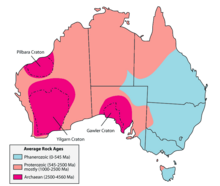
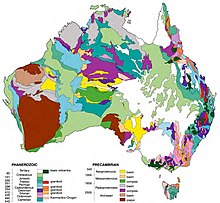
The geology of Queensland can be subdivided into several regions with different histories. Along the east coast is a complex of Palaezoic to Cainozoic rocks while much of the rest of the state is covered by Cretaceous and Cainozoic rocks.[1] A Precambrian basement is found in the north west and Cape York regions. The Thomson Orogen occurs in the central and southern parts of Queensland, but is mostly covered by younger basins.
The North Queensland Orogen is along the coast from Charters Towers to Princess Charlotte Bay. The Bowen Gunndedah Sydney basin can be considered as one system that extends into Queensland. The New England Orogen is on the coastal parts from the border with New South Wales north to Ayr.[2]
Devonian
[edit]The Drummond Basin is a geological basin in central and northern Queensland which consists of Late Devonian to early Carboniferous shallow-marine and continental sediments.[3]
Precambrian
[edit]The Precambrian basement in Queensland is west of the Tasman Line. It includes elements such as the Mount Isa Orogen and the Georgetown Inlier.[4] The Mount Isa Orogen started with sediments, volcanics and intrusive rocks, and was deformed and metamorphosed during the Barramundi Orogeny 1870 Mya. Sedimentary layers formed on top, firstly felsic volcanic rocks from 1870 to 1850 Mya. Shallow water sediments formed from 1790 to 1705 Mya. Fine grained sediments and carbonate rocks formed from 1675 to 1590. Then this was folded in the Isan Orogeny 1620 to 1520 Mya, overlapping with sedimentation. At 1620 Mya the compressive force was north-south, but this changed to east-west at 1520 Mya The Kalkadoon Botholith and Ewn intruded the central Kalkadoon-Ewen Province between 180 and 1850 Mya. The Sybella Batholith intruded the Western Fold Belt around 1670 Mya. Other batholiths are the Wonga, Williams, Naraku ranging from 1750 to 1490 Mya.[5]
The Murphy Province crosses over into the Northern Territory, consisting of the Murphy Metamorphics, the Nicholson Granite and Cliffdale Volcanics. It is from 1820 to 1730 Mya. North of the Murphy Province is the McArthur Basin, also crossing the Northern Territory border. It consists of the Tawallah Group of sediments and volcanics from 1725 Mya and the McArthur Group tuff at 1740 Mya. The South Nicholson Basin is a basin straddling the Queensland-Northern Territory border, south of the above provinces.[5]
The Savannah Province on Cape York initially formed around 1585 to 1550 Mya as sediments, but are now converted to slate, phyllite, schist, gneiss and quartzite. They were intruded bydolerite and amphibolite. The Etheridge Province lies to the east. It started as a rift in the continent, between 1700 and 1650 Mya. This was deformed and intruded with granite and metamorphosed at 1550 Mya. The Croydon Province contains the Croydon Volcanic Group of acid volcanids, the Esmeralda Supersuite granite, and quartz rich sediments of the Inorunie Group.[5]
Cretaceous
[edit]The relatively shallow Eromanga Sea was an inland sea that covered large parts of Queensland and Central Australia at least four times during the early Cretaceous. The Winton Formation represent remnants of the river plains that filled the basin left by the Eromanga Sea. The formation is a major source of dinosaur fossils. The Toolebuc Formation which contains strata dating back to the early Cretaceous and is partly located in Queensland and the Northern Territory.
Bowen-Gunnedah-Sydney Basin System
[edit]Stretching of the continental crust of the New England Orogen in the Permian period formed the Bowen-Gunnedah-Sydney Basin System. This was a foreland basin from Permian into the Triassic. Granites from this time also intruded. From middle to Late Triassic an ocean arc collided. This folded and trusted the surface contents of the basin starting in the east extending to the west.[2]
North Queensland Orogen
[edit]The North Queensland Orogen is also denotated by the North Lachlan Orogen. The northernmost part is called the Hodgekinson Fold Belt.[4]
North Queensland Highlands
[edit]The North Queensland Highlands is a physiographic region in northern Queensland. It includes the Chillagoe Belt, Normanby Platform, Atherton Tableland, Mount Emu Lava Plains and the Cairns Littoral.
Basins
[edit]Bowen
[edit]The Bowen Basin is partly overlaid by the Surat Basin. The basin contains the largest coal reserves in Australia. Open cut and underground coal mines are located in the north of the basin. Ports at Hay Point, Queensland and Gladstone provide access for coal to export markets. In the Denison Trough in the west of the basin contraction has generated a range of geometries.[6]
Clarence-Moreton
[edit]The Jurassic to Cretaceous Clarence Moreton Basin is found in South East Queensland across the border to New South Wales.
Eromanga
[edit]The Eromanga and Surat Basins are superimposed on the older rocks of the Lachlan Orogen. They are components of the Great Artesian Basin. Beneath the Eromanga basin in the mantle below 200 km is a region of fast seismic wave transmission.[4] The Surat Basin is made up of Jurassic through to Cretaceous aged sediments derived from Triassic and Permian arc rocks of the Hunter-Bowen orogeny.
Galilee
[edit]The Galilee Basin is a permian geological basin in the western Queensland region of Australia.
Cooper
[edit]The Cooper Basin is located in South West Queensland and is partly overlain by the Eromanga Basin. It contains some most important on-shore petroleum and natural gas deposits in Australia.
Government
[edit]
The Queensland Government appointed its first geologist Christopher D'Oyly Hale Aplin on 1 April 1868, and the second one Richard Daintree on 12 May 1868 to explore the northern regions. Their job was to look for gold. The jobs only lasted for one to two years as the parliament cut off funding for the Geological Survey. Daintree produced the first geological map of Queensland in 1872.
In 1875 Augustus Charles Gregory was appointed as the geologist for the southern part of Queensland, and Robert Logan Jack started work in 1877 in Townsville. The focus extended beyond gold to coal as well.[7] In 1892 the Geological Survey moved from Townsville to Brisbane, establishing a museum. In 1893 the office was flooded and it moved to the intersection of George and Queen Streets.[8]
Mining
[edit]
Queensland has significant coal, coal seam gas and bauxite deposits and some oil shale and natural gas reserves. Other minerals mined in the state include copper, lead, silver, zinc, gold, phosphate rock, magnesite and silica sand. Gemstones such as sapphire, opal and chrysoprase are also mined in commercial quantities. Opal fields extend from the Koroit opal field in South West Queensland into New South Wales.
Fossils
[edit]Significant fossil finds have been discovered at Riversleigh and Murgon fossil site.
See also
[edit]- Allaru Formation
- Lachlan Fold Belt
- Mining in Australia
- Wallumbilla Formation
- Geological Survey of Queensland
References
[edit]- ^ Macdonald, J. Reid; Mary Lee Macdonald, Patricia Vickers-Rich, Leaellyan S. V. Rich & Thomas H. Rich (1997). Fossil collectors guide. Kangaroo Press. p. 147. ISBN 086417845X.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ a b R A Glen (28 July 2006). "The Tasmanides of eastern Australia: A Collage of Accretionary Orogens Documenting Neoproterozoic to Triassic Interaction with the Proto-Pacific Plate" (PDF). International Geoscience Program ICP-480. Ulaanbaatar, Mongolia. pp. 28–31. Archived from the original (PDF) on 17 December 2008. Retrieved 14 November 2010.
- ^ "Drummond Basin". Geoscience Australia. Archived from the original on 4 April 2011. Retrieved 8 November 2012.
- ^ a b c F. J. Simons; et al. (10 May 1999). "The deep structure of the Australian continent from surface wave tomography" (PDF). Lithos. pp. 17–43. Retrieved 11 September 2013.[permanent dead link]
- ^ a b c Queensland Minerals. "Geological Framework" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2011.
- ^ McClay, Kenneth R. (2004). Thrust Tectonics and Hydrocarbon Systems, Volume 82. AAPG. p. 535. ISBN 0891813632. Retrieved 7 November 2012.
- ^ "History of the Geological Survey of Queensland". 14 February 2009. Archived from the original on 18 February 2011.
- ^ "History of the Geological Survey of Queensland". 30 October 2008. Archived from the original on 13 March 2011.