
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | UND Adriyatik |
| Owner | U.N Ro-Ro İşletmeleri A.Ş |
| Operator | U.N Ro-Ro İşletmeleri A.Ş |
| Port of registry | Istanbul, |
| Route | Pendik (Istanbul), Turkey - Trieste, Italy. |
| Builder | Flensburger Schiffbau-Gesellschaft |
| Yard number | 714 |
| Laid down | 2 April 2001 |
| Launched | 29 June 2001 |
| In service | 1 September 2001 |
| Homeport | Istanbul, Turkey |
| Identification | IMO number: 9215488 |
| Fate | Caught fire in the Adriatic Sea on 6 February 2008 |
| Notes |
|
| General characteristics | |
| Tonnage | 22.900 |
| Displacement | 9,000 t (8,900 long tons; 9,900 short tons) |
| Length | 193 m (633 ft) |
| Beam | 26.04 m (85.4 ft) |
| Draft | 7.4 m (24 ft) |
| Depth | 26 m (85 ft) |
| Propulsion | 2 × MAK 9M43 |
| Speed | 21.5 kn (24.7 mph; 39.8 km/h) |
| Capacity | 3214 Lane meters |
| Notes | Source:[1] |
The MS UND Adriyatik is a RO-RO freighter owned by the Turkish company U.N Ro-Ro İşletmeleri A.Ş.[2] It went into service on 1 September 2001, after being built in the Flensburger Schiffbau Gesellschaft (FSG) shipyard in Flensburg, Germany. It was used for transporting goods between Pendik (Istanbul), Turkey and Trieste, Italy.[3] UND Adriyatik caught fire on 6 February 2008 off the coast of Istria, Croatia, just outside Croatian territorial waters.[4]
Fire and salvaging operations timeline
[edit]Croatia's sea and transport ministry said the ship caught fire 13 nautical miles (24 km) west of the Adriatic Sea town of Rovinj on the early morning hours of 6 February 2008, just outside the Croatian territorial sea inside of the newly established Croatian Ecological and Fisheries Protection Zone. An SOS was launched at 4:04 local time.[5] It said that the 193-metre (633 ft) long ship was sailing from Istanbul to Trieste and was carrying 200 trucks and nine tons of dangerous material, in addition to between 100 and 200 tons of ship fuel, causing fears of environmental damage. The ship's 22 crew members and nine passengers were rescued by the Greek ship Ikarus Palace that was sailing nearby and were on their way to Venice.[4]
An official said Croatian fire-fighting planes and one tug boat arrived soon at the scene and were trying to extinguish the blaze. The planes were quickly withdrawn as they had no effect. As the fire started inside the ship, there was no way of extinguishing it from the outside. However, tug boats continued to pour water on the ship's hull, in an effort to lower its temperature and prevent its deformation.[4][6]
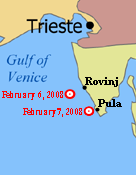
There were fears of an explosion if the fire was to reach the fuel tanks. Also, the water currents were pushing the ship towards the Croatian coast.[5] Floating barrages were placed around the ship, but no oil leaked.[7]
On the morning of 7 February, the ship, still on fire, was standing some 5 miles (8.0 km) south-west of the Brijuni islands, a national park. At that time Croatian officials still hoped that strong east winds would push the ship out of their territorial sea, but instead the ship approached Pula, the largest city on Istra peninsula. According to Croatian sources, the fire was under control and there was no further threat of an ecological disaster. Several maritime fire-fighting specialists from the Netherlands arrived on the scene (after long check-in procedure on a Pula airport, because airport official demanded papers for their special equipment) but were unable to board the ship.[8] Those firefighters worked for Smit International and were hired by the ship's owning company and were known for their role in the salvaging operations of the Russian submarine Kursk.[9] The ship salvage phase was documented on the National Geographic Channel's Salvage Code Red program.
The specialists from the Netherlands were at last able to board the ship on 8 February, when they extinguished the blaze completely and then the ship could be towed to a harbour.[10] Negotiations were underway as to which port to tow the ship.[11] Several sources reported the most probable destination was the Italian port of Trieste though some media reported that the port authorities of Trieste have declined this option.[12]
The ship remained 5 mi off Pula until 17 February, when Italian tugboats began pulling it towards Trieste. Reportedly, the Norwegian classification organisation Det Norske Veritas confirmed all security measures were in place to allow that.[13] On 19 February it arrived in Trieste.[14]
On 2 February 2009 the ship was towed to the "Beşiktaş Gemi Inşa" shipyard in Yalova, Turkey, for future repairs at the shipyard's 235 x 38 meters drydock.[15] On 13 March 2009 it was reported that the length of the ship will be extended, following the one year-long repairs, by an additional 30 meters (to the total of 223 meters).[16]
References
[edit]- ^ "The ferry site". www.ferry-site.dk.
- ^ "Redirect". exchange.dnv.com. Archived from the original on 13 February 2008. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ^ "U.N-RORO - Our Fleet". Archived from the original on 17 July 2007.
- ^ a b c Fable, Silvana (6 February 2008). "Specijalci s Kurska gase požar unutar plamtećeg broda". jutarnji.hr (in Croatian). Archived from the original on 10 February 2008. Retrieved 6 February 2008.
- ^ a b "Stanje na mjestu havarije turskog broda je pod nadzorom, smanjen intenzitet požara" (in Croatian). Archived from the original on 7 February 2008. Retrieved 6 February 2008.
- ^ "Požar na turskom brodu znatno smanjen". www.index.hr.
- ^ "Croatia contains cargo ship fire". BBC News. 7 February 2008. Retrieved 13 May 2010.
- ^ "Počelo tegljenje izgorjelog turskog broda, ali ne zna se kamo". www.index.hr.
- ^ "Hrvatska radiotelevizija/Croatian radiotelevision" (in Croatian). Archived from the original on 10 February 2008. Retrieved 7 February 2008.
- ^ Smit International website on salvaging project of ‘UND Adriyatik', visited 12 February 2012
- ^ "Požar na brodu jenjava, nema opasnosti od onečišćenja" (in Croatian). Archived from the original on 9 February 2008. Retrieved 8 February 2008.
- ^ "Za turski brod najizglednija tršćanska luka?". www.index.hr.
- ^ "barkun.hr". Archived from the original on 19 February 2008.
- ^ "barkun.hr".[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Adriyatik Beşiktaş Tersanesi'ne yanaştı". Deniz Haber (in Turkish). Archived from the original on 20 February 2012. Retrieved 13 January 2018.
- ^ http://www.referansgazetesi.com/haber.aspx?HBR_KOD=118796&KTG_KOD=443[permanent dead link]
External links
[edit]Ship details:
News reports:
- Croatia contains cargo ship fire (BBC)
- CNN Türk report (in Turkish)
Photos and videos:
- Video of the ship in flames (in Croatian)
- Photos of the burning ship (in Croatian)
