| Mammillothalamic tract | |
|---|---|
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | tractus mammillothalamicus |
| TA98 | A14.1.08.671 A14.1.08.954 |
| TA2 | 5757 |
| FMA | 83849 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The mammillothalamic tract (MMT) (also mammillary fasciculus, mammillothalamic fasciculus, thalamomammillary fasciculus, bundle of Vicq d'Azyr) is an efferent pathway of the mammillary bodies which project to the anterior nuclei of the thalamus. The mammillothalamic tract is part of the Papez circuit (involved in spatial memory), starting and finishing in the hippocampus.[1] The fibers of the MMT are heavily myelinated.[2][3][4]
It arises from the medial and lateral nuclei of the mammillary bodies, and from fibers that are directly continued from the fornix of the hippocampus.[3][4] It connects the mammillary bodies to the dorsal tegmental nuclei, the ventral tegmental nuclei, and the anterior thalamic nuclei.[3][4][5]
Structure
[edit]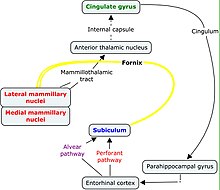
Axons divide within the gray matter; the thicker fibres form the MTT while the finer branches descend as the mammillotegmental fasciculus.[3] The MTT spreads fan-like as it terminates in the medial dorsal nucleus.[3] The axons from these nuclei form part of the thalamocortical radiations.[6]
Function
[edit]The mammillary bodies directly or indirectly connect to the amygdala, hippocampus, and thalami as major structures in the limbic system.[6] The mammillothalamic tract carries signals from the mammillary bodies via the anterior thalamus to support spatial memory.[3][4]
Clinical significance
[edit]Infarction of the region including the mammillothalamic tract has been associated with acute Korsakoff syndrome.[7]
History
[edit]The mammillothalamic tract was first described by the French physician, Félix Vicq d'Azyr, from whom it takes its alternate name (bundle of Vicq d'Azyr).[3]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Shah, A., Jhawar, S. S., & Goel, A. (2012). Analysis of the anatomy of the Papez circuit and adjoining limbic system by fiber dissection techniques. [Article]. Journal of Clinical Neuroscience, 19(2), 289-298. doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2011.04.039.
- ^ Patestas, Maria A.; Gartner, Leslie P. (2016). A Textbook of Neuroanatomy (2nd ed.). Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley-Blackwell. p. 434. ISBN 978-1-118-67746-9.
- ^ a b c d e f g Dillingham, C. M; Frizzati, A; Nelson, A. J; Vann, S. D (2015). "How do mammillary body inputs contribute to anterior thalamic function?". Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 54: 108–119. doi:10.1016/j.neubiorev.2014.07.025. PMC 4462591. PMID 25107491.
- ^ a b c d Aggleton, J. P; O'Mara, S. M; Vann, S. D; Wright, N. F; Tsanov, M; Erichsen, J. T (2010). "Hippocampal–anterior thalamic pathways for memory: Uncovering a network of direct and indirect actions". European Journal of Neuroscience. 31 (12): 2292–2307. doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07251.x. PMC 2936113. PMID 20550571.
- ^ Haines DE (2003). Neuroanatomy: Atlas of Structures, Sections, and Systems, 6th ed (page 148). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. ISBN 978-0781746779.
- ^ a b Kamali, Arash; Zhang, Caroline C.; Riascos, Roy F.; Tandon, Nitin; Bonafante-Mejia, Eliana E.; Patel, Rajan; Lincoln, John A.; Rabiei, Pejman; Ocasio, Laura; Younes, Kyan; Hasan, Khader M. (2018-03-27). "Diffusion tensor tractography of the mammillothalamic tract in the human brain using a high spatial resolution DTI technique". Scientific Reports. 8 (1): 5229. Bibcode:2018NatSR...8.5229K. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-23452-w. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 5869722. PMID 29588461.
- ^ Yoneoka Y, Takeda N, Inoue A, et al. (2004). "Acute Korsakoff syndrome following mammillothalamic tract infarction". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 25 (6): 964–8. PMID 15205131.
External links
[edit]- ancil-115 at NeuroNames - "mammillothalamic tract"
- hier-407 at NeuroNames - "mammillothalamic tract of hypothalamus"
- hier-356 at NeuroNames - "mammillothalamic tract of thalamus"
- https://web.archive.org/web/20080505050804/http://isc.temple.edu/neuroanatomy/lab/atlas/dan2/