This article needs additional citations for verification. (December 2012) |
Eastern Visayas
Sinirangan Kabisay-an Sidlakang Kabisay-an Silangang Visayas | |
|---|---|
 Location in the Philippines | |
| Coordinates: 11°14′N 125°03′E / 11.24°N 125.05°E | |
| Country | |
| Island group | Visayas |
| Regional center and largest city | Tacloban |
| Area | |
• Total | 23,251.10 km2 (8,977.30 sq mi) |
| Highest elevation (Alto Peak) | 1,325 m (4,347 ft) |
| Population (2020 census)[1] | |
• Total | 4,547,150 |
| • Density | 200/km2 (510/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (PST) |
| ISO 3166 code | PH-08 |
| Provinces | |
| Independent cities | |
| Component cities | |
| Municipalities | 136 |
| Barangays | 4,390 |
| Cong. districts | 12 |
| Languages |
|
| GDP (2023) | ₱568.7 billion $10.22 billion[2] |
| Growth rate | |
| HDI | |
| HDI rank | 11th in the Philippines (2019) |
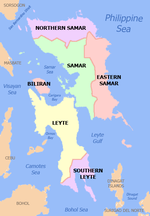
Eastern Visayas (Waray: Sinirangan Kabisay-an; Cebuano: Sidlakang Kabisay-an; Tagalog: Silangang Kabisayaan; Filipino: Silangang Visayas) is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region VIII. It consists of three main islands: Samar, Leyte, and Biliran. The region has six provinces: Biliran, Leyte, Northern Samar, Samar, Eastern Samar, Southern Leyte, one independent city, Ormoc, and one highly urbanized city, Tacloban (its regional center and largest city).[3] The highly urbanized city of Tacloban is the sole regional center. These provinces and cities occupy the easternmost islands of the Visayas group of islands, hence the region's name. Some historians believe that the oldest ancient kingdom in the Philippines is found in this region, the Lakanate of Lawan, which plays a significant role in the Polynesian and Austronesian intermigration.
Eastern Visayas faces the Philippine Sea to the east. The region's most famous landmark is the San Juanico Bridge, which links the islands of Samar and Leyte. As of 2020, the Eastern Visayas region has a population of 4,547,150 inhabitants,[1] making it the least populous region in the Visayas.
Etymology
[edit]The current name of the region was derived from the position of its islands, which are all situated in the easternmost part of the Visayas.
Geography
[edit]Eastern Visayas lies on the east-central section of the Philippine archipelago. It consists of three main islands, Leyte, Biliran, and Samar, which form the easternmost coasts of the archipelago. It is bounded on the east and north by the Philippine Sea with the San Bernardino Strait separating Samar from southeastern Luzon; on the west by the Camotes and Visayan seas, and on the south by the Bohol Sea with the Surigao Strait separating Leyte from northeastern Mindanao. It has a total land area of 2,156,285 hectares (5,328,300 acres) or 7.2% of the country's total land area.[4] 52% of its total land area is classified as forestland and 48% as alienable and disposable land.
Climate
[edit]There are two types of climate prevailing in the region under the Coronas system of classification: Type II and Type IV. Type II climate is characterized by having no dry season but a pronounced maximum rainfall from November to January. Samar Island and the eastern part of Leyte Island fall under this type of climate. Type IV, on the other hand, has an even distribution of rainfall year-round and a short period of dry season that can be observed starting in February up to May. This type of climate is well exhibited in the western half of Leyte Island and in some portions of Samar, which covers the municipality of Motiong up to San Isidro in Northern Samar.
As the region directly faces the Philippine Sea, typhoons coming from the east frequently strike the region, often at their peak intensities. This, along with the Bicol Region, are the most typhoon-prone areas in the Philippines. In 2013, the region was struck by Typhoon Haiyan, locally known as Super Typhoon Yolanda, which later became the deadliest and most destructive typhoon to hit the Philippines in the satellite era.
Natural resources
[edit]The region's sea and inland waters are rich sources of salt, freshwater fish, and other marine products. It is one of the main fish-exporting regions of the country. There are substantial forest reserves in the interiors of the islands. Its mineral deposits include chromite, uranium (in Samar), gold, silver, manganese, magnesium, bronze, nickel, clay, coal, limestone, pyrite and sand and gravel. It also has abundant geothermal energy and water resources to support the needs of medium and heavy industries.
Administrative divisions
[edit]Provinces
[edit]Eastern Visayas consists of 6 provinces, 1 highly urbanized city, 1 independent component city, 5 component cities, 136 municipalities and 4,390 barangays.
| Province or HUC | Capital | Population (2020)[5] | Area[6] | Density | Cities | Muni. | Barangay | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| km2 | sq mi | /km2 | /sq mi | |||||||||
| Biliran | Naval | 3.9% | 179,312 | 536.01 | 206.95 | 330 | 850 | 0 | 8 | 132 | ||
| Eastern Samar | Borongan City | 10.5% | 477,168 | 4,617.16 | 1,782.70 | 100 | 260 | 1 | 22 | 597 | ||
| Leyte | Tacloban | 39.1% | 1,776,847 | 6,335.44 | 2,446.13 | 280 | 730 | 3 | 40 | 1,503 | ||
| Northern Samar | Catarman | 14.1% | 639,186 | 3,694.96 | 1,426.63 | 170 | 440 | 0 | 24 | 569 | ||
| Samar | Catbalogan City | 17.4% | 793,183 | 6,048.03 | 2,335.16 | 130 | 340 | 2 | 24 | 951 | ||
| Southern Leyte | Maasin City | 9.4% | 429,573 | 1,801.46 | 695.55 | 240 | 620 | 1 | 18 | 500 | ||
| Tacloban | † | — | 5.5% | 251,881 | 201.72 | 77.88 | 1,200 | 3,100 | — | — | 138 | |
| Total | 4,547,150 | 23,234.78 | 8,971.00 | 200 | 490 | 7 | 136 | 4,390 | ||||
|
† Tacloban is a highly-urbanized city; figures are excluded from Leyte province.
| ||||||||||||
Governors and vice governors
[edit]| Province | Image | Governor | Political Party | Vice Governor | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
Gerard Roger Espina | Nacionalista | Brigido Caneja III | ||

|
Ben Evardone | PFP | Maria Caridad Goteesan | ||

|
Jericho Petilla | NPC | Leonardo Javier Jr. | ||

|
Edwin Ongchuan | NUP | Clarence Dato | ||

|
Sharee Ann Tan | Nacionalista | Arnold Vasquez Tan | ||

|
Damian Mercado | PFP | Rosa Emilia Mercado | ||
Cities
[edit]- † Regional center
| City | Population (2020)[5] | Area[7] | Density | City class | Income class | Founding year | Province | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baybay | 111,848 | 459.34 | 177.35 | 240 | 620 | Component | 4th | 1620 (cityhood: 2007) | Leyte |
| Borongan | 71,961 | 475.00 | 183.40 | 150 | 390 | Component | 5th | 1619 (cityhood: 2007) | Eastern Samar |
| Calbayog | 186,960 | 880.74 | 340.06 | 210 | 540 | Component | 1st | 1785 (cityhood: 1948) | Samar |
| Catbalogan | 106,440 | 274.22 | 105.88 | 390 | 1,000 | Component | 5th | 1596 (cityhood: 2007) | Samar |
| Maasin | 87,446 | 211.71 | 81.74 | 410 | 1,100 | Component | 4th | 1770 (cityhood: 2000) | Southern Leyte |
| Ormoc | 230,998 | 613.60 | 236.91 | 380 | 980 | Independent component | 1st | 1834 (cityhood: 1947) | Leyte |
| † Tacloban | 251,881 | 201.72 | 77.88 | 1,200 | 3,100 | Highly urbanized | 1st | 1770 (cityhood: 1953) | Leyte |
Demographics
[edit]
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Source: Philippine Statistics Authority[1][8] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Languages
[edit]The native languages of Eastern Visayas are:
- Abaknon, spoken in Capul Island in Northern Samar.
- Baybayanon, spoken in Baybay in Leyte.
- Boholano, spoken in Southern Leyte.
- Cebuano, spoken in western parts of Biliran and Leyte widely used in Southern Leyte.
- Waray-Waray, spoken in Biliran, Leyte, Southern Leyte, Samar, Northern Samar, and Eastern Samar. It is the regional lingua franca.
Economy
[edit]Eastern Visayas is primarily an agricultural region with rice, corn, coconut, sugarcane and banana as its major crops.
Primary sources of revenue are manufacturing, wholesale and retail trade and services. Mining, farming, fishing and tourism contribute significantly to the economy. Manufacturing firms include mining companies, fertilizer plants, sugar central, rice and corn mills and other food processing plants. Tacloban is the hub of investment, trade and development in the region.
Other industries include coconut oil extraction, alcohol distilling, beverage manufacture and forest products. Home industries include hat and basket weaving, metal craft, needlecraft, pottery, ceramics, woodcraft, shell craft and bamboo craft.
Culture
[edit]
Dances
[edit]Tinikling, the Philippines' national dance is folkdance that originated from the region. But the most popular cultural dance among Waraynons is the Kuratsa, danced during feast celebrations and special gatherings. The Leyte Kalipayan Dance Company, a local cultural group, held highly successful performances around the world.
Music
[edit]Waray people are music lovers whose folkloric music are mostly ballads in form, famous of which is Iroy nga Tuna (Motherland), a patriotic song.
Festivals
[edit]Since 2018, Eastern Visayas has held the 'Oktubafest' every October to showcase the best local wine made from coconut palm called tuba.[17][18]
Infrastructure
[edit]
Transportation
[edit]The region's Leyte and Samar islands serve as main link between Luzon and Mindanao by land transport. A total of nine airports, are strategically located in different parts of the six provinces that define the region. Daniel Z. Romualdez Airport in Tacloban is the main gateway by air to the region. There are seaports in Tacloban, Baybay, Laoang, Catbalogan, Calbayog, Borongan, Allen, Ormoc, Bato, Hilongos, Maasin, Sogod, and Naval.
The Pan-Philippine Highway passes through the entire province, starting from Allen in Northern Samar until Liloan in Southern Leyte, where it continues in Mindanao through a ferry service. The Palo-Carigara-Ormoc road is a spur of the aforementioned highway, connecting Cebu City to the network through a ferry ride from Ormoc.
Bridges connect all the islands in the region. Apart from the famed San Juanico Bridge, which connects the islands of Samar and Leyte, the Biliran Bridge, constructed in 1975, connects Biliran to the island of Leyte. The Wawa Bridge also connects Panaon Island to the island of Leyte.
Power and energy
[edit]The region is the top producer of geothermal energy supply in the country. The province of Leyte hosts the biggest geothermal plant in the Philippines. Still, geothermal exploration is ongoing in the nearby province of Biliran. With abundance of river system, the region has potential in hydroelectric production. The strait of San Juanico between Leyte and Samar islands has been declared as potential source for water current and tidal energy sources.
Education
[edit]Eastern Visayas is home to several state universities, including the prestigious University of the Philippines Tacloban College. The region is also home to the University of Eastern Philippines (UEP), located in Catarman, Northern Samar, which holds the most number of baccalaureate and post-baccalaureate courses among universities in the region.
The Zonal Agricultural University for the Visayas under the National Agriculture Education System concept, Visayas State University (VSU) is also in the region, located in Baybay. Also, the region is home to Palompon Institute of Technology, a maritime school in the Philippines providing deck and engine cadet. Its main campus is located in the municipality of Palompon, Leyte province.
The Eastern Visayas State University is Leyte's state university with five extension campuses. Southern Leyte State University with five extension campuses, is the only state university in the province of Southern Leyte. In Biliran, Naval State University is the province state university. For Eastern Samar, the Eastern Samar State University is the only state university of the province with four extension campus while Samar State University is Samar's state university with two extension campuses. Northwest Samar State University serves Samar Province's first district. For teacher education, the Leyte Normal University specializes in education courses.
Notable people
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c Census of Population (2015). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved June 20, 2016.
- ^ a b "2021 to 2023 Gross Regional Domestic Product (GRDP)". openstat.psa.gov.ph. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved April 26, 2024.
- ^ "Eastern Visayas in Visayas Philippines". Archived from the original on November 26, 2012. Retrieved December 1, 2012.
- ^ "Evis.net.ph - evis Resources and Information".
- ^ a b Census of Population (2020). "Region VIII (Eastern Visayas)". Total Population by Province, City, Municipality and Barangay. Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved July 8, 2021.
- ^ "PSGC Interactive; List of Provinces". Philippine Statistics Authority. Archived from the original on January 17, 2013. Retrieved March 29, 2016.
- ^ "PSGC Interactive; List of Cities". Philippine Statistics Authority. Archived from the original on April 29, 2011. Retrieved March 29, 2016.
- ^ "Population and Annual Growth Rates for The Philippines and Its Regions, Provinces, and Highly Urbanized Cities" (PDF). 2010 Census and Housing Population. Philippine Statistics Authority. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 28, 2013. Retrieved August 10, 2013.
- ^ "Poverty incidence (PI):". Philippine Statistics Authority. Retrieved December 28, 2020.
- ^ "Estimation of Local Poverty in the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. November 29, 2005.
- ^ "2009 Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. February 8, 2011.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. August 27, 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. August 27, 2016.
- ^ "Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population, by Region and Province: 1991, 2006, 2009, 2012 and 2015". Philippine Statistics Authority. August 27, 2016.
- ^ "Updated Annual Per Capita Poverty Threshold, Poverty Incidence and Magnitude of Poor Population with Measures of Precision, by Region and Province: 2015 and 2018". Philippine Statistics Authority. June 4, 2020.
- ^ "2021 Full Year Official Poverty Statistics of the Philippines" (PDF). Philippine Statistics Authority. August 15, 2022. Retrieved April 28, 2024.
- ^ "Oktubafest staging part of the 75th Leyte Gulf Landings anniversary". September 24, 2019.
- ^ "Eastern Visayas to stage best coco wine in 'Oktubafest'". Philippine News Agency.
External links
[edit] Media related to Eastern Visayas at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Eastern Visayas at Wikimedia Commons Eastern Visayas travel guide from Wikivoyage
Eastern Visayas travel guide from Wikivoyage Geographic data related to Eastern Visayas at OpenStreetMap
Geographic data related to Eastern Visayas at OpenStreetMap