 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
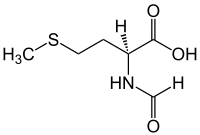
| IUPAC name
N-Formylmethionine
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
(S)-2-Formylamino-4-methylsulfanylbutanoic acid | |
| Other names
2-Formylamino-4-methylsulfanyl-butyric acid; Formylmethionine; N-Formyl(methyl)homocysteine
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| Abbreviations | fMet |
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H11NO3S | |
| Molar mass | 177.22 g/mol |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling:[1] | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H319 | |
| P264+P265, P280, P305+P351+P338, P337+P317 | |
| Supplementary data page | |
| N-Formylmethionine (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
N-Formylmethionine (fMet,[2] HCO-Met,[3] For-Met[3]) is a derivative of the amino acid methionine in which a formyl group has been added to the amino group. It is specifically used for initiation of protein synthesis from bacterial and organellar genes, and may be removed post-translationally.
fMet plays a crucial part in the protein synthesis of bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts. It is not used in cytosolic protein synthesis of eukaryotes, where eukaryotic nuclear genes are translated. It is also not used by Archaea. In the human body, fMet is recognized by the immune system as foreign material, or as an alarm signal released by damaged cells, and stimulates the body to fight against potential infection.
Function in protein synthesis
[edit]Translation
[edit]fMet is required for efficient initiation of protein synthesis in most groups of bacteria. The 30S ribosome–mRNA complex specifically recruits tRNAs with a formylated amino acid – tRNAfMet attached to fMet in the natural case.[4]
Because the fMet directs initiation, proteins in bacteria start (N-terminus) with a fMet residue instead of a methionine. Further occurrences of the "AUG" codon will result in a normal methionine, because a normal "elongating" tRNAMet is used.[4]
The addition of the formyl group to methionine is catalyzed by the enzyme methionyl-tRNA formyltransferase. This modification is done after methionine has been loaded onto tRNAfMet by aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase. Methionine itself can be loaded either onto tRNAfMet or tRNAMet. However, formyltransferase will catalyze the addition of the formyl group to methionine only if methionine has been loaded onto tRNAfMet, not onto tRNAMet. This is because the formyltransferase recognizes specific features of tRNAfMet.[4]
The mitochondria of eukaryotic cells, including those of humans, and the chloroplasts of plant cells also initiate protein synthesis with fMet. Given that mitochondria and chloroplasts have this initial protein synthesis with fMet in common with bacteria, this has been cited as evidence for the endosymbiotic theory.[5]
Unexpectedly, formyltransferase can also act upon eukaryotic initiator tRNA in living yeast cells. Even under normal conditions, the nuclear-encoded formyltransferase is not completely imported into mitochondria; even more is left in the cytosol under stress. These cytosolic formyltransferase produce fMet-tRNAi, which can be used by cytosolic ribosomes to produce proteins with a N-terminal fMet. These proteins are targeted for degradation by specific processes in the cell.[6]
Further processing
[edit]The N-terminal fMet is removed from majority of proteins, both host and recombinant, by a sequence of two enzymatic reactions. First, peptide deformylase (PDF) deformylates it, converting the residue back to a normal methionine. Then methionine aminopeptidase (MetAP) removes the residue from the chain.[7] MetAP only acts on proteins with second-position residues that are less bulky than valine.[8]
The N-terminal fMet, if not removed by PDF, seems to act as a degron, a signal for protein degradation.[8]
Variation
[edit]The formyl group is not strictly required for initiation. Bacteria with their formyltransferase knocked out, which prevents Met-tRNAfMet (i.e. methionine loaded onto tRNAfMet) from turning into fMet-tRNAfMet, can have varying degrees of residual ability to start protein synthesis. E. coli, S. pneumoniae and B. subtilis show almost no remaining translation ability, while P. aeruginosa, S. aureus, H. influenzae, and possibly S. faecalis still churn out plenty of protein. In P. aeruginosa, this ability is facilitated by bacterial initiation factor 2, which can carry both Met-tRNAfMet and fMet-tRNAfMet to the ribosome.[9]
Relevance to immunology
[edit]Because fMet is present in proteins made by bacteria but not in those made by eukaryotes (other than in bacterially derived organelles), the immune system might use it to help distinguish self from non-self. Polymorphonuclear cells can bind proteins starting with fMet, and use them to initiate the attraction of circulating blood leukocytes and then stimulate microbicidal activities such as phagocytosis.[10][11][12]
Since fMet is present in proteins made by mitochondria and chloroplasts, more recent theories do not see it as a molecule that the immune system can use to distinguish self from non-self.[13] Instead, fMet-containing oligopeptides and proteins appear to be released by the mitochondria of damaged tissues as well as by damaged bacteria, and can thus qualify as an "alarm" signal, as discussed in the Danger model of immunity. The prototypical fMet-containing oligopeptide is N-formylmethionine-leucyl-phenylalanine (FMLP) which activates leukocytes and other cell types by binding with these cells' formyl peptide receptor 1 (FPR1) and formyl peptide receptor 2 (FPR2) G protein coupled receptors (see also formyl peptide receptor 3). Acting through these receptors, the fMet-containing oligopeptides and proteins are part of the innate immune system; they function to initiate acute inflammation responses but under other conditions function to inhibit and resolve these responses. fMet-containing oligopeptides and proteins also function in other physiological and pathological responses.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "N-Formyl-DL-methionine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov.
- ^ PubChem. "N-Formyl-DL-methionine". pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov. Retrieved 2020-10-24.
- ^ a b Nomenclature and Symbolism for Amino Acids and Peptides, 3AA-18 and 3AA-19
- ^ a b c Shetty, S; Shah, RA; Chembazhi, UV; Sah, S; Varshney, U (28 February 2017). "Two highly conserved features of bacterial initiator tRNAs license them to pass through distinct checkpoints in translation initiation". Nucleic Acids Research. 45 (4): 2040–2050. doi:10.1093/nar/gkw854. PMC 5389676. PMID 28204695.
- ^ Alberts, Bruce (18 November 2014). Molecular biology of the cell (Sixth ed.). New York, NY. p. 800. ISBN 978-0-8153-4432-2. OCLC 887605755.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Varshavsky, Alexander (8 January 2019). "N-degron and C-degron pathways of protein degradation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 116 (2): 358–366. Bibcode:2019PNAS..116..358V. doi:10.1073/pnas.1816596116. PMC 6329975. PMID 30622213.
- ^ Sherman F, Stewart JW, Tsunasawa S (July 1985). "Methionine or not methionine at the beginning of a protein". BioEssays. 3 (1): 27–31. doi:10.1002/bies.950030108. PMID 3024631. S2CID 33735710.
- ^ a b Piatkov, KI; Vu, TT; Hwang, CS; Varshavsky, A (2015). "Formyl-methionine as a degradation signal at the N-termini of bacterial proteins". Microbial Cell (Graz, Austria). 2 (10): 376–393. doi:10.15698/mic2015.10.231. PMC 4745127. PMID 26866044.
- ^ Piatkov, KI; Vu, TT; Hwang, CS; Varshavsky, A (2015). "Formyl-methionine as a degradation signal at the N-termini of bacterial proteins". Microbial Cell (Graz, Austria). 2 (10): 376–393. doi:10.15698/mic2015.10.231. PMC 4745127. PMID 26866044.
- ^ Immunology at MCG 1/phagstep
- ^ "The Innate Immune System: Pattern-Recognition Receptors, Antigen-Nonspecific Antimicrobial Body Molecules, and Cytokines". Archived from the original on 2010-07-27.
- ^ Detmers PA, Wright SD, Olsen E, Kimball B, Cohn ZA (September 1987). "Aggregation of complement receptors on human neutrophils in the absence of ligand". The Journal of Cell Biology. 105 (3): 1137–45. doi:10.1083/jcb.105.3.1137. PMC 2114803. PMID 2958480.
- ^ Zhang Q, Raoof M, Chen Y, Sumi Y, Sursal T, Junger W, Brohi K, Itagaki K, Hauser CJ (Mar 4, 2010). "Circulating mitochondrial DAMPs cause inflammatory responses to injury". Nature. 464 (7285): 104–107. Bibcode:2010Natur.464..104Z. doi:10.1038/nature08780. PMC 2843437. PMID 20203610.
External links
[edit]- N-Formylmethionine at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)