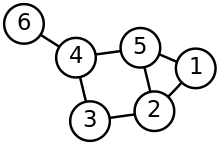
In graph theory, an adjacent vertex of a vertex v in a graph is a vertex that is connected to v by an edge. The neighbourhood of a vertex v in a graph G is the subgraph of G induced by all vertices adjacent to v, i.e., the graph composed of the vertices adjacent to v and all edges connecting vertices adjacent to v.
The neighbourhood is often denoted or (when the graph is unambiguous) . The same neighbourhood notation may also be used to refer to sets of adjacent vertices rather than the corresponding induced subgraphs. The neighbourhood described above does not include v itself, and is more specifically the open neighbourhood of v; it is also possible to define a neighbourhood in which v itself is included, called the closed neighbourhood and denoted by . When stated without any qualification, a neighbourhood is assumed to be open.
Neighbourhoods may be used to represent graphs in computer algorithms, via the adjacency list and adjacency matrix representations. Neighbourhoods are also used in the clustering coefficient of a graph, which is a measure of the average density of its neighbourhoods. In addition, many important classes of graphs may be defined by properties of their neighbourhoods, or by symmetries that relate neighbourhoods to each other.
An isolated vertex has no adjacent vertices. The degree of a vertex is equal to the number of adjacent vertices. A special case is a loop that connects a vertex to itself; if such an edge exists, the vertex belongs to its own neighbourhood.
Local properties in graphs
[edit]
If all vertices in G have neighbourhoods that are isomorphic to the same graph H, G is said to be locally H, and if all vertices in G have neighbourhoods that belong to some graph family F, G is said to be locally F.[1] For instance, in the octahedron graph, shown in the figure, each vertex has a neighbourhood isomorphic to a cycle of four vertices, so the octahedron is locally C4.
For example:
- Any complete graph Kn is locally Kn-1. The only graphs that are locally complete are disjoint unions of complete graphs.
- A Turán graph T(rs,r) is locally T((r-1)s,r-1). More generally any Turán graph is locally Turán.
- Every planar graph is locally outerplanar. However, not every locally outerplanar graph is planar.
- A graph is triangle-free if and only if it is locally independent.
- Every k-chromatic graph is locally (k-1)-chromatic. Every locally k-chromatic graph has chromatic number .[2]
- If a graph family F is closed under the operation of taking induced subgraphs, then every graph in F is also locally F. For instance, every chordal graph is locally chordal; every perfect graph is locally perfect; every comparability graph is locally comparable; every (k)-(ultra)-homogeneous graph is locally (k)-(ultra)-homogeneous.
- A graph is locally cyclic if every neighbourhood is a cycle. For instance, the octahedron is the unique connected locally C4 graph, the icosahedron is the unique connected locally C5 graph, and the Paley graph of order 13 is locally C6. Locally cyclic graphs other than K4 are exactly the underlying graphs of Whitney triangulations, embeddings of graphs on surfaces in such a way that the faces of the embedding are the cliques of the graph.[3] Locally cyclic graphs can have as many as edges.[4]
- Claw-free graphs are the graphs that are locally co-triangle-free; that is, for all vertices, the complement graph of the neighbourhood of the vertex does not contain a triangle. A graph that is locally H is claw-free if and only if the independence number of H is at most two; for instance, the graph of the regular icosahedron is claw-free because it is locally C5 and C5 has independence number two.
- The locally linear graphs are the graphs in which every neighbourhood is an induced matching.[5]
- The Johnson graphs are locally grid, meaning that each neighborhood is a rook's graph.[6]
Neighbourhood of a set
[edit]For a set A of vertices, the neighbourhood of A is the union of the neighbourhoods of the vertices, and so it is the set of all vertices adjacent to at least one member of A.
A set A of vertices in a graph is said to be a module if every vertex in A has the same set of neighbours outside of A. Any graph has a uniquely recursive decomposition into modules, its modular decomposition, which can be constructed from the graph in linear time; modular decomposition algorithms have applications in other graph algorithms including the recognition of comparability graphs.
See also
[edit]- Markov blanket
- Moore neighbourhood
- Von Neumann neighbourhood
- Second neighborhood problem
- Vertex figure, a related concept in polyhedra
- Link (simplicial complex), a generalization of the neighborhood to simplicial complexes
Notes
[edit]References
[edit]- Cohen, Arjeh M. (1990), "Local recognition of graphs, buildings, and related geometries" (PDF), in Kantor, William M.; Liebler, Robert A.; Payne, Stanley E.; Shult, Ernest E. (eds.), Finite Geometries, Buildings, and Related Topics: Papers from the Conference on Buildings and Related Geometries held in Pingree Park, Colorado, July 17–23, 1988, Oxford Science Publications, Oxford University Press, pp. 85–94, MR 1072157; see in particular pp. 89–90
- Fronček, Dalibor (1989), "Locally linear graphs", Mathematica Slovaca, 39 (1): 3–6, hdl:10338.dmlcz/136481, MR 1016323
- Hartsfeld, Nora; Ringel, Gerhard (1991), "Clean triangulations", Combinatorica, 11 (2): 145–155, doi:10.1007/BF01206358, S2CID 28144260.
- Hell, Pavol (1978), "Graphs with given neighborhoods I", Problèmes combinatoires et théorie des graphes, Colloques internationaux C.N.R.S., vol. 260, pp. 219–223.
- Larrión, F.; Neumann-Lara, V.; Pizaña, M. A. (2002), "Whitney triangulations, local girth and iterated clique graphs", Discrete Mathematics, 258 (1–3): 123–135, doi:10.1016/S0012-365X(02)00266-2.
- Malnič, Aleksander; Mohar, Bojan (1992), "Generating locally cyclic triangulations of surfaces", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 56 (2): 147–164, doi:10.1016/0095-8956(92)90015-P.
- Sedláček, J. (1983), "On local properties of finite graphs", Graph Theory, Lagów, Lecture Notes in Mathematics, vol. 1018, Springer-Verlag, pp. 242–247, doi:10.1007/BFb0071634, ISBN 978-3-540-12687-4.
- Seress, Ákos; Szabó, Tibor (1995), "Dense graphs with cycle neighborhoods", Journal of Combinatorial Theory, Series B, 63 (2): 281–293, doi:10.1006/jctb.1995.1020.
- Wigderson, Avi (1983), "Improving the performance guarantee for approximate graph coloring", Journal of the ACM, 30 (4): 729–735, doi:10.1145/2157.2158, S2CID 32214512.


![{\displaystyle N_{G}[v]}](https://wikimedia.org/api/rest_v1/media/math/render/svg/70d0730ce5bb03368f6dda06206b1e59278c8bf4)

