|
Featured picture tools: |
These featured pictures, as scheduled below, appeared as the picture of the day (POTD) on the English Wikipedia's Main Page in February 2005.
You can add an automatically updating POTD template to your user page using {{Pic of the day}} (version with blurb) or {{POTD}} (version without blurb). For instructions on how to make custom POTD layouts, see Wikipedia:Picture of the day.
February 1
[edit]
|
The Space Shuttle Columbia seconds after engine ignition in 1981. For the first two missions only, the external fuel tank was painted white. The Space Shuttle became the major focus of NASA in the late 1970s and the 1980s. Planned to be frequently launchable and mostly reusable vehicle, four space shuttles were built by 1985. The first to launch, Columbia did so on April 12, 1981. Photo credit: NASA |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 2
[edit]
|
The Eiffel Tower in Paris is one of the world's most recognisable buildings and a symbol of France. The 300 m (986 ft) high tower was designed by Gustave Eiffel as a gateway to the Exposition Universelle of 1889. It was the world's tallest structure for forty years. Eiffel used his experience in building railway bridges when designing the tower, prefabricating the 18,038 wrought iron pieces off site then assembling the pieces with the help of 300 workers. Photo credit: Tristan Nitot |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 3
[edit]
|
The redback spider is a potentially dangerous spider found throughout Australia. A successful bite from a female redback injects a neurotoxin into the blood stream. Individuals bitten often describe the bite as extremely painful. In September 2004, inmates at Grafton maximum security prison in New South Wales were found to be keeping redback spiders. Media reported a prisoner's allegation that other inmates had been breeding the spiders, milking them, and injecting the venom for a high. However, the authorities uncovered no supporting evidence (e.g. syringes), and concluded the spiders were kept simply as pets. Photo credit: Fir0002 |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 4
[edit]
|
Surface tension is caused by the attraction between molecules of a liquid, due to van der Waals forces. In the bulk of the liquid, molecules are pulled in all directions, resulting in a net force of zero. At the surface, molecules are pulled inwards, but there are no liquid molecules on the outside to balance these forces, so the surface molecules are subject to an inward force of molecular attraction which is balanced by the resistance of the liquid to compression. Photo credit: W. M. Connolley |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 5
[edit]
|
The Battle of Normandy (D-Day) is one of the best-known battles of World War II. The invasion force included 4000 landing craft, 130 warships for bombardment and 12,000 aircraft to support the landings. In order to persuade the Germans that the invasion would really be coming to the Pas de Calais, the Allies prepared a massive deception plan, called Operation Fortitude. An entirely fictitious First U.S. Army Group was created, with fake buildings and equipment, and false radio messages were sent. Photo credit: U.S. Army's First Division |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 6
[edit]
|
Biodiversity is the diversity of and in living nature. Diversity, at its heart, implies the number of different kinds of objects, such as species. To increase the genetic diversity of U.S. corn, the Germplasm Enhancement for Maize (GEM) project seeks to combine exotic germplasm, such as this unusually colored and shaped maize from Latin America, with domestic corn lines. Photo credit: Keith Weller (USDA) |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 7
[edit]
|
Camouflage is a survival technique employed by many animals. The most common approach is disruptive camouflage, in which the skin is patterned with shapes and colours to match those in the natural background — making it difficult or confusing to detect the outline of the animal. This young cuttlefish uses a more advanced adaptive camouflage strategy. Like chameleons, cuttlefish have the ability to change their surface pigmentation to adapt to the colours of their environment. Cuttlefish also use fast-changing, vivid skin patterns as a means of communication between themselves. Photo credit: Raul654 |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 8
[edit]
|
The Peafowl are most notable for the male's extravagant tail, a result of sexual selection, which it displays as part of courtship. The male is called a peacock, the female a peahen. In user-friendly English, however, peacock is used to mean any peafowl. Many of the brilliant colors of the peacock plumage are due to an optical interference phenomenon called Bragg reflection. Peacock is the national bird of India and is featured in coins and currencies of the country. Photo credit: Adrian Pingstone |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 9
[edit]
|
A selection of fresh conkers from a Horse-chestnut. They are not true nuts, but rather capsules. The soft whitish-brown wood can be used for cheap furniture, boxes and firewood. The nuts are poisonous, but some Native American tribes leached the pulverized nuts to make them edible. Crushed buckeye nuts have been used by poachers to kill fish for easy capture. Some animals, notably deer, are resistant to the toxins. Photo credit: Photo credit: Solipsist |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 10
[edit]
|
The Himalayan mountain range with Mount Everest as seen from the International Space Station. The Himalaya separates India and the Northern Areas of Pakistan on the south and southwest from the vast Tibetan plateau (now part of China) on the north. Four of the world's fourteen eight-thousanders, mountains higher than 8000 m, can be seen, Makalu (8462 m), Everest (8850 m), Lhotse (8516 m) and Cho Oyu (8201 m). Photo credit: NASA |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 11
[edit]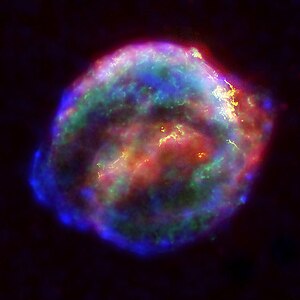
|
This Supernova remnant of Kepler's Supernova (SN 1604) is made up of the materials left behind by the gigantic explosion of a star. There are two possible routes to this end: either a massive star may cease to generate fusion energy in its core, and collapse inward under the force of its own gravity, or a white dwarf star may accumulate material from a companion star until it reaches a critical mass and undergoes a similar collapse. In either case, the resulting supernova explosion expels much or all of the stellar material with great force. Photo credit: NASA |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 12
[edit]|
The oil extracted from Sunflower seeds, is used for cooking, as a carrier oil and is used to produce biodiesel. The meal remaining after the seeds have been processed for oil is used as a livestock feed. Some recently developed varieties have drooping heads. These varieties are less attractive to gardeners growing the flowers as ornamental plants, but appeal to farmers, because they reduce bird damage and losses from some plant diseases. Photo credit: Bruce Fritz (USDA) | |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 13
[edit]
|
The Matterhorn is located on the border between Switzerland and Italy, towering over the Swiss town of Zermatt and the Italian town Breuil-Cervinia in the Val Tournanche. It was the last major mountain of the Alps to be climbed, not merely because of its technical difficulty, but of the fear it inspired in early mountaineers. The first serious attempts began around 1858, mostly from the Italian side, but despite appearances, the southern routes are harder, and parties repeatedly found themselves on difficult slippery rock and had to turn back. Photo credit: Stan Shebs |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 14
[edit]
|
The Cathedral of Magdeburg (known as Magdeburger Dom in German) is the first gothic cathedral in Germany and with a height of 104 m the highest cathedral in Eastern Germany. The current cathedral was constructed over the period of 300 years starting from 1209, and the completion of the steeples took place only in 1520. In 2004 a funding drive for a new organ that was started in 1997 was completed, collecting 2 Million Euro. The new organ has been ordered from a company near Potsdam, constructing a 36 ton instrument with 93 registers and approximately 5000 pipes. The construction is planned to be completed in 2007, and the new organ will hopefully be used for the first time in 2008. Photo credit: Chris 73 |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 15
[edit]
|
Strelitzia is a South African genus of perennial plants named after the duchy of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, home of the former Queen Charlotte of England. The common name of the genus is "bird of paradise", because of the resemblance of its flowers to the bird of that name. Photo credit: Photo credit: Scott Bauer USDA |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 16
[edit]
|
An image of Pollen taken by a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM), a type of electron microscope capable of producing high resolution images of a sample surface. Due to the manner in which the image is created, SEM images have a characteristic 3-dimensional quality and are useful for judging the surface structure of the sample.
Photo credit: Rippel Electron Microscope Facility |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 17
[edit]
|
The Bald Eagle is a raptor that is indigenous to North America, and is the national symbol of the United States of America. The species was on the brink of extinction late in the 20th century but has largely recovered and now has a stable population. Its diet is varied, including fish, smaller birds, rodents, and sometimes food scavenged or stolen from campsites and picnics.
Photo credit: Adrian Pingstone |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 18
[edit]
|
The American White Ibis is a species of wading bird of the ibis family, indigenous to the southern USA and the Caribbean. It lives in marshy wetlands, and on beaches, and has become common in city parks. They build a stick nest in a tree or bush over water, and 2-5 eggs are laid. This ibis feeds on various fish, frogs and other water creatures, and also insects. Adults are 65 cm long with a 95 cm wingspan. They are all-white except for black wing-tips and red bills and legs. Juveniles are largely brown with duller bare parts.
Photo credit: Jaap Folmer |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 19
[edit] Square A is exactly the same shade of grey as square B. |
An optical illusion is any illusion that deceives the human visual system into perceiving something that is not present or incorrectly perceiving what is present. There are physiological illusions and cognitive illusions. A mirage is an example of a natural illusion that is an optical phenomenon, another example is the variation in the apparent size of the Moon (smaller when overhead, larger when near the horizon), this is not an optical phenomenon, but rather a cognitive or perceptual illusion.
Photo credit: Edward H. Adelson |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 20
[edit]
|
The Very Large Array is a radio astronomy observatory that consists of 27 independently movable radio antennae, each of which has a dish diameter of 25 meters and weighs 230 tons. There are four commonly used configurations, designated A (the largest, when the furthest dishes are 36 km apart) through D (the tightest, when all 27 are within 600 m of the center point).
Photo credit: Hajor |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 21
[edit]
|
The Battle of Passchendaele, otherwise known as the Third Battle of Ypres, was one of the major battles of World War I, fought by British, ANZAC and Canadian soldiers against the German army near Ypres (Ieper in Flemish) in West Flanders, northwestern Belgium over the control of the village of Passchendaele. As the village is now known as Passendale, the term Passchendaele alone is now used to refer to this battle. The label "Passchendaele" should properly apply only to the battle's later actions in October–November 1917, but has come to be applied also to the entire campaign from July 31. After three months of fierce fighting, the Canadian Corps took Passchendaele on November 6 1917, ending the battle. Passendale today forms part of the community of Zonnebeke, Belgium.
Photo credit: Imperial War Museum |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 22
[edit]
|
Water colored red by Iron. Iron comprises 95 percent of all the metal tonnage produced worldwide. Its combination of low cost and high strength make it indispensable, especially in applications like automobiles, the hulls of large ships, and structural components for buildings. The first signs of use of iron come from the Sumerians and the Egyptians, where around 4000 BC, small items were being fashioned from iron recovered from meteorites. Photo credit: NASA |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 23
[edit]
|
Pillar corals are a type of hard coral which live in the western Atlantic Ocean. They are one of the digitate corals which resemble fingers, or a cluster of cigars growing up from the sea floor, but without any secondary branching. Pillar corals can grow to be up to 2.5 m (8 ft) tall. They can grow on both flat and sloping sea floors at a depth of between 1 and 20 m (65 ft). They are one of the few types of hard coral whose polyps can commonly be seen feeding during the day.
Photo credit: NOAA |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 24
[edit]
|
A wakizashi is a traditional Japanese sword, with a shoto blade between 12 and 24 inches long (30 – 60 cm). It is the smaller cousin of the katana and together the two swords were worn as a matched pair, or daisho, by samurai warriors. Towards the end of the Edo period, samurai swords became elaborate status symbols, with lavish decoration on the hilt and scabbard displaying the owner's wealth. Photo credit: Chris 73 |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 25
[edit]
|
Pollen, like on this Gerbera, is a fine powder consisting of pollen grains, which carry the male gametes of seed plants. The transfer of pollen grains to the female reproductive structure can be mediated by the wind, in which case the plant is described as wind-loving, these plants typically produce great quantities of very lightweight pollen grains. Insect-loving plants produce pollen that is relatively heavy and sticky, for dispersal by insect pollinators attracted to their flowers. Photo credit: pdphoto.org |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 26
[edit]
|
Migrant Mother, Dorothea Lange's 1936 photograph of Florence Owens Thompson and her daughters, became the most famous image of the Great Depression in the United States. Its one of the classic photographs of the 20th century, and is now an icon of resilience in the face of adversity. In actual fact, Thompson wasn't the destitute pea picker implied by the photograph. She had only stopped at the camp temporarily whilst her sons and partner tried to get their car repaired. Photo credit: Dorothea Lange (FSA) |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 27
[edit]
|
The London Millennium Footbridge, opened on June 10 2000, was a Millennium Project designed by Foster and Partners with Sir Anthony Caro. It is the first new bridge across the Thames in London since Tower Bridge in 1894. On its opening day the bridge exhibited alarmingly large lateral vibrations. The initial small sideways movements encouraged pedestrians to walk in synchronisation with the sway, forcing the vibrations to a level where they became uncomfortable. As a result the bridge was swiftly nicknamed the Wobbly Bridge. Two days later the bridge was closed for several months of remedial work to correct the problem. Photo credit: Paul Lomax |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
February 28
[edit]
|
"The Blue Marble" is a famous photograph of Earth. NASA officially credits the image to the entire Apollo 17 crew — Eugene Cernan, Ronald Evans and Jack Schmitt — all of whom took photographic images during the mission. Apollo 17 passed over Africa during daylight hours and Antarctica is also illuminated. The photograph was taken approximately five hours after the spacecraft's launch, while en route to the Moon. Apollo 17, notably, was the last manned lunar mission; no humans since have been at a range where taking a "whole-Earth" photograph such as "The Blue Marble" would be possible. Photo credit: The Apollo 17 crew |
Text version ( view - edit - talk - history ) - Condensed version ( view - edit )
Picture of the day archives and future dates