intuitively, the directional derivative of f at a point x represents the rate of change of f, in the direction of v.
Using only direction of vector
[edit]
In a Euclidean space, some authors[4] define the directional derivative to be with respect to an arbitrary nonzero vector v after normalization, thus being independent of its magnitude and depending only on its direction.[5]
This definition gives the rate of increase of f per unit of distance moved in the direction given by v. In this case, one has or in case f is differentiable at x,
Restriction to a unit vector
[edit]In the context of a function on a Euclidean space, some texts restrict the vector v to being a unit vector. With this restriction, both the above definitions are equivalent.[6]
Properties
[edit]Many of the familiar properties of the ordinary derivative hold for the directional derivative. These include, for any functions f and g defined in a neighborhood of, and differentiable at, p:
- sum rule:
- constant factor rule: For any constant c,
- product rule (or Leibniz's rule):
- chain rule: If g is differentiable at p and h is differentiable at g(p), then
In differential geometry
[edit]Let M be a differentiable manifold and p a point of M. Suppose that f is a function defined in a neighborhood of p, and differentiable at p. If v is a tangent vector to M at p, then the directional derivative of f along v, denoted variously as df(v) (see Exterior derivative), (see Covariant derivative), (see Lie derivative), or (see Tangent space § Definition via derivations), can be defined as follows. Let γ : [−1, 1] → M be a differentiable curve with γ(0) = p and γ′(0) = v. Then the directional derivative is defined by This definition can be proven independent of the choice of γ, provided γ is selected in the prescribed manner so that γ(0) = p and γ′(0) = v.
The Lie derivative
[edit]The Lie derivative of a vector field along a vector field is given by the difference of two directional derivatives (with vanishing torsion): In particular, for a scalar field , the Lie derivative reduces to the standard directional derivative:
The Riemann tensor
[edit]Directional derivatives are often used in introductory derivations of the Riemann curvature tensor. Consider a curved rectangle with an infinitesimal vector along one edge and along the other. We translate a covector along then and then subtract the translation along and then . Instead of building the directional derivative using partial derivatives, we use the covariant derivative. The translation operator for is thus and for , The difference between the two paths is then It can be argued[7] that the noncommutativity of the covariant derivatives measures the curvature of the manifold: where is the Riemann curvature tensor and the sign depends on the sign convention of the author.
In group theory
[edit]Translations
[edit]In the Poincaré algebra, we can define an infinitesimal translation operator P as (the i ensures that P is a self-adjoint operator) For a finite displacement λ, the unitary Hilbert space representation for translations is[8] By using the above definition of the infinitesimal translation operator, we see that the finite translation operator is an exponentiated directional derivative: This is a translation operator in the sense that it acts on multivariable functions f(x) as
In standard single-variable calculus, the derivative of a smooth function f(x) is defined by (for small ε) This can be rearranged to find f(x+ε): It follows that is a translation operator. This is instantly generalized[9] to multivariable functions f(x) Here is the directional derivative along the infinitesimal displacement ε. We have found the infinitesimal version of the translation operator: It is evident that the group multiplication law[10] U(g)U(f)=U(gf) takes the form So suppose that we take the finite displacement λ and divide it into N parts (N→∞ is implied everywhere), so that λ/N=ε. In other words, Then by applying U(ε) N times, we can construct U(λ): We can now plug in our above expression for U(ε): Using the identity[11] we have And since U(ε)f(x) = f(x+ε) we have Q.E.D.
As a technical note, this procedure is only possible because the translation group forms an Abelian subgroup (Cartan subalgebra) in the Poincaré algebra. In particular, the group multiplication law U(a)U(b) = U(a+b) should not be taken for granted. We also note that Poincaré is a connected Lie group. It is a group of transformations T(ξ) that are described by a continuous set of real parameters . The group multiplication law takes the form Taking as the coordinates of the identity, we must have The actual operators on the Hilbert space are represented by unitary operators U(T(ξ)). In the above notation we suppressed the T; we now write U(λ) as U(P(λ)). For a small neighborhood around the identity, the power series representation is quite good. Suppose that U(T(ξ)) form a non-projective representation, i.e., The expansion of f to second power is After expanding the representation multiplication equation and equating coefficients, we have the nontrivial condition Since is by definition symmetric in its indices, we have the standard Lie algebra commutator: with C the structure constant. The generators for translations are partial derivative operators, which commute: This implies that the structure constants vanish and thus the quadratic coefficients in the f expansion vanish as well. This means that f is simply additive: and thus for abelian groups, Q.E.D.
Rotations
[edit]The rotation operator also contains a directional derivative. The rotation operator for an angle θ, i.e. by an amount θ = |θ| about an axis parallel to is Here L is the vector operator that generates SO(3): It may be shown geometrically that an infinitesimal right-handed rotation changes the position vector x by So we would expect under infinitesimal rotation: It follows that Following the same exponentiation procedure as above, we arrive at the rotation operator in the position basis, which is an exponentiated directional derivative:[12]
Normal derivative
[edit]A normal derivative is a directional derivative taken in the direction normal (that is, orthogonal) to some surface in space, or more generally along a normal vector field orthogonal to some hypersurface. See for example Neumann boundary condition. If the normal direction is denoted by , then the normal derivative of a function f is sometimes denoted as . In other notations,
In the continuum mechanics of solids
[edit]Several important results in continuum mechanics require the derivatives of vectors with respect to vectors and of tensors with respect to vectors and tensors.[13] The directional directive provides a systematic way of finding these derivatives.
The definitions of directional derivatives for various situations are given below. It is assumed that the functions are sufficiently smooth that derivatives can be taken.
Derivatives of scalar valued functions of vectors
[edit]Let f(v) be a real valued function of the vector v. Then the derivative of f(v) with respect to v (or at v) is the vector defined through its dot product with any vector u being
for all vectors u. The above dot product yields a scalar, and if u is a unit vector gives the directional derivative of f at v, in the u direction.
Properties:
- If then
- If then
- If then
Derivatives of vector valued functions of vectors
[edit]Let f(v) be a vector valued function of the vector v. Then the derivative of f(v) with respect to v (or at v) is the second order tensor defined through its dot product with any vector u being
for all vectors u. The above dot product yields a vector, and if u is a unit vector gives the direction derivative of f at v, in the directional u.
Properties:
- If then
- If then
- If then
Derivatives of scalar valued functions of second-order tensors
[edit]Let be a real valued function of the second order tensor . Then the derivative of with respect to (or at ) in the direction is the second order tensor defined as for all second order tensors .
Properties:
- If then
- If then
- If then
Derivatives of tensor valued functions of second-order tensors
[edit]Let be a second order tensor valued function of the second order tensor . Then the derivative of with respect to (or at ) in the direction is the fourth order tensor defined as for all second order tensors .
Properties:
- If then
- If then
- If then
- If then
See also
[edit]- Del in cylindrical and spherical coordinates – Mathematical gradient operator in certain coordinate systems
- Differential form – Expression that may be integrated over a region
- Ehresmann connection – Differential geometry construct on fiber bundles
- Fréchet derivative – Derivative defined on normed spaces
- Gateaux derivative – Generalization of the concept of directional derivative
- Generalizations of the derivative – Fundamental construction of differential calculus
- Semi-differentiability
- Hadamard derivative
- Lie derivative – A derivative in Differential Geometry
- Material derivative – Time rate of change of some physical quantity of a material element in a velocity field
- Structure tensor – Tensor related to gradients
- Tensor derivative (continuum mechanics)
- Total derivative – Type of derivative in mathematics
Notes
[edit]- ^ R. Wrede; M.R. Spiegel (2010). Advanced Calculus (3rd ed.). Schaum's Outline Series. ISBN 978-0-07-162366-7.
- ^ The applicability extends to functions over spaces without a metric and to differentiable manifolds, such as in general relativity.
- ^ If the dot product is undefined, the gradient is also undefined; however, for differentiable f, the directional derivative is still defined, and a similar relation exists with the exterior derivative.
- ^ Thomas, George B. Jr.; and Finney, Ross L. (1979) Calculus and Analytic Geometry, Addison-Wesley Publ. Co., fifth edition, p. 593.
- ^ This typically assumes a Euclidean space – for example, a function of several variables typically has no definition of the magnitude of a vector, and hence of a unit vector.
- ^ Hughes Hallett, Deborah; McCallum, William G.; Gleason, Andrew M. (2012-01-01). Calculus : Single and multivariable. John wiley. p. 780. ISBN 9780470888612. OCLC 828768012.
- ^ Zee, A. (2013). Einstein gravity in a nutshell. Princeton: Princeton University Press. p. 341. ISBN 9780691145587.
- ^ Weinberg, Steven (1999). The quantum theory of fields (Reprinted (with corr.). ed.). Cambridge [u.a.]: Cambridge Univ. Press. ISBN 9780521550017.
- ^ Zee, A. (2013). Einstein gravity in a nutshell. Princeton: Princeton University Press. ISBN 9780691145587.
- ^ Cahill, Kevin Cahill (2013). Physical mathematics (Repr. ed.). Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-1107005211.
- ^ Larson, Ron; Edwards, Bruce H. (2010). Calculus of a single variable (9th ed.). Belmont: Brooks/Cole. ISBN 9780547209982.
- ^ Shankar, R. (1994). Principles of quantum mechanics (2nd ed.). New York: Kluwer Academic / Plenum. p. 318. ISBN 9780306447907.
- ^ J. E. Marsden and T. J. R. Hughes, 2000, Mathematical Foundations of Elasticity, Dover.
References
[edit]- Hildebrand, F. B. (1976). Advanced Calculus for Applications. Prentice Hall. ISBN 0-13-011189-9.
- K.F. Riley; M.P. Hobson; S.J. Bence (2010). Mathematical methods for physics and engineering. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 978-0-521-86153-3.
- Shapiro, A. (1990). "On concepts of directional differentiability". Journal of Optimization Theory and Applications. 66 (3): 477–487. doi:10.1007/BF00940933. S2CID 120253580.
External links
[edit]![]() Media related to Directional derivative at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Directional derivative at Wikimedia Commons

































![{\displaystyle (1+\delta '\cdot D)(1+\delta \cdot D)S^{\rho }-(1+\delta \cdot D)(1+\delta '\cdot D)S^{\rho }=\sum _{\mu ,\nu }\delta '^{\mu }\delta ^{\nu }[D_{\mu },D_{\nu }]S_{\rho }.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/16bc9cd9d4bae49561e46e2bb1ade2f241a21595)
![{\displaystyle [D_{\mu },D_{\nu }]S_{\rho }=\pm \sum _{\sigma }R^{\sigma }{}_{\rho \mu \nu }S_{\sigma },}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/32da9ce5c5713758361d02d266530759354ec070)







![{\displaystyle [1+\varepsilon \,(d/dx)]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/f1af787ff07e53b33609086c1888d2b2fd239ced)





![{\displaystyle [U({\boldsymbol {\varepsilon }})]^{N}=U(N{\boldsymbol {\varepsilon }})=U({\boldsymbol {\lambda }}).}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/a0bf68a8ddea4b223e57aeb96125b6b252ef9974)
![{\displaystyle [U({\boldsymbol {\varepsilon }})]^{N}=\left[1+{\boldsymbol {\varepsilon }}\cdot \nabla \right]^{N}=\left[1+{\frac {{\boldsymbol {\lambda }}\cdot \nabla }{N}}\right]^{N}.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/c5cb18356a03f1395fb84f7ae1a1969aaa05896b)
![{\displaystyle \exp(x)=\left[1+{\frac {x}{N}}\right]^{N},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/72cd3c66555f47bbb7bb2894720f878de7e958df)
![{\displaystyle [U({\boldsymbol {\varepsilon }})]^{N}f(\mathbf {x} )=f(\mathbf {x} +N{\boldsymbol {\varepsilon }})=f(\mathbf {x} +{\boldsymbol {\lambda }})=U({\boldsymbol {\lambda }})f(\mathbf {x} )=\exp \left({\boldsymbol {\lambda }}\cdot \nabla \right)f(\mathbf {x} ),}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d948442f3d9aeed6f9ffcca821983b35f7a11f5d)









![{\displaystyle [t_{b},t_{c}]=i\sum _{a}(-f^{abc}+f^{acb})t_{a}=i\sum _{a}C^{abc}t_{a},}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/d682fb34fea7e6e3db932ef59372745c8e7bc54b)
![{\displaystyle \left[{\frac {\partial }{\partial x^{b}}},{\frac {\partial }{\partial x^{c}}}\right]=0.}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/bfdf13b5bcc7ed6bd7e78c471510e16087a8cc2d)











![{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial f}{\partial \mathbf {n} }}=\nabla f(\mathbf {x} )\cdot \mathbf {n} =\nabla _{\mathbf {n} }{f}(\mathbf {x} )={\frac {\partial f}{\partial \mathbf {x} }}\cdot \mathbf {n} =Df(\mathbf {x} )[\mathbf {n} ].}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/6a4f10487f6111dbab2f9d600d023737d01899fe)
![{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial f}{\partial \mathbf {v} }}\cdot \mathbf {u} =Df(\mathbf {v} )[\mathbf {u} ]=\left[{\frac {d}{d\alpha }}~f(\mathbf {v} +\alpha ~\mathbf {u} )\right]_{\alpha =0}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/308eadd1b18b96a60ef33e8df365bccc97f0faea)






![{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial \mathbf {f} }{\partial \mathbf {v} }}\cdot \mathbf {u} =D\mathbf {f} (\mathbf {v} )[\mathbf {u} ]=\left[{\frac {d}{d\alpha }}~\mathbf {f} (\mathbf {v} +\alpha ~\mathbf {u} )\right]_{\alpha =0}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e8835d592f0ae810b9b57fa81f345a4850f1f1ce)









![{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial f}{\partial {\boldsymbol {S}}}}:{\boldsymbol {T}}=Df({\boldsymbol {S}})[{\boldsymbol {T}}]=\left[{\frac {d}{d\alpha }}~f({\boldsymbol {S}}+\alpha ~{\boldsymbol {T}})\right]_{\alpha =0}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/3916392ebeebca9ebddb31e76edb1c9f8c08b586)







![{\displaystyle {\frac {\partial {\boldsymbol {F}}}{\partial {\boldsymbol {S}}}}:{\boldsymbol {T}}=D{\boldsymbol {F}}({\boldsymbol {S}})[{\boldsymbol {T}}]=\left[{\frac {d}{d\alpha }}~{\boldsymbol {F}}({\boldsymbol {S}}+\alpha ~{\boldsymbol {T}})\right]_{\alpha =0}}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/e2072ee23ca460f6f32851f397b5879a47033c3b)







