 | |
| Monoclonal antibody | |
|---|---|
| Type | Whole antibody |
| Source | Chimeric (mouse/human) |
| Target | CD20 |
| Clinical data | |
| Trade names | Rituxan, Mabthera, others |
| Biosimilars | rituximab-abbs,[1] rituximab-pvvr,[2] rituximab-arrx,[3] Blitzima[4] Ituxredi,[5][6] Riabni,[3] Rixathon,[7] Riximyo,[8] Ruxience,[2] Truxima[1] |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a607038 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| Drug class | Monoclonal antibody |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 100% (IV) |
| Elimination half-life | 30 to 400 hours (varies by dose and length of treatment) |
| Excretion | Uncertain: may undergo phagocytosis and catabolism in RES |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.224.382 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C6416H9874N1688O1987S44 |
| Molar mass | 143860.04 g·mol−1 |
| | |
Rituximab, sold under the brand name Rituxan among others, is a monoclonal antibody medication used to treat certain autoimmune diseases and types of cancer.[18] It is used for non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (in children and adults, but not recommended in elderly patients), rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, pemphigus vulgaris, myasthenia gravis and Epstein–Barr virus-positive mucocutaneous ulcers.[18][19][20][21] It is given by slow intravenous infusion (injected slowly through an IV line).[18]
The most common side effects with intravenous infusions are reactions related to the infusion (such as fever, chills and shivering) while most common serious side effects are infusion reactions, infections and heart-related problems.[16] Similar side effects are seen when it is injected under the skin, with the exception of reactions around the injections site (pain, swelling and rash), which occur more frequently with the skin injections.[16]
Severe side effects include reactivation of hepatitis B in those previously infected, progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy, toxic epidermal necrolysis, and death.[18][22] It is unclear if use during pregnancy is safe for the developing fetus or newborn baby.[9][18]
Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody against the protein CD20, which is primarily found on the surface of immune system B cells.[23] When it binds to this protein it triggers cell death.[18]
Rituximab was approved for medical use in 1997.[23] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[24] Rituxan is co-marketed by Biogen and Genentech in the US, by Roche elsewhere except Japan, and co-marketed by Chugai Pharmaceuticals and Zenyaku Kogyo in Japan.[25][26]
Medical uses
[edit]Rituximab is a chimeric monoclonal antibody targeted against CD20, a surface antigen present on B cells. It acts by depleting normal as well as pathogenic B cells while sparing plasma cells and hematopoietic stem cells, which do not express the CD20 surface antigen.[27]
In the United States, rituximab is indicated to treat:
- non-Hodgkin lymphoma[15]
- chronic lymphocytic leukemia[15]
- rheumatoid arthritis having inadequate response to one or more TNF inhibitors[15]
- vasculitides such as granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis[15]
- moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris[15]
- in combination with chemotherapy for children (≥ 6 months to < 18 years) with previously untreated, advanced stage, CD20-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), Burkitt lymphoma (BL), Burkitt-like lymphoma (BLL), or mature acute B-cell leukemia (B-AL).[15][28]
In the European Union, rituximab is indicated for the treatment of follicular lymphoma and diffuse large B cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma (two types of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, a blood cancer);[16] chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL, another blood cancer affecting white blood cells);[16] severe rheumatoid arthritis (an inflammatory condition of the joints);[16] two inflammatory conditions of blood vessels known as granulomatosis with polyangiitis (GPA) and microscopic polyangiitis (MPA);[16] moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris, an autoimmune disease characterised by widespread blistering and erosion of the skin and mucous membranes (the linings of internal organs). 'Autoimmune' means that the disease is caused by the immune system (the body's natural defences) attacking the body's own cells.[16]
Blood cancers
[edit]Rituximab is used to treat cancers of the white blood system such as leukemias and lymphomas, including non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and nodular lymphocyte predominant Hodgkin's lymphoma.[29][30] This also includes Waldenström's macroglobulinemia, a type of non-Hodgkin lymphoma.[18] Rituximab in combination with hyaluronidase human, sold under the brand names Mabthera SC[14] and Rituxan Hycela,[31] is used to treat follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.[31] It is used in combination with fludarabine and cyclophosphamide to treat previously untreated and previously treated CD20-positive chronic lymphocytic leukemia.[15]
Autoimmune diseases
[edit]Rituximab has been shown to be an effective rheumatoid arthritis treatment in three randomised controlled trials and is now licensed for use in refractory rheumatoid disease.[32] In the United States, it has been FDA approved for use in combination with methotrexate for reducing signs and symptoms in adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis (RA) who have had an inadequate response to one or more anti-TNF-alpha therapy. In the European Union, the license is slightly more restrictive: it is licensed for use in combination with methotrexate in patients with severe active RA who have had an inadequate response to one or more anti-TNF therapy.[33]
There is some evidence for efficacy, but not necessarily safety, in a range of other autoimmune diseases, and rituximab is widely used off-label to treat difficult cases of multiple sclerosis,[34][35] systemic lupus erythematosus, chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy and autoimmune anemias.[36][37] The most dangerous, although among the most rare, side effect is progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy infection, which is usually fatal; however, only a very small number of cases have been recorded occurring in autoimmune diseases.[36][38]
Other autoimmune diseases that have been treated with rituximab include autoimmune hemolytic anemia, pure red cell aplasia, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP),[39] idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP),[40][41] Evans syndrome,[42] vasculitis (e.g., granulomatosis with polyangiitis), bullous skin disorders (for example, pemphigus, pemphigoid—with very encouraging results of approximately 85% rapid recovery in pemphigus, according to a 2006 study),[43] type 1 diabetes mellitus, Sjögren syndrome, anti-NMDA receptor encephalitis and Devic's disease(Anti-AQP4 disease, MOG antibody disease),[44] Graves' ophthalmopathy,[45] autoimmune pancreatitis,[46] Opsoclonus myoclonus syndrome (OMS),[47] and IgG4-related disease.[48] There is some evidence that it is ineffective in treating IgA-mediated autoimmune diseases.[49]
Adverse events
[edit]Serious adverse events, which can cause death and disability, include:[15][18]
- Severe infusion reaction
- Cardiac arrest
- Cytokine release syndrome
- Tumor lysis syndrome, causing acute kidney injury
- Infections[50]
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy caused by JC virus reactivation[51]
- Hepatitis B reactivation
- Other viral infections[52]
- Immune toxicity, with depletion of B cells in 70% to 80% of lymphoma patients
- Pulmonary toxicity[53]
- Bowel obstruction and perforation[54]
A concern with continuous rituximab treatment is the difficulty to induce a proper vaccine response.[55][unreliable medical source?] This was brought into focus during the COVID-19 pandemic, where persons with multiple sclerosis and rituximab treatment had higher risk of severe COVID-19.[56][unreliable medical source?][57] In persons previously treated with rituximab for multiple sclerosis, nine of ten patients who delayed re-dosing until B cell counts passed 40/μL developed protective levels of antibodies after vaccination with the Pfizer–BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine.[58][unreliable medical source?]
Mechanisms of action
[edit]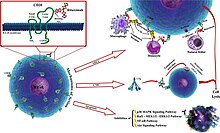

The antibody binds to the cell surface protein CD20. CD20 is widely expressed on B cells, from early pre-B cells to later in differentiation, but it is absent on terminally differentiated plasma cells. Although the function of CD20 is unknown, it may play a role in Ca2+ influx across plasma membranes, maintaining intracellular Ca2+ concentration and allowing activation of B cells.
Rituximab is relatively ineffective in elimination of cells with low CD20 cell-surface levels.[60] It tends to stick to one side of B cells, where CD20 is, forming a cap and drawing proteins over to that side. The presence of the cap changes the effectiveness of natural killer (NK) cells in destroying these B cells. When an NK cell latched onto the cap, it had an 80% success rate at killing the cell. In contrast, when the B cell lacked this asymmetric protein cluster, it was killed only 40% of the time.[61]
The following effects have been found:[62]
- The Fc portion of rituximab mediates antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC).[63]
- Rituximab has a general regulatory effect on the cell cycle.
- Preferential elimination of malignant B cells with high CD20 levels and high BCR signaling propensity, especially in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL).[60]
- It increases MHC II and adhesion molecules LFA-1 and LFA-3 (lymphocyte function-associated antigen).
- It elicits shedding of CD23.
- It downregulates the B cell receptor.
- It induces apoptosis of CD20+ cells.
- Rituximab also induces a release of some chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells from immune niches, which might make them more sensitive to chemotherapy used in combination with an anti-CD20 antibody.[63]
The combined effect results in the elimination of B cells (including the cancerous ones) from the body, allowing a new population of healthy B cells to develop from lymphoid stem cells.
Rituximab binds to amino acids 170–173 and 182–185 on CD20, which are physically close to each other as a result of a disulfide bond between amino acids 167 and 183.[64]
History
[edit]Rituximab was developed by IDEC Pharmaceuticals under the name IDEC-C2B8. The US patent for the drug was issued in 1998 and expired in 2015.[65]
Based on its safety and effectiveness in clinical trials,[66] rituximab was approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in 1997 to treat B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphomas resistant to other chemotherapy regimens.[67][68] Rituximab, in combination with CHOP chemotherapy, is superior to CHOP alone in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and many other B-cell lymphomas.[69] In 2010, it was authorized by the European Commission for maintenance treatment after initial treatment of follicular lymphoma.[70]
It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[24]
Originally available for intravenous injection (e.g. over 2.5 hrs), in 2016, it gained EU approval in a formulation for subcutaneous injection for B-cell CLL/lymphoma (CLL).[71]
In June 2017, the US FDA granted regular approval to the combination of rituximab and hyaluronidase human (brand name Rituxan Hycela) for adults with follicular lymphoma, diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.[72] The combination is not indicated for the treatment of non-malignant conditions.[31][72] The combination was approved based on clinical studies SABRINA/NCT01200758 and MabEase/NCT01649856.[31]
In September 2019, the US FDA approved rituximab injection to treat granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis in children two years of age and older in combination with glucocorticoids (steroid hormones).[73] It is the first approved treatment for children with these rare vasculitis diseases, in which a person's small blood vessels become inflamed, reducing the amount of blood that can flow through them.[73] This can cause serious problems and damage to organs, most notably the lungs and the kidneys.[73] It also can impact the sinuses and skin.[73] Rituximab was approved by the FDA to treat adults with granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis in 2011.[73]
In December 2021, the US FDA approved rituximab in combination with chemotherapy for children aged 6 months to 18 years with previously untreated, advanced stage, CD20-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, Burkitt-like lymphoma, or mature B-cell acute leukemia.[28][74] Efficacy was evaluated in Inter-B-NHL Ritux 2010, a global multicenter, open-label, randomized 1:1 trial of participants six months in age or older with previously untreated, advanced stage, CD20-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, Burkitt-like lymphoma, or B-cell acute leukemia.[74] Advanced stage was defined as stage III with elevated lactose dehydrogenase level (lactose dehydrogenase greater than twice the institutional upper limit of normal values) or stage IV B-cell non-Hodgkin's lymphoma or B-cell acute leukemia.[74] Participants were randomized to Lymphome Malin B chemotherapy that consisted of corticosteroids, vincristine, cyclophosphamide, high-dose methotrexate, cytarabine, doxorubicin, etoposide, and triple drug (methotrexate/cytarabine/corticosteroid) intrathecal therapy alone or in combination with rituximab or non-US licensed rituximab, administered as six infusions of rituximab IV at a dose of 375 mg/m2 as per the Lymphome Malin B scheme.[74]
Society and culture
[edit]Legal status
[edit]Rituximab was approved for medical use in the United States in November 1997.[15][67]
Biosimilars
[edit]Biosimilars are approved in the United States, India, the European Union, Switzerland, Japan, and Australia.[citation needed] The US FDA approved rituximab-abbs (Truxima) in 2018,[1][75][76] rituximab-pvvr (Ruxience) in 2019,[2] and rituximab-arrx (Riabni) in 2020.[3]
In July 2024, the Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use of the European Medicines Agency adopted a positive opinion, recommending the granting of marketing authorization to Dr. Reddy's Laboratories / Holding GmbH for their rituximab biosimilar Ituxredi, intended for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, rheumatoid arthritis, granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis and pemphigus vulgaris.[5] Ituxredi was authorized for medical use in the European Union in September 2024.[5][6] Dr Reddy's Rituximab biosimilar Reditux was approved in India in 2007.[77]
Economics
[edit]In 2014, Genentech reclassified Rituxan as a specialty drug, a class of drugs that are only available through specialty distributors in the US.[78] Because wholesalers discounts and rebates no longer apply, hospitals would pay more.[78]
Patents on rituximab have expired in the European Union[79][80][81] and in the United States.[82][83][84] Biosimilars were approved in the United States, India, the European Union, Switzerland, Japan, and Australia. The US FDA approved rituximab-abbs (Truxima) in 2018,[1][75][76] rituximab-pvvr (Ruxience) in 2019,[2] and rituximab-arrx (Riabni) in 2020.[3][85][86] Truxima and Riabni are approximately $3600 per 500 mg, wholesale - 10% less than Rituxan, while Ruxience is 24% less than Rituxan.[87][88] Dr Reddy's rituximab ituxredi retails for under 10,000 rupees ($118) per 100 mg in India.[89]
Tailored-dosing
[edit]Tailored-dose rituximab is more cost-effective than fixed-dose. It is both more effective and less expensive.[90][91]
Research
[edit]Rituximab has been reported as a possible cofactor in a chronic hepatitis E infection in a person with lymphoma. Hepatitis E infection is normally an acute infection, suggesting the drug in combination with lymphoma may have weakened the body's immune response to the virus.[92]
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome
[edit]In 2009, a patient receiving methotrexate-induced B-cell depletion for cancer treatment, experienced a transient remittal of their myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) symptoms. While initial trials using Rituximab were promising, a phase 3 trial published in 2019 did not find an association between Rituximab treatment and improvements in ME/CFS.[93][94]
Intrathecal
[edit]For CNS diseases, rituximab could be administered intrathecally and this possibility is under study.[95]
Other anti-CD20 monoclonals
[edit]The efficacy and success of rituximab has led to some other anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies being developed:
- ocrelizumab, humanized (90%-95% human) B cell-depleting agent.
- ofatumumab (HuMax-CD20) a fully human B cell-depleting agent.[96]
- Third-generation anti-CD20s such as obinutuzumab have a glycoengineered Fc fragment (Fc)[97] with enhanced binding to Fc gamma receptors, which increase ADCC (antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity).[98] This strategy for enhancing a monoclonal antibody's ability to induce ADCC takes advantage of the fact that the displayed Fc glycan controls the antibody's affinity for Fc receptors.[99]
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d e "Truxima- rituximab-abbs injection solution". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 25 March 2021. Retrieved 26 March 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "Ruxience- rituximab-pvvr injection solution". DailyMed. Retrieved 26 March 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "Riabni- rituximab-arrx injection solution". DailyMed. Archived from the original on 25 March 2021. Retrieved 26 March 2021.
- ^ "Blitzima EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 13 July 2017. Archived from the original on 9 September 2021. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ a b c "Ituxredi EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 25 July 2024. Retrieved 27 July 2024. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ a b "Ituxredi Product information". Union Register of medicinal products. 23 September 2024. Retrieved 24 September 2024.
- ^ "Rixathon EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 15 June 2017. Archived from the original on 9 September 2021. Retrieved 7 January 2024.
- ^ "Summary Basis of Decision (SBD) for Riximyo". Health Canada. 23 October 2014. Archived from the original on 30 May 2022. Retrieved 29 May 2022.
- ^ a b "Rituximab Use During Pregnancy". Drugs.com. 16 December 2019. Archived from the original on 30 August 2019. Retrieved 2 February 2020.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 October 2023.
- ^ Rituximab (rch) (CAS registry number: 174722-31-7) Archived 30 November 2015 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Health product highlights 2021: Annexes of products approved in 2021". Health Canada. 3 August 2022. Archived from the original on 25 March 2024. Retrieved 25 March 2024.
- ^ "Mabthera 100 mg Concentrate for Solution for Infusion - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 13 March 2021. Archived from the original on 21 January 2022. Retrieved 26 March 2021.
- ^ a b "Mabthera 1400 mg Solution for Subcutaneous Injection - Summary of Product Characteristics (SmPC)". (emc). 13 March 2021. Retrieved 26 March 2021.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Rituxan- rituximab injection, solution". DailyMed. 6 November 2019. Archived from the original on 4 August 2020. Retrieved 2 February 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Mabthera EPAR". European Medicines Agency. 17 September 2018. Archived from the original on 9 September 2021. Retrieved 8 September 2021. Text was copied from this source which is copyright European Medicines Agency. Reproduction is authorized provided the source is acknowledged.
- ^ "Mabthera PI". Union Register of medicinal products. 3 June 1998. Retrieved 5 July 2024.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Rituximab". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 27 March 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ Tandan R, Hehir MK, Waheed W, Howard DB (August 2017). "Rituximab treatment of myasthenia gravis: A systematic review". Muscle & Nerve. 56 (2): 185–196. doi:10.1002/mus.25597. PMID 28164324. S2CID 19504332.
- ^ Singer O, McCune WJ (May 2017). "Update on maintenance therapy for granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis". Current Opinion in Rheumatology. 29 (3): 248–253. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000382. PMID 28306595. S2CID 35805200.
- ^ Dojcinov SD, Fend F, Quintanilla-Martinez L (March 2018). "EBV-Positive Lymphoproliferations of B- T- and NK-Cell Derivation in Non-Immunocompromised Hosts". Pathogens. 7 (1): 28. doi:10.3390/pathogens7010028. PMC 5874754. PMID 29518976.
- ^ "FDA Drug Safety Communication: Boxed Warning and new recommendations to decrease risk of hepatitis B reactivation with the immune-suppressing and anti-cancer drugs Arzerra (ofatumumab) and Rituxan (rituximab)". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 29 February 2016. Archived from the original on 28 April 2020. Retrieved 2 February 2020.
- ^ a b Bosch X, Ramos-Casals M, Khamashta MA (2013). Drugs Targeting B-Cells in Autoimmune Diseases. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 1–4. ISBN 9783034807067. Archived from the original on 5 November 2017.
- ^ a b World Health Organization (2023). The selection and use of essential medicines 2023: web annex A: World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 23rd list (2023). Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/371090. WHO/MHP/HPS/EML/2023.02.
- ^ "FDA Approves Rituxan Plus Chemotherapy for the Most Common Type of Adult Leukemia" (Press release). Biogen. 18 February 2010. Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 30 June 2021.
- ^ "FDA Approves Genentech's Rituxan (rituximab) in Children With Two Rare Blood Vessel Disorders" (Press release). Genentech. 27 September 2019. Retrieved 27 August 2024 – via Business Wire.
- ^ De A, Ansari A, Sharma N, Sarda A (2017). "Shifting Focus in the Therapeutics of Immunobullous Disease". Indian Journal of Dermatology. 62 (3): 282–290. doi:10.4103/ijd.IJD_199_17. PMC 5448263. PMID 28584371.
- ^ a b "FDA approves rituximab plus chemotherapy for pediatric cancer indications". U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 3 December 2021. Archived from the original on 3 December 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ Saini KS, Azim HA, Cocorocchio E, Vanazzi A, Saini ML, Raviele PR, et al. (August 2011). "Rituximab in Hodgkin lymphoma: is the target always a hit?". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 37 (5): 385–390. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2010.11.005. PMID 21183282.
- ^ Eichenauer DA, Engert A (December 2017). "Nodular lymphocyte-predominant Hodgkin lymphoma: a unique disease deserving unique management". Hematology. American Society of Hematology. Education Program. 2017 (1): 324–328. doi:10.1182/asheducation-2017.1.324. PMC 6142570. PMID 29222274.
- ^ a b c d "Rituxan Hycela- rituximab and hyaluronidase injection, solution". DailyMed. 3 December 2019. Archived from the original on 27 March 2021. Retrieved 2 February 2020.
- ^ Edwards JC, Szczepanski L, Szechinski J, Filipowicz-Sosnowska A, Emery P, Close DR, et al. (June 2004). "Efficacy of B-cell-targeted therapy with rituximab in patients with rheumatoid arthritis". The New England Journal of Medicine. 350 (25): 2572–2581. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa032534. PMID 15201414.
- ^ Tak PP, Kalden JR (May 2011). "Advances in rheumatology: new targeted therapeutics". Arthritis Research & Therapy. 13 (Suppl 1): S5. doi:10.1186/1478-6354-13-S1-S5. PMC 3123966. PMID 21624184.
- ^ McGinley MP, Moss BP, Cohen JA (January 2017). "Safety of monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of multiple sclerosis". Expert Opinion on Drug Safety. 16 (1): 89–100. doi:10.1080/14740338.2017.1250881. PMID 27756172. S2CID 36762194.
- ^ He D, Guo R, Zhang F, Zhang C, Dong S, Zhou H (December 2013). "Rituximab for relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis". The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (12): CD009130. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD009130.pub3. PMID 24310855.
- ^ a b Paul M (20 May 2009). "Popular Cancer Drug Linked to Often Fatal 'Brain Eating' Virus". Northwestern University News and Information. Archived from the original on 29 May 2010. Retrieved 22 May 2009.
- ^ "Popular Cancer Drug Linked To Often Fatal Brain Virus". ScienceDaily. 9 May 2009. Retrieved 5 July 2024.
- ^ "FDA Warns of Safety Concern Regarding Rituxan in New Patient Population". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 18 December 2006. Archived from the original on 13 May 2009. Retrieved 29 April 2013.
- ^ Froissart A, Veyradier A, Hié M, Benhamou Y, Coppo P (November 2015). "Rituximab in autoimmune thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura: A success story". European Journal of Internal Medicine. 26 (9): 659–665. doi:10.1016/j.ejim.2015.07.021. PMID 26293834.
- ^ Braendstrup P, Bjerrum OW, Nielsen OJ, Jensen BA, Clausen NT, Hansen PB, et al. (April 2005). "Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody treatment for adult refractory idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura". American Journal of Hematology. 78 (4): 275–280. doi:10.1002/ajh.20276. PMID 15795920. S2CID 42218074.
- ^ Patel V, Mihatov N, Cooper N, Stasi R, Cunningham-Rundles S, Bussel JB (2007). "Long-term responses seen with rituximab in patients with ITP" (PDF). Correspondence. Community Oncology. 4 (2): 107. doi:10.1016/s1548-5315(11)70061-4. Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 September 2007. Retrieved 18 April 2007.
- ^ Shanafelt TD, Madueme HL, Wolf RC, Tefferi A (November 2003). "Rituximab for immune cytopenia in adults: idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, autoimmune hemolytic anemia, and Evans syndrome". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 78 (11): 1340–1346. doi:10.4065/78.11.1340. PMID 14601692.
- ^ Ahmed AR, Spigelman Z, Cavacini LA, Posner MR (October 2006). "Treatment of pemphigus vulgaris with rituximab and intravenous immune globulin". The New England Journal of Medicine. 355 (17): 1772–1779. doi:10.1056/nejmoa062930. PMID 17065638.
- ^ Jacob A, Weinshenker BG, Violich I, McLinskey N, Krupp L, Fox RJ, et al. (November 2008). "Treatment of neuromyelitis optica with rituximab: retrospective analysis of 25 patients". Archives of Neurology. 65 (11): 1443–1448. doi:10.1001/archneur.65.11.noc80069. PMID 18779415.
- ^ "Rituximab Treatment of Patients with Severe, Corticosteroid-Resistant Thyroid-Associated Ophthalmopathy". Archived from the original on 22 August 2017. Retrieved 19 October 2011.
- ^ Hart PA, Chari ST (11 June 2013). "Immunomodulators and Rituximab in the Management of Autoimmune Pancreatitis". Pancreapedia. doi:10.3998/panc.2013.20.
- ^ Pranzatelli MR, Tate ED, Travelstead AL, Longee D (January 2005). "Immunologic and clinical responses to rituximab in a child with opsoclonus-myoclonus syndrome". Pediatrics. 115 (1): e115 – e119. doi:10.1542/peds.2004-0845. PMID 15601813.
- ^ Khosroshahi A, Wallace ZS, Crowe JL, Akamizu T, Azumi A, Carruthers MN, et al. (July 2015). "International Consensus Guidance Statement on the Management and Treatment of IgG4-Related Disease". Arthritis & Rheumatology. 67 (7): 1688–1699. doi:10.1002/art.39132. PMID 25809420. S2CID 39750214.
- ^ He Y, Shimoda M, Ono Y, Villalobos IB, Mitra A, Konia T, et al. (June 2015). "Persistence of Autoreactive IgA-Secreting B Cells Despite Multiple Immunosuppressive Medications Including Rituximab". JAMA Dermatology. 151 (6): 646–650. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.59. PMID 25901938.
- ^ Kyriakidis I, Mantadakis E, Stiakaki E, Groll AH, Tragiannidis A (October 2022). "Infectious Complications of Targeted Therapies in Children with Leukemias and Lymphomas". Cancers. 14 (20): 5022. doi:10.3390/cancers14205022. PMC 9599435. PMID 36291806.
- ^ Molloy ES, Calabrese LH (September 2012). "Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy associated with immunosuppressive therapy in rheumatic diseases: evolving role of biologic therapies". Arthritis and Rheumatism. 64 (9): 3043–3051. doi:10.1002/art.34468. PMID 22422012.
- ^ Grammatikos A, Donati M, Johnston SL, Gompels MM (30 August 2021). "Peripheral B Cell Deficiency and Predisposition to Viral Infections: The Paradigm of Immune Deficiencies". Frontiers in Immunology. 12: 731643. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.731643. PMC 8435594. PMID 34527001.
- ^ Burton C, Kaczmarski R, Jan-Mohamed R (June 2003). "Interstitial pneumonitis related to rituximab therapy". The New England Journal of Medicine. 348 (26): 2690–1, discussion 2690–1. doi:10.1056/NEJM200306263482619. PMID 12826649.
- ^ "Reports of Bowel Obstruction and Perforation with Rituxan (rituximab)" (PDF). Roche Canada. 10 November 2006. Archived from the original (PDF) on 27 March 2014.
- ^ Oren S, Mandelboim M, Braun-Moscovici Y, Paran D, Ablin J, Litinsky I, et al. (July 2008). "Vaccination against influenza in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: the effect of rituximab on the humoral response". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 67 (7): 937–941. doi:10.1136/ard.2007.077461. PMID 17981914. S2CID 21878513.
- ^ Spelman T, Forsberg L, McKay K, Glaser A, Hillert J (June 2022). "Increased rate of hospitalisation for COVID-19 among rituximab-treated multiple sclerosis patients: A study of the Swedish multiple sclerosis registry". Multiple Sclerosis. 28 (7): 1051–1059. doi:10.1177/13524585211026272. PMID 34212816. S2CID 235710318.
- ^ Reyes S, Ramsay M, Ladhani S, Amirthalingam G, Singh N, Cores C, et al. (December 2020). "Protecting people with multiple sclerosis through vaccination". Practical Neurology. 20 (6): 435–445. doi:10.1136/practneurol-2020-002527. PMID 32632038.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: overridden setting (link) - ^ Tolf A, Wiberg A, Müller M, Nazir FH, Pavlovic I, Laurén I, et al. (May 2022). "Factors Associated With Serological Response to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients With Multiple Sclerosis Treated With Rituximab". JAMA Network Open. 5 (5): e2211497. doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2022.11497. PMC 9096596. PMID 35544139. S2CID 248695128.
- ^ Seyfizadeh N, Seyfizadeh N, Hasenkamp J, Huerta-Yepez S (January 2016). "A molecular perspective on rituximab: A monoclonal antibody for B cell non Hodgkin lymphoma and other affections". Critical Reviews in Oncology/Hematology. 97: 275–290. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2015.09.001. PMID 26443686.
- ^ a b Pavlasova G, Borsky M, Svobodova V, Oppelt J, Cerna K, Novotna J, et al. (September 2018). "Rituximab primarily targets an intra-clonal BCR signaling proficient CLL subpopulation characterized by high CD20 levels". Leukemia. 32 (9): 2028–2031. doi:10.1038/s41375-018-0211-0. PMID 30030508.
- ^ Rudnicka D, Oszmiana A, Finch DK, Strickland I, Schofield DJ, Lowe DC, et al. (June 2013). "Rituximab causes a polarization of B cells that augments its therapeutic function in NK-cell-mediated antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity". Blood. 121 (23): 4694–4702. doi:10.1182/blood-2013-02-482570. PMID 23613524.
- ^ Shaw T, Quan J, Totoritis MC (November 2003). "B cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis: the rituximab (anti-CD20) experience". Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. 62 (Suppl 2): ii55 – ii59. doi:10.1136/ard.62.suppl_2.ii55. PMC 1766758. PMID 14532151.
- ^ a b Borsky M, Hrabcakova V, Novotna J, Brychtova Y, Doubek M, Panovska A, et al. (December 2021). "Rituximab induces rapid blood repopulation by CLL cells mediated through their release from immune niches and complement exhaustion". Leukemia Research. 111: 106684. doi:10.1016/j.leukres.2021.106684. PMID 34438120.
- ^ Binder M, Otto F, Mertelsmann R, Veelken H, Trepel M (September 2006). "The epitope recognized by rituximab". Blood. 108 (6): 1975–1978. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-04-014639. PMID 16705086.
- ^ "Rituximab". go.drugbank.com. Archived from the original on 5 January 2014. Retrieved 14 March 2023.
- ^ Maloney DG, Grillo-López AJ, White CA, Bodkin D, Schilder RJ, Neidhart JA, et al. (September 1997). "IDEC-C2B8 (Rituximab) anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in patients with relapsed low-grade non-Hodgkin's lymphoma". Blood. 90 (6): 2188–2195. doi:10.1182/blood.V90.6.2188. PMID 9310469.
- ^ a b "Rituximab Product Approval Information". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 20 February 2009. Archived from the original on 10 February 2017.
- ^ Scott SD (1998). "Rituximab: a new therapeutic monoclonal antibody for non-Hodgkin's lymphoma". Cancer Practice. 6 (3): 195–197. doi:10.1046/j.1523-5394.1998.006003195.x. PMID 9652253.
- ^ Harrison's Principles of Internal Medicine, Longo et al. McGraw Hill Medical 2011 page 931
- ^ "Roche Gets EC Nod for Follicular Lymphoma Maintenance Therapy". 29 October 2010. Archived from the original on 31 October 2010.
- ^ Stanton D (31 May 2016). "EU approves second indication for subcutaneous form of Roche's rituximab". BioPharma-Reporter. Archived from the original on 7 June 2016. Retrieved 9 June 2016.
- ^ a b "FDA approves rituximab plus hyaluronidase combination for Treatment of FL, DLBCL and CLL". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 22 June 2017. Retrieved 5 July 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c d e "FDA approves first treatment for children with rare diseases that cause inflammation of small blood vessels". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 27 September 2019. Retrieved 5 July 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b c d "FDA D.I.S.C.O. Burst Edition: FDA approvals of Rituxan (rituximab) plus chemotherapy for pediatric cancer indications, and Keytruda (pembrolizumab) for adjuvant treatment of Stage IIB or IIC melanoma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2 December 2021. Retrieved 5 July 2024.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
- ^ a b "FDA approves first biosimilar for treatment of adult patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) (Press release). 28 November 2018. Archived from the original on 15 December 2019. Retrieved 11 November 2019.
- ^ a b "FDA approves Truxima as biosimilar to Rituxan for non-Hodgkin's lympho". U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 28 November 2018. Retrieved 5 July 2024.
- ^ "Rituximab Biosimilar to Launch in Turkish Market". Center for Biosimilars. 13 March 2018. Retrieved 24 October 2024.
- ^ a b Saporito B (27 October 2014). "Hospitals Furious at Cancer-Drug Price Hikes". Time. Archived from the original on 20 October 2015. Retrieved 26 October 2015.
- ^ "Recombinant antibodies for human therapy". Google Patents. 24 July 1992. Retrieved 27 July 2024.
- ^ "Chimeric anti-CD20 antibody, rituxan, for use in the treatment of chronic lymphocytic leukemia". Google Patents. 9 November 1999. Retrieved 27 July 2024.
- ^ Storz U (2014). "Rituximab: how approval history is reflected by a corresponding patent filing strategy". mAbs. 6 (4): 820–37. doi:10.4161/mabs.29105. PMC 4171018. PMID 24866199.
- ^ "Treatment of hematologic malignancies associated with circulating tumor cells using chimeric anti-CD20 antibody". Google Patents. 9 November 1999. Retrieved 27 July 2024.
- ^ "Methods related to rituximab". Google Patents. 31 May 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2024.
- ^ Inserro A (25 March 2019). "Roche Settles With Pfizer Over Rituximab Patent". Center for Biosimilars. Retrieved 27 July 2024.
- ^ "Biosimilars of Rituximab". Generics and Biosimilars Initiative. 14 April 2017. Archived from the original on 24 February 2024. Retrieved 29 April 2017.
- ^ Lahiri D, Osterman C (2 November 2018). "Novartis abandons effort for U.S. approval of biosimilar rituximab". Reuters. Archived from the original on 3 November 2018. Retrieved 3 November 2018.
- ^ "Teva, Celltrion Maintain Slender Discount to Rituxan". Center for Biosimilars. 4 May 2020. Archived from the original on 30 March 2024. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "Amgen Rituximab Biosimilar Gains FDA Approval". The Center For Biosimilars. 17 December 2020. Archived from the original on 23 April 2021. Retrieved 23 April 2021.
The pharmaceutical company said Riabni will be marketed at a discount to the reference product of 23.7% below wholesale acquisition cost (WAC), or a WAC of $716.80 per 100 mg and $3584 per 500 mg single-dose vial. These costs are 15.2% less than the WAC for the biosimilar rituximab Truxima, Amgen said. The company added that Riabni's average sales price will be 16.7% below the current average for Rituxan.
- ^ "Dr Reddy's launches half-price version of MabThera - PharmaTimes". pharmatimes.com. 3 May 2007. Retrieved 19 November 2024.
- ^ Contreras K, Orozco V, Puche E, González CA, García-Padilla P, Rodríguez MP, et al. (March 2022). "Cost-Effectiveness of Rituximab (Fixed Schedule vs Tailored Dose) Compared With Azathioprine Maintenance Therapy in Adults With Generalized Antineutrophil Cytoplasm Antibody-Associated Vasculitis in Colombia". Value in Health Regional Issues. 28: 98–104. doi:10.1016/j.vhri.2021.08.002. PMID 34922060.
- ^ Romero G, Ticchioni M, Cohen M, Rosenthal-Allieri MA, Mondot L, Lebrun Frenay C (March 2016). "Neuromyelitis optica: Contribution of therapeutic responses markers monitoring in patients given rituximab". Revue Neurologique. 172 (3): 220–224. doi:10.1016/j.neurol.2015.12.004. PMID 26915311.
- ^ Kriston L, Härter M, Hölzel L (March 2009). "Challenges in reporting meta-analyses of diagnostic accuracy studies". Letters. Annals of Internal Medicine. 150 (6): 430. doi:10.7326/0003-4819-150-6-200903170-00025. PMID 19293085.
- ^ Fluge Ø, Rekeland IG, Lien K, Thürmer H, Borchgrevink PC, Schäfer C, et al. (May 2019). "B-Lymphocyte Depletion in Patients With Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial". Annals of Internal Medicine. 170 (9): 585–593. doi:10.7326/M18-1451. PMID 30934066. S2CID 91186383.
- ^ Seton KA, Espejo-Oltra JA, Giménez-Orenga K, Haagmans R, Ramadan DJ, Mehlsen J, et al. (European ME Research Group for Early Career Researchers (Young EMERG)) (January 2024). "Advancing Research and Treatment: An Overview of Clinical Trials in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (ME/CFS) and Future Perspectives". Journal of Clinical Medicine. 13 (2): 325. doi:10.3390/jcm13020325. PMC 10816159. PMID 38256459.
- ^ Bonnan M, Ferrari S, Bertandeau E, Demasles S, Krim E, Miquel M, et al. (2014). "Intrathecal rituximab therapy in multiple sclerosis: review of evidence supporting the need for future trials". Current Drug Targets. 15 (13): 1205–1214. doi:10.2174/1389450115666141029234644. PMID 25355180.
- ^ "Genmab.com / HuMax-CD20 (ofatumumab)". Archived from the original on 11 September 2007. Retrieved 3 December 2007.
- ^ "Fc-structure". Archived from the original on 10 November 2007. Retrieved 3 December 2007.
- ^ Eccles SA (2001). "Monoclonal antibodies targeting cancer: 'magic bullets' or just the trigger?". Breast Cancer Research. 3 (2): 86–90. doi:10.1186/bcr276. PMC 138676. PMID 11250751.
- ^ Maverakis E, Kim K, Shimoda M, Gershwin ME, Patel F, Wilken R, et al. (February 2015). "Glycans in the immune system and The Altered Glycan Theory of Autoimmunity: a critical review". Journal of Autoimmunity. 57 (6): 1–13. doi:10.1016/j.jaut.2014.12.002. PMC 4340844. PMID 25578468.
Further reading
[edit]- Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: rituximab subcutaneous injection (Report). NICE. September 2014.
- Salles G, Barrett M, Foà R, Maurer J, O'Brien S, Valente N, et al. (October 2017). "Rituximab in B-Cell Hematologic Malignancies: A Review of 20 Years of Clinical Experience". Advances in Therapy. 34 (10): 2232–2273. doi:10.1007/s12325-017-0612-x. PMC 5656728. PMID 28983798.
- Smith MR (October 2003). "Rituximab (monoclonal anti-CD20 antibody): mechanisms of action and resistance". Oncogene. 22 (47): 7359–68. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1206939. PMID 14576843.
External links
[edit]- "Discovery – Development of Rituximab". National Cancer Institute. 7 March 2014.