Tadeusz Sendzimir | |
|---|---|
 Sendzimir on a mural in Szczecin, 2018. | |
| Born | Tadeusz Sędzimir July 15, 1894 |
| Died | September 1, 1989 (aged 95) Jupiter, Florida, U.S.[1] |
| Nationality | Polish |
| Education | Lviv Polytechnic |
| Occupation(s) | Engineer, inventor |
| Known for | Sendzimir mill Sendzimir process |
| Spouse(s) | Barbara Alferieff (1922–1942) Bertha Madelaine Bernoda (1945) |
| Awards | Gold Cross of Merit (1938)[2] Bessemer Gold Medal (1965) Brinell Gold Medal (1974) |
Tadeusz Sendzimir (English: /ˈsɛndzɪmɪər/ SEND-zim-eer;[3] originally Sędzimir,[a] Polish: [taˈdɛ.uʂ sɛɲˈd͡ʑimir]; July 15, 1894 – September 1, 1989) was a Polish engineer and inventor of international renown. He held 120 patents in mining and metallurgy, 73 of which were awarded to him in the United States.[4]
He developed revolutionary methods of processing steel and metals used in every industrialized nation of the world. He was awarded many distinctions and honours including the Polish Gold Cross of Merit (1938), the Bessemer Gold Medal (1965) and the Brinell Gold Medal of the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences in Stockholm (1974).
Early years
[edit]
Sendzimir was the eldest son of Kazimierz Sędzimir belonging to the Clan of Ostoja[5][6] and Wanda Jaskółowska.[7] Fascinated by machinery as a child, he built his own camera at the age of 13. After studying at the 4th Classical Gymnasium (Gimnazjum Klasyczne) in Lwów he entered the Politechnika Lwowska.[8] However when Lwów was captured by Russian troops the Polytechnic Institute was closed and he moved to Kiev. There he worked in auto services and in the Russian-American Chamber of commerce where he learned Russian and English.
The Russian Revolution of 1917 forced Sendzimir to flee to Vladivostok, then to Shanghai, where Sendzimir built the first factory in China which produced screws, nails and wire. Financial support was provided by the Russian-Asian Bank, at the time headed by Poles (Władysław Jezierski and Zygmunt Jastrzębski).
Immigration and research
[edit]In 1922 Sendzimir married Barbara Alferieff. His first son Michael was born two years later. Designing and making his own machines, Sendzimir began experimenting with a new way to galvanize steel. Despite galvanization, the products still had a tendency to oxidize. Sendzimir discovered that the problem was due to the zinc bonding to a thin layer of iron hydroxide on its surface, rather than to the iron.
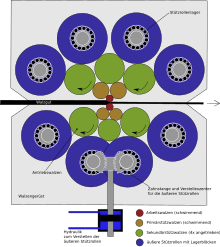
In 1929 Sendzimir approached several American industrialists with his findings, but since the Great Depression had begun, he was unsuccessful in gaining their interest. Returning to Poland in 1930, he established his original rolling mill; a year later, he contributed to constructing a galvanising plant in Kostuchna near Katowice employing the technology of continuous hot-dip galvanising of steel sheets. It became known worldwide as the Sendzimir process. This process was explained by him in the following words: "Let's imagine a piece of a hard pastry. We are rolling it on the pastry-board to decrease its thickness. However it would be faster and easier if we asked someone to stretch it by holding the edges". In 1934, at the Pokój Steelworks in Ruda Śląska, he implemented another of his inventions: a method of cold rolling of thin sheet metal in industrial production.[9]
A steel mill in Butler, Pennsylvania was established by Sendzimir in 1936. By 1938 Armco Steel became interested in his work and they formed a partnership with him, the Armzen Company, to oversee the worldwide expansion of his galvanizing and mill technology. In the spring of 1939 Sendzimir moved to Middletown, Ohio. Sendzimir's patented mill could roll hard materials down to very light gauges. The U.S. company, T. Sendzimir, Inc., was formed by him in Waterbury, Connecticut, in the 1940s.
In 1945, he married Bertha Bernoda. The following year he became a citizen of the United States. With the beginning of the Cold War, Sendzimir and his achievements were ignored by Communist Poland and he was not even mentioned in the Polish Encyklopedia Powszechna (Universal Encyclopedia). This changed when Edward Gierek, a new leader of the Polish United Workers' Party, came to power. Sendzimir was awarded an Officer Cross of the Order Polonia Restituta (Krzyż Oficerski Orderu Odrodzenia Polski).[10]
In 1975 Sendzimir received the honorary degree of doctor honoris causa from the AGH University of Science and Technology in Kraków. Sendzimir's successful methods for galvanizing steel eventually were implemented in the first Z-mill rolling silicon steel, making it pliable enough for use in air defense radar.[11] Between 1953 and 1989 he introduced the first productive Z-mill to Great Britain, and to Japan and Canada in the 1950s and 1960s. In 1974 Sendzimir invented a spiral steel looper used in both the United States and Japan.
Ninety percent of the world's galvanized steel production went through the Sendzimir process by the early 1980s. Poland, France, the United Kingdom, Japan, and Canada purchased his steel mills and technologies over the years. Most notably, Sendzimir was a major financial and personal supporter of the Kościuszko Foundation, the Polish Institute of Arts and Sciences of America and Alliance College in Pennsylvania. Sendzimir died after a massive stroke and was buried by his family in a zinc-plated coffin made according to his design.
Quote
[edit]- "I have been carrying family and my only capital - a new method of zinc-plating to another coast of the Pacific."
Remembrance
[edit]On the 100th anniversary of the Statue of Liberty he was one of those prominent immigrants honored for their contributions to America.
In 1989, his life and work were the subject of a documentary film entitled Sendzimir.
In 1990 Poland's large steel plant in Kraków (formerly the Lenin Steelworks) was renamed to Tadeusz Sendzimir Steelworks.[12] The AIST Tadeusz Sendzimir Memorial Medal was established in the same year.[13]
See also
[edit]- Sendzimir process
- Ostoja coat of arms
- Clan of Ostoja
- Timeline of Polish science and technology
- List of Polish inventors and discoverers
Notes
[edit]- ^ As of the 17th century version. The surname was changed after the second arrival to the United States.
References
[edit]- ^ Polski Słownik Biograficzny.
- ^ "M.P. 1936 nr 263 poz. 469". isap.sejm.gov.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Sendzimir". Oxford English Dictionary (Online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/OED/1048285947. (Subscription or participating institution membership required.)
- ^ Sarmatian Review XV.1.
- ^ Geni
- ^ Vanda Sendzimir: Steel will: the life of Tad Sendzimir. Nowy Jork: Hippocrene Books, 1994. ISBN 0-7818-0169-9
- ^ "Tadeusz Sędzimir - polski Edison". poland.us (in Polish). 6 November 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Tadeusz Sendzimir – the father of modern metallurgy". sendzimir.org.pl. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Giants of Polish Science - Tadeusz Sendzimir". ipn.gov.pl. 8 March 2021. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Tadeusz Sendzimir". historia.agh.edu.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Sendzimir Mill". hanrm.com. 3 June 2019. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "IPN o T. Sendzimirze jako "gigancie polskiej nauki": był polskim Edisonem metalurgii". dzieje.pl. 8 March 2021. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ^ "Tadeusz Sendzimir Memorial Medal for Innovation in Steel Manufacturing Technology". aist.org. Retrieved 10 May 2023.
Sources
[edit]- Vanda Sendzimir. Steel Will: The Life of Tad Sendzimir. New York, Hippocrene Books, 1994.
- M. Kalisz. Walcownia znaczy Sendzimir. "Przekrój", 1973, nr. 1468.
- O. Budrewicz. Ocynkowane życie. "Perspektywy", 1974, nr. 38.