Beihai
北海市 Bwzhaij Pakhoi | |
|---|---|
 Beihai Silver Beach | |
 Location of Beihai in Guangxi | |
| Coordinates (Beihai government): 21°28′52″N 109°07′12″E / 21.481°N 109.120°E | |
| Country | People's Republic of China |
| Region | Guangxi |
| Municipal seat | Haicheng District |
| Area | |
| 3,337 km2 (1,288 sq mi) | |
| Elevation | 21 m (69 ft) |
| Population (2010 census) | |
| 1,539,300 | |
| • Density | 460/km2 (1,200/sq mi) |
| • Urban | 572,000 |
| • Metro | 405,600 |
| GDP[1] | |
| • Prefecture-level city | CN¥ 150.4 billion US$ 23.3 billion |
| • Per capita | CN¥ 80,710 US$ 12,510 |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (China Standard) |
| Postal code | 536000 |
| Area code | 779 |
| ISO 3166 code | CN-GX-05 |
| Vehicle registration | 桂E |
| Website | www |
| Beihai | |||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
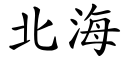 "Beihai", as written in Chinese | |||||||||||||||||
| Chinese name | |||||||||||||||||
| Chinese | 北海 | ||||||||||||||||
| Postal | Pakhoi | ||||||||||||||||
| Literal meaning | north of the sea | ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
| Zhuang name | |||||||||||||||||
| Zhuang | Bwzhaij | ||||||||||||||||
| 1957 orthography | Bɯƨhaiз | ||||||||||||||||
Beihai (Chinese: 北海; pinyin: Běihǎi; Postal romanization: Pakhoi[2]) is a prefecture-level city in the south of Guangxi, People's Republic of China. Its status as a seaport on the north shore of the Gulf of Tonkin has granted it historical importance as a port of international trade for Guangxi, Hunan, Hubei, Sichuan, Guizhou, and Yunnan.[3] Between the years 2006 and 2020, Beihai was predicted to be the world's fastest growing city.[4][needs update][better source needed] Beihai has a large shipyard, but most of the money generated in the city is derived from trade.
In addition, it governs the small islands of Weizhou and Xieyang, and is directly west of Leizhou Peninsula.
Subdivisions
[edit]Up to 2022, Beihai contains 3 districts and 1 county, which are subdivided into 7 urban sub-districts, 22 towns, 1 townships, 95 neighborhood committees, 336 village committees. (see also Administrative divisions of the People's Republic of China#Levels)[5]
- Haicheng District (海城区)
- Yinhai District (银海区)
- Tieshangang District (铁山港区)
- Hepu County (合浦县)
| Map |
|---|
History
[edit]
After the 1876 Sino-British Treaty of Yantai, eight Western nations (the UK, US, Germany, Austria-Hungary, France, Italy, Portugal, and Belgium) set up consulates, hospitals, churches, schools, and maritime customs. Today, 15 of these western buildings remain in Beihai. It officially became an international tourist spot (旅游对外开放城市) in 1982.
City timeline
[edit]- December 4, 1949: Beihai became a town of Hepu County under the Chinese Communist Party.
- January 1951: a province-administered city of Guangdong
- May 1951: entrusted to Guangxi
- March 1952: officially administered by Guangxi
- May 1955: Administered by Guangdong again
- 1956: reduced to a county-level city
- 1958: reduced to Beihai People's Commune of Hepu County
- 1959: county-class town
- 1964: restored to county-class city
- June 1965: Administered by Guangxi again
- October 1983: restored to prefecture-level city
Climate
[edit]Beihai has a monsoon-influenced humid subtropical climate (Köppen Cwa), with mild to warm winters and long, hot (but not especially) summers, and very humid conditions year-round. The monthly 24-hour average temperature ranges from 14.6 °C (58.3 °F) in January to 29.0 °C (84.2 °F) in July, while extremes have ranged from 2.6 to 37.1 °C (37 to 99 °F). Rain is both the heaviest and most frequent from June to September, when 70% of the annual rainfall also occurs. This is in contrast to the autumn and winter months, where only 20 to 40 millimetres (0.79 to 1.57 in) of rain falls per month. The area receives about 2,000 hours of sunshine annually.[3] Extremes since 1951 have ranged from 2.0 °C (36 °F) (unofficial record of 0 °C (32 °F) was set in January 1893 on an unknown date) to 37.1 °C (99 °F).[6]
| Climate data for Beihai (1991–2020 normals, extremes 1971–2020) | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 27.9 (82.2) |
29.9 (85.8) |
31.5 (88.7) |
33.4 (92.1) |
35.8 (96.4) |
36.2 (97.2) |
36.2 (97.2) |
37.1 (98.8) |
36.4 (97.5) |
34.7 (94.5) |
32.0 (89.6) |
28.8 (83.8) |
37.1 (98.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 18.7 (65.7) |
20.3 (68.5) |
23.1 (73.6) |
27.3 (81.1) |
30.6 (87.1) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.9 (89.4) |
31.8 (89.2) |
31.3 (88.3) |
29.3 (84.7) |
25.6 (78.1) |
21.0 (69.8) |
26.9 (80.4) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 14.7 (58.5) |
16.4 (61.5) |
19.4 (66.9) |
23.7 (74.7) |
27.2 (81.0) |
28.9 (84.0) |
29.1 (84.4) |
28.6 (83.5) |
27.6 (81.7) |
25.0 (77.0) |
21.1 (70.0) |
16.6 (61.9) |
23.2 (73.8) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 12.0 (53.6) |
13.9 (57.0) |
16.9 (62.4) |
21.3 (70.3) |
24.6 (76.3) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.6 (79.9) |
26.0 (78.8) |
24.8 (76.6) |
22.0 (71.6) |
18.0 (64.4) |
13.7 (56.7) |
20.5 (69.0) |
| Record low °C (°F) | 2.0 (35.6) |
2.5 (36.5) |
3.5 (38.3) |
9.6 (49.3) |
15.0 (59.0) |
19.2 (66.6) |
20.2 (68.4) |
18.7 (65.7) |
16.1 (61.0) |
12.0 (53.6) |
6.4 (43.5) |
2.0 (35.6) |
2.0 (35.6) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 38.2 (1.50) |
30.5 (1.20) |
50.5 (1.99) |
71.6 (2.82) |
127.3 (5.01) |
299.4 (11.79) |
384.5 (15.14) |
440.4 (17.34) |
217.4 (8.56) |
83.3 (3.28) |
48.8 (1.92) |
29.9 (1.18) |
1,821.8 (71.73) |
| Average precipitation days (≥ 0.1 mm) | 7.8 | 8.5 | 12.2 | 10.0 | 10.4 | 13.7 | 16.0 | 17.1 | 12.4 | 6.4 | 5.4 | 6.2 | 126.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 78 | 82 | 84 | 83 | 81 | 82 | 82 | 84 | 80 | 75 | 74 | 72 | 80 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 93.9 | 80.3 | 82.3 | 118.4 | 197.1 | 185.7 | 208.3 | 193.8 | 194.5 | 204.2 | 165.0 | 126.9 | 1,850.4 |
| Percent possible sunshine | 28 | 25 | 22 | 31 | 48 | 46 | 51 | 49 | 53 | 57 | 50 | 38 | 42 |
| Source 1: China Meteorological Administration[7][8]NOAA[9] | |||||||||||||
| Source 2: Weather China[3] | |||||||||||||
Language
[edit]- Qin-Lian Yue
It is the mostly common vernacular languages group in Beihai, including old language (Limchownese Language and Nga Language) and new language (kinds accents of Cantonese).- Limchownese Language
(Chinese: 廉州話), the name stemming from the Town of Lianzhou, the capital of County of Hepu, which was the central and capital town for several modern cities nearby in early history. Or Hoppo Language (Chinese: 合浦話), has been named by the County of Hepu, which was the major city in Gulf of Tonkin of ancient China. Or Rural Language (Chinese: 村下話), literally speaking, the language was most widely used until the Cantonese and Tanka immigrants from the zone of Pearl River - capital district of Province of Guangdong with their Cantonese Language have been dominating South of Hepu - modern District of Haicheng, focal point of Beihai, where downtown has been moved to from Town of Lianzhou since 19th century after Chefoo Convention which demanded Beihai as a treaty port. Or Jute-planter Language (Chinese: 麻佬話), whose name was from 'jute-planter' (Chinese: 麻佬) is used to describe the Limchownese-speaking people tend to broadly plant jute. The term is widely used in East of Hepu. Limchownese is mostly widely used in Beihai, and regarded as the first language and mother tongue by the most of native. People in County of Hepu and District of Yinhai only speak Limchownese as monolingual (only regional languages are listed, or as 'dialects' regarded by Government of China, Mandarin that is national language of China isn't counted here). However, citizens in District of Haicheng - the zone of chief administration mostly speak it as bilingual, Pakhoi Cantonese is more mainstream here, the elder are mostly proficient for the 2 languages, the young might only speak the latter and are mostly able to listen, understand and simulate the former language. - Nga Language
(Chinese: 我話, literally 'my language') named by the pronunciation of 'I' (Chinese: 我) /ŋa/, some call Maritime Language (Chinese: 海邊話), another elder speakers call Hoppo Language (Chinese: 合浦話), for distinguishing from sharing the same name of with Limchownese Language, they call Limchownese 'Outer Language' (Chinese: 坡外話). Linguistically, Nga Language is closely related to Limchownese Language, sometimes regarded as a dialect of it. Nga Language is mostly spoken in District of Tieshangang, and some in District of Yinhai and Town of Zakou border on Tieshangang. Nga Language and Limchownese Language are able to be talked each other in some extent (approximately 50-60 percent and more), but a little confusion about understand and tone. And it's easy to learn and simulate Limchownese for the people speaking Nga Language. Historical name for Tieshangang was 'pearl pool' (Chinese: 珠廠), so the many ancient people who spoke this language called 'the pearl fishers' (Chinese: 珠民) in historical information. The pearl played the most significant role in Beihai's ancient history. - Costal Language
(Chinese: 海邊話), also named Civilian Language (Chinese: 百姓話) is spoken in Town of Shatian. This language is debatable Which language group it belongs to, sometimes it will be stated as Min Language. However, it shares many indigenous words with Limchownese Language and Nga Language. - Pakhoi Cantonese
(Chinese: 北海白話, literally 'vernacular of Beihai'), abbreviated as Pakhoi Language (Chinese: 北海話), vernacular or Common Language (Chinese: 白话), the dialect of Cantonese, is the second most-spoken language in Beihai. After Cantonese and Tanka immigrants brought their language and culture while settled in Beihai in 19th century, it has been changed by the influence of native through time. 'Limchownese-Cantonese' is the most appropriate term to explain it. Pakhoi Cantonese has experienced strong influence from Limchownese language, especially native conventional vocabularies and phrase different from Cantonese Language, some are originated from Kra–Dai languages without Chinese characters to write (sometimes meaningless homonyms are used to write), others are diverse or very rare Sintic words to use. And its pronunciations are also influenced, some Chinese characters each have 2 different pronunciations - Limchownese-Cantonese pronunciation and native Cantonese pronunciation, depending on their different vocabulary which means combining more than 2 characters (or words from Kra–Dai languages) to form a phrase. And some expressions have 2 different phrases - native Cantonese phrase and Limchownese phrase. - Naamhong Cantonese (Chinese: 南康白話), is only spoken in the downtown of Town of Nankang. It is close to Pakhoi Cantonese but with an obviously different tone. However, the most widely used in Town of Nankang is Nga Language, mostly in hinterland.
- Limchownese Language
- Cantonese varieties of mixed Yue
The local Cantonese accents of Beihai with native Qin-Lian Yue and Yuehai Yue (widely known as 'Cantonese of Guangzhou') mixed.- Tanka Cantonese
(Chinese: 蜑家話) is spoken by Tanka People who are mostly living in Waishaqiao (Chinese: 外沙橋) the north bank of Beihai, some very elderly people speak in the absolute Tanka accent, the middle age and the young speak in mixed accents with Pakhoi Cantonese. - Overseas-Chinese Cantonese
(Chinese: 華僑白話) is spoken by the people living in Town of Qiaogang, majorly consist of Chinese-vietnamese refugees expelled during the anti-China protest in Vietnam in 1975. Overseas-Chinese accents are complex, the minority speak in Cantonese accent or Tanka accent, the majority speak in a mixed accent with Pakhoi Cantonese or Limchownese Language. - Saanhau Cantonese
(Chinese: 山口白話) is only spoken in the downtown of Town of Shankou which is the border Province of Guangxi and Province of Guangdong. It is close to Guangzhou Cantonese.
- Tanka Cantonese
- West Guangdong-South Guangxi Hakka
- Ngai Language
(Chinese: 涯話, literally 'my language') named by the pronunciation of 'I' (Chinese: 我) /ŋai/, 涯 is the meaningless 'borrowed characters' based on its similar pronunciation, or New-immigrants Language (Chinese: 新民話) is the third most-speaking language. It is linguistically divided as a dialect of Hakka Language, but some speakers distinguish themselves from Hakka (Because most of Ngai people consider that they don't share a origins with Hakka people). The speakers mainly gather in several towns of Eastern Hepu and Weizhou Island (the mother tongue for about 60% islanders). Most of Ngai people's ancestors moved from Dingzhou, Province of Fujian to Beihai during Ming and Qing dynasties.
- Ngai Language
- Leizhou-Hainan Min
- Leizhou Min
(Chinese: 雷話) is rare in Beihai and only used in some villages of Tieshangang and Weizhou Island (the mother tongue for about 15% islanders). The speakers are descendants of Immigrants from Leizhou. Weizhou Island was governed by District of Leizhou, then was transferred to Hepu (including nowaday Beihai). - Bomei Language
(Chinese: 波美話) is a dialect of Min language, only spoken by very small people living around Beihai Fucheng Airport. The speakers are mostly descendants of the Immigrants from Dianbai.
- Leizhou Min
- Eastern Min
Others
[edit]Mandarin is of increasing prevalence as a result of the Chinese government's general promotion of it.
Transportation
[edit]Air transportation
[edit]Beihai is served by Beihai Fucheng Airport (BHY). It serves domestic destinations and also Hong Kong.
Rail
[edit]Beihai is served by a railway branch from Nanning. There are passenger trains to Nanning and Guilin.[10] At the end of 2013, the introduction of high-speed (D-series) train service to Beihai was announced as well.[11]
Road
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ "广西统计年鉴-2021", tjj.gxzf.gov.cn
- ^ Theodore Shabad (1956). China's Changing Map: A Political and Economic Geography of the Chinese People's Republic. New York: Frederick A. Praeger. p. 166. LCCN 55-11530. OCLC 916993074.
With the exception of Shiukwan on the Canton-Hankow railroad, Kwangtung's regional centers are situated along the coast, notably in the Canton delta. There, in addition to Canton, are the cities of Fatshan, Kongmoon and Shekki. The metropolis of western Kwangtung is Tsamkong, and Pakhoi is the chief town of the western panhandle.
- ^ a b c 北海城市介绍 (in Simplified Chinese). Weather China. Retrieved 2012-02-25.
- ^ City Mayors: World's fastest growing urban areas
- ^ the Yearbook of Beihai. "Overview of Beihai". Beihai Government.
- ^ "中国各地城市的历史最低气温". weibo.com. Retrieved 2024-09-15.
- ^ 中国气象数据网 – WeatherBk Data (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ^ "Experience Template" 中国气象数据网 (in Simplified Chinese). China Meteorological Administration. Retrieved 28 May 2023.
- ^ "Beihai Climate Normals 1991-2020". NOAA.
- ^ Beihai train schedule (in Chinese)
- ^ 广西再开通运营9对动车组 陈武宣布高铁开通. huochepiao.com. 2013-12-31. Archived from the original on 2014-11-29. Retrieved 2014-01-02. (Guangxi opens new CRH service, with 9 pairs of train a day. Chen Wu announces the opening of high-speed service), 2013-12-31




