| Singaling Hkamti | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| State of the Shan States | |||||||||
| 1820–1948 | |||||||||
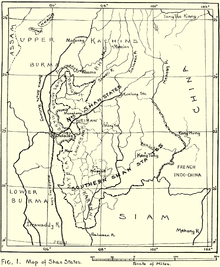 1917 map of the Burmese Shan States with the two Hkamti enclaves in Upper Burma in the upper left corner | |||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
• 1901 | 2,546 km2 (983 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1901 | 2,048 | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
• State founded | 1820 | ||||||||
• Integrated into Burma | 1948 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Singaling Hkamti (Burmese: ခန္တီးကလေး; Burmese: Kantigale; also known as Zingalein Kamti and Zingkaling Hkamti) was a Shan state in what is today Burma. It was an outlying territory, away from the main Shan State area. The state was located on both sides of the Chindwin River, in what is present-day Hkamti District, Sagaing Region. Its capital was Singaling Hkamti town.
History
[edit]Singaling Hkamti was founded in 1820. It was a tributary state of the King of Burma until 1887, when the Shan states submitted to British rule after the fall of the Konbaung dynasty. Its inhabitants were mostly Shan people who were said to have come from Hkamti Long. Before the time of rule by the British the state was often raided by the Kachin people.[1] The state was integrated into Burma after independence from the British in 1948.
Rulers
[edit]The rulers of Singaling Hkamti bore the title Myosa.[2]
Myosas
[edit]- 1820 - 1844 Sao Nyi Kaung
- 1844 - 1853 Sao Ai
- 1853 - 1882 Sao Hi
- 1882 - 1887 Vacant
- 1887 - 1892 Sao Ni Taung (b. 1861 - d. 1892)
- 1892 - 1893 Sao E -Regent (1st time) (b. 1856 - d. 1927)
- 1892 - 1894 Sao Hon (b. 1887 - d. 1894)
- 1894 - 1898 Ma Pu (f) (d. c.1898)
- 1894 - 1898 Sao E -Regent (2nd time) (s.a.)
- 1898 - 1927 Sao E (s.a.)
- 1927 - 1952 Maung Ba Thein
References
[edit]External links
[edit]25°59′N 95°41′E / 25.983°N 95.683°E