| |

| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
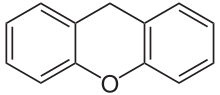
| Preferred IUPAC name
9H-Xanthene[1] | |
| Other names
Dibenzo[a,e]pyran
10H-9-Oxaanthracene | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| 133939 | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.001.996 |
| EC Number |
|
| 83576 | |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C13H10O | |
| Molar mass | 182.222 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Yellow solid |
| Melting point | 101 to 102 °C (214 to 216 °F; 374 to 375 K)[2] |
| Boiling point | 310 to 312 °C (590 to 594 °F; 583 to 585 K)[2] |
| Hazards[3] | |
| GHS labelling: | |

| |
| Warning | |
| H317 | |
| P280 | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Xanthene (9H-xanthene, 10H-9-oxaanthracene) is the organic compound with the formula CH2[C6H4]2O. It is a yellow solid that is soluble in common organic solvents. Xanthene itself is an obscure compound, but many of its derivatives are useful dyes.[4]
Xanthene dyes
[edit]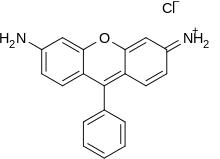
Dyes that contain a xanthene core include bikaverin, fluorescein, eosins, and rhodamines. Xanthene dyes tend to be fluorescent, yellow to pink to bluish red, brilliant dyes. Many xanthene dyes can be prepared by condensation of derivates of phthalic anhydride with derivates of resorcinol or 3-aminophenol.
Further reading
[edit]- Neckers, Douglas C.; Valdes-Aguilera Oscar M. (1993). "Photochemistry of the Xanthene Dyes". Advances in Photochemistry. 18: 315–94. doi:10.1002/9780470133491.ch4. ISBN 9780470133491.
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (2014). Nomenclature of Organic Chemistry: IUPAC Recommendations and Preferred Names 2013. The Royal Society of Chemistry. p. 213. doi:10.1039/9781849733069. ISBN 978-0-85404-182-4.
- ^ a b Xanthene at Sigma-Aldrich
- ^ "Xanthene 99%". Sigma Aldrich.
- ^ Gessner, Thomas; Mayer, Udo (2000). "Triarylmethane and Diarylmethane Dyes". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a27_179. ISBN 978-3527306732.