 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
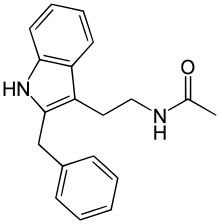
| Formula | C19H20N2O |
| Molar mass | 292.382 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
Luzindole (N-0774; N-acetyl-2-benzyltryptamine), is a drug used in scientific research to study the role of melatonin in the body. Luzindole acts as a selective melatonin receptor antagonist,[1] with approximately 11- to 25-fold greater affinity for the MT2 over the MT1 receptor.[2][3] In animal studies, it has been observed to disrupt the circadian rhythm as well as produce antidepressant effects.[2][4]
Synthesis
[edit]Although the "hydrogen bomb" method was reported as 54% yield by Dubococvich, Boehringer Sohn achieved 96% for this step. The difference is that B.I. conducted their hydrogenation under normal pressure at 50°C for 5 hours, whereas Dubocovich conducted theirs at 100 lbs/in2 hydrogen heated to 35°C. This proves that the hydrogenation step proceeds favorably under milder conditions.

The Pictet–Spengler reaction between tryptamine [61-54-1] (1) and benzaldehyde gives 1-Phenyl-tetrahydrocarboline [3790-45-2] (2). Catalytic hydrogenation leads to 2-Benzyltryptamine [22294-23-1] (3). Acylation with acetic anhydride only gave 21% yield of Luzindole (4).

2-iodoaniline [615-43-0] (1) Propargylbenzene [10147-11-2] (2) 2-(3-phenylprop-1-ynyl)aniline, PC85868179 (3) 2-benzylindole [3377-72-8] (4) 1-Dimethylamino-2-nitroethylene [1190-92-7] (5) (6)
One pot Luzindole synthesis:[9]
References
[edit]- ^ Dubocovich ML (September 1988). "Luzindole (N-0774): a novel melatonin receptor antagonist". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 246 (3): 902–10. PMID 2843633.
- ^ a b Dubocovich ML, Yun K, Al-Ghoul WM, Benloucif S, Masana MI (September 1998). "Selective MT2 melatonin receptor antagonists block melatonin-mediated phase advances of circadian rhythms". The FASEB Journal. 12 (12): 1211–20. doi:10.1096/fasebj.12.12.1211. PMID 9737724. S2CID 566199.
- ^ Browning C, Beresford I, Fraser N, Giles H (March 2000). "Pharmacological characterization of human recombinant melatonin mt(1) and MT(2) receptors". British Journal of Pharmacology. 129 (5): 877–86. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0703130. PMC 1571913. PMID 10696085.
- ^ Dubocovich ML, Mogilnicka E, Areso PM (July 1990). "Antidepressant-like activity of the melatonin receptor antagonist, luzindole (N-0774), in the mouse behavioral despair test". European Journal of Pharmacology. 182 (2): 313–25. doi:10.1016/0014-2999(90)90290-M. PMID 2168835.
- ^ Margarita L. Dubocovich, et al. WO1989001472A1 ().
- ^ Margarita L. Dubocovich, et al., U.S. patent 5,283,343 (1994 to Discovery Therapeutics Inc).
- ^ Schroeder Dr Hans-D, et al. DE1445516 (1968 to CH Boehringer Sohn AG and Co KG).
- ^ Tsotinis, Andrew; Afroudakis, Pandelis (2008). "Melatonin Receptor Antagonist Luzindole: A Facile New Synthesis". Letters in Organic Chemistry. 5 (6): 507–509. doi:10.2174/157017808785740561. ISSN 1570-1786.
- ^ Righi, Marika; Topi, Francesca; Bartolucci, Silvia; Bedini, Annalida; Piersanti, Giovanni; Spadoni, Gilberto (2012). "Synthesis of Tryptamine Derivatives via a Direct, One-Pot Reductive Alkylation of Indoles". The Journal of Organic Chemistry. 77 (14): 6351–6357. doi:10.1021/jo3010028.