| Río Conchos | |
|---|---|
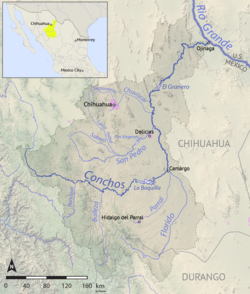 Map of the Conchos | |
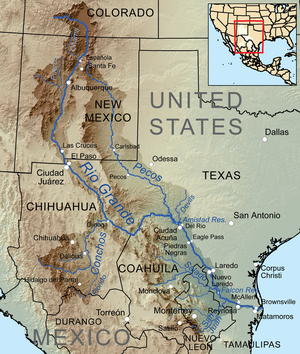 Map of the Rio Grande watershed, showing the Rio Conchos joining the Rio Grande near Ojinaga. | |
| Location | |
| Country | Mexico |
| State | Chihuahua (state) |
| Physical characteristics | |
| Source | Sierra Madre Occidental |
| • location | Guadalupe, Chihuahua |
| Mouth | Rio Grande |
• location | Ojinaga, Chihuahua |
• coordinates | 29°35′N 104°25′W / 29.583°N 104.417°W[1] |
| Length | 560 km (350 mi) |
| Basin size | 68,400 km2 (26,400 sq mi) |
| Discharge | |
| • location | IBWC station 08-3730.00, near Ojinaga[2] |
| • average | 24 m3/s (850 cu ft/s)[2] |
| • minimum | 0.09 m3/s (3.2 cu ft/s) |
| • maximum | 1,490 m3/s (53,000 cu ft/s) |
The Río Conchos (Conchos River) is a large river in the Mexican state of Chihuahua. It joins the Río Bravo del Norte (known in the United States as the Rio Grande) at the town of Ojinaga, Chihuahua.
Description
[edit]The Rio Conchos is the main river in the state of Chihuahua and the Rio Grande's largest tributary.[3] The Conchos has several reservoirs that make use of its water for agricultural and hydropower uses.
Course
[edit]The Conchos rises in the Sierra Madre Occidental in the municipality of Bocoyna, Chihuahua, where it heads east and receives several tributaries along the way. At Valle de Zaragoza municipality, Chihuahua, it is stopped at the La Boquilla Dam, the largest in Chihuahua forming Toronto Lake. It then heads east again, forming Colina Lake and then passes through Camargo, Chihuahua, the main agricultural center in the region, where it receives the Florido as a tributary.
From there, the Conchos heads north, receiving the San Pedro near Delicias, Chihuahua, entering the Chihuahua Desert and cutting a path through it, before turning to the northeast. At Aldama, Chihuahua, it is dammed by the Presa El Granero, then cuts through the Peguis Canyon, before forming a last dam (Toribio Ortega) near Ojinaga. At Ojinaga, it joins the Rio Bravo (Rio Grande in the U.S.).
Ecology
[edit]The World Wide Fund for Nature (WWF) has included the Rio Conchos in its Global 200 Freshwater Ecoregions assessment. The Global 200 is a list of freshwater ecoregions (rivers systems and lakes, for example) that the WWF considers of global importance for biodiversity conservation. The WWF's assessment of the Rio Conchos rates its biological distinctiveness as "globally outstanding" and its conservation status as critically endangered, putting it in the "priority I" category of needing conservation attention.[4]
The Rio Conchos contains the only free-flowing large river environment left in the Rio Grande drainage basin. Its river and spring habitat ecosystems are relatively intact and support a highly endemic fish fauna.[5] Twelve of its forty-seven native fish are endemic, as are twelve of its 46 native reptile and amphibian species. The strong biodiversity has survived in part because the river's ecology has not been affected by channel modifications. The Rio Conchos region is significant not only for its surface water biota, but also its specialized spring and cave habitats, which contribute to the region's high endemism. However, conditions are being damaged by industrial pollution, sewage, agricultural wastes, flow regulation, exotic species, and overgrazing. Other threats include poor land and water management practices, such as clear-cutting along the upper Rio Conchos.[4]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Rio Conchos at GEOnet Names Server
- ^ a b "Water Bulletin Number 75: Flow of the Rio Grande and Related Data; From Elephant Butte Dam, New Mexico to the Gulf of Mexico". International Boundary and Water Commission. 2005. Retrieved 17 July 2010.
- ^ Benke, Arthur C.; Colbert E. Cushing (2005). Rivers of North America. Academic Press. pp. 186–192. ISBN 978-0-12-088253-3.
- ^ a b Abell, Robin A.; David M. Olsen; Eric Dinerstein; Patrick T. Hurley; et al. (2000). Freshwater Ecoregions of North America: A Conservation Assessment. Island Press. pp. 93, 103, 188–189. ISBN 978-1-55963-734-3.
- ^ De la Maza-Benignos, M. (ed). 2009. Los Peces del Río Conchos. Alianza World Wildlife Fund-Fundación Gonzalo Río Arronte http://awsassets.panda.org/downloads/peces2010_web.pdf