| |
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Hydrogen iodide
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
Iodane | |
| Other names
Hydroiodic acid (aqueous solution)
Iodine hydride | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.030.087 |
| EC Number |
|
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII | |
| UN number | 1787 2197 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| HI | |
| Molar mass | 127.912 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Colorless gas |
| Odor | acrid |
| Density | 2.85 g/mL (−47 °C) |
| Melting point | −50.80 °C (−59.44 °F; 222.35 K) |
| Boiling point | −35.36 °C (−31.65 °F; 237.79 K) |
| approximately 245 g/100 ml | |
| Acidity (pKa) | −10 (in water, estimate);[1] −9.5 (±1.0)[2] 2.8 (in acetonitrile)[3] |
| Conjugate acid | Iodonium |
| Conjugate base | Iodide |
Refractive index (nD)
|
1.466 (16 °C)[4] |
| Structure | |
| Terminus | |
| 0.38 D | |
| Thermochemistry[4] | |
Heat capacity (C)
|
29.2 J·mol−1·K−1 |
Std molar
entropy (S⦵298) |
206.6 J·mol−1·K−1 |
Std enthalpy of
formation (ΔfH⦵298) |
26.5 kJ·mol−1 |
Gibbs free energy (ΔfG⦵)
|
1.7 kJ·mol−1 |
Enthalpy of fusion (ΔfH⦵fus)
|
2.87 kJ·mol−1 |
Enthalpy of vaporization (ΔfHvap)
|
17.36 kJ·mol−1 |
| Hazards | |
| Occupational safety and health (OHS/OSH): | |
Main hazards
|
Toxic, corrosive, harmful and irritant |
| GHS labelling: | |
 
| |
| Danger | |
| H302, H314 | |
| P260, P264, P280, P301+P330+P331, P303+P361+P353, P304+P340, P305+P351+P338, P310, P321, P363, P405, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |
LD50 (median dose)
|
345 mg/kg (rat, orally)[5] |
| Safety data sheet (SDS) | hydrogen iodide |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Hydrogen fluoride Hydrogen chloride Hydrogen bromide Hydrogen astatide |
| Supplementary data page | |
| Hydrogen iodide (data page) | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Hydrogen iodide (HI) is a diatomic molecule and hydrogen halide. Aqueous solutions of HI are known as hydroiodic acid or hydriodic acid, a strong acid. Hydrogen iodide and hydroiodic acid are, however, different in that the former is a gas under standard conditions, whereas the other is an aqueous solution of the gas. They are interconvertible. HI is used in organic and inorganic synthesis as one of the primary sources of iodine and as a reducing agent.
Properties of hydrogen iodide
[edit]HI is a colorless gas that reacts with oxygen to give water and iodine. With moist air, HI gives a mist (or fumes) of hydroiodic acid. It is exceptionally soluble in water, giving hydroiodic acid. One liter of water will dissolve 425 liters of HI gas, the most concentrated solution having only four water molecules per molecule of HI.[6]
Hydroiodic acid
[edit]Hydroiodic acid is not pure hydrogen iodide, but a mixture containing it. Commercial "concentrated" hydroiodic acid usually contains 48–57% HI by mass. The solution forms an azeotrope boiling at 127 °C with 57% HI, 43% water. The high acidity is caused by the dispersal of the ionic charge over the anion. The iodide ion radius is much larger than the other common halides, which results in the negative charge being dispersed over a large space. By contrast, a chloride ion is much smaller, meaning its negative charge is more concentrated, leading to a stronger interaction between the proton and the chloride ion. This weaker H+···I− interaction in HI facilitates dissociation of the proton from the anion and is the reason HI is the strongest acid of the hydrohalides.
- HI(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + I−(aq) Ka ≈ 1010
- HBr(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Br−(aq) Ka ≈ 109
- HCl(g) + H2O(l) → H3O+(aq) + Cl−(aq) Ka ≈ 106
Synthesis
[edit]The industrial preparation of HI involves the reaction of I2 with hydrazine, which also yields nitrogen gas:[7]
- 2 I2 + N2H4 → 4 HI + N2
When performed in water, the HI must be distilled.
HI can also be distilled from a solution of NaI or other alkali iodide in concentrated phosphoric acid (note that concentrated sulfuric acid will not work for acidifying iodides, as it will oxidize the iodide to elemental iodine).
Another way HI may be prepared is by bubbling hydrogen sulfide steam through an aqueous solution of iodine, forming hydroiodic acid (which is distilled) and elemental sulfur (this is filtered):[8]
- H2S + I2 → 2 HI + S
Additionally, HI can be prepared by simply combining H2 and I2: This is a reversible reaction (using conditions 250°C)
- H2 + I2 → 2 HI
This method is usually employed to generate high-purity samples.
For many years, this reaction was considered to involve a simple bimolecular reaction between molecules of H2 and I2. However, when a mixture of the gases is irradiated with the wavelength of light equal to the dissociation energy of I2, about 578 nm, the rate increases significantly. This supports a mechanism whereby I2 first dissociates into 2 iodine atoms, which each attach themselves to a side of an H2 molecule and break the H−H bond:[9]
- H2 + I2 + (578 nm radiation) → H2 + 2I → I···H···H···I → 2HI
In the laboratory, another method involves hydrolysis of PI3, the iodine analog of PBr3. In this method, I2 reacts with phosphorus to create phosphorus triiodide, which then reacts with water to form HI and phosphorous acid:
- 3 I2 + 2 P + 6 H2O → 2 PI3 + 6 H2O → 6 HI + 2 H3PO3
Key reactions and applications
[edit]Solutions of hydrogen iodide are easily oxidized by air:
- 4 HI + O2 → 2 H2O + 2 I2
- HI + I2 ⇌ HI3[10]
HI3 is dark brown in color, which makes aged solutions of HI often appear dark brown.
Like HBr and HCl, HI adds to alkenes:[11]
- HI + H2C=CH2 → H3CCH2I
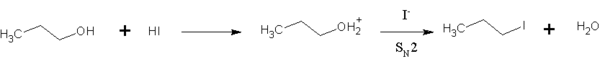
HI is also used in organic chemistry to convert primary alcohols into alkyl iodides.[12] This reaction is an SN2 substitution, in which the iodide ion replaces the "activated" hydroxyl group (water):
HI is preferred over other hydrogen halides because the iodide ion is a much better nucleophile than bromide or chloride, so the reaction can take place at a reasonable rate without much heating. This reaction also occurs for secondary and tertiary alcohols, but substitution occurs via the SN1 pathway.
HI (or HBr) can also be used to cleave ethers into alkyl iodides and alcohols, in a reaction similar to the substitution of alcohols. This type of cleavage is significant because it can be used to convert a chemically stable[12] and inert ether into more reactive species. In this example diethyl ether is split into ethanol and iodoethane:
The reaction is regioselective, as iodide tends to attack the less sterically hindered ether carbon. If an excess of HI is used, the alcohol formed in this reaction will be converted to a 2nd equivalent of alkyl iodide, as in the conversion of primary alcohols into alkyl iodides.
HI is subject to the same Markovnikov and anti-Markovnikov guidelines as HCl and HBr.
Although harsh by modern standards, HI was commonly employed as a reducing agent early on in the history of organic chemistry. Chemists in the 19th century attempted to prepare cyclohexane by HI reduction of benzene at high temperatures, but instead isolated the rearranged product, methylcyclopentane (see the article on cyclohexane). As first reported by Kiliani,[13] hydroiodic acid reduction of sugars and other polyols results in the reductive cleavage of several or even all hydroxy groups, although often with poor yield and/or reproducibility.[14] In the case of benzyl alcohols and alcohols with α-carbonyl groups, reduction by HI can provide synthetically useful yields of the corresponding hydrocarbon product (ROH + 2HI → RH + H2O + I2).[11] This process can be made catalytic in HI using red phosphorus to reduce the formed I2.[15]
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ Bell, R.P. The Proton in Chemistry. 2nd ed., Cornell University Press, Ithaca, NY, 1973.
- ^ Trummal, A.; Lipping, L.; Kaljurand, I.; Koppel, I. A.; Leito, I. "Acidity of Strong Acids in Water and Dimethyl Sulfoxide" J. Phys. Chem. A. 2016, 120, 3663-3669. doi:10.1021/acs.jpca.6b02253
- ^ Raamat, E.; Kaupmees, K.; Ovsjannikov, G.; Trummal, A.; Kütt, A.; Saame, J.; Koppel, I.; Kaljurand, I.; Lipping, L.; Rodima, T.; Pihl, V.; Koppel, I. A.; Leito, I. "Acidities of strong neutral Brønsted acids in different media." J. Phys. Org. Chem. 2013, 26, 162-170. doi:10.1002/poc.2946
- ^ a b CRC handbook of chemistry and physics: a ready-reference book of chemical and physical data. William M. Haynes, David R. Lide, Thomas J. Bruno (2016-2017, 97th ed.). Boca Raton, Florida. 2016. ISBN 978-1-4987-5428-6. OCLC 930681942.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ Hydrogen iodide: toxicity
- ^ Holleman, A. F.; Wiberg, E. "Inorganic Chemistry" Academic Press: San Diego, 2001. ISBN 0-12-352651-5.
- ^ Greenwood, N. N. and A. Earnshaw. The Chemistry of the Elements. 2nd ed. Oxford: Butterworth-Heineman. p 809–815. 1997.
- ^ Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac (1815), "A Memoir on Iodine", Annals of Philosophy, 5: 101
- ^ Holleman, A. F. Wiberg, E. Inorganic Chemistry. San Diego: Academic Press. p. 371, 432–433. 2001.
- ^ Magnuson, J.A.; Wolfenden, J.H. (December 1, 1956). "Hydrogen Tri-iodide". Journal of Physical Chemistry. 60 (12): 1665–1666. doi:10.1021/j150546a021. Retrieved May 26, 2022.
- ^ a b Breton, G. W., P. J. Kropp, P. J.; Harvey, R. G. "Hydrogen Iodide" in Encyclopedia of Reagents for Organic Synthesis (Ed: L. Paquette) 2004, J. Wiley & Sons, New York. doi:10.1002/047084289X.
- ^ a b Bruice, Paula Yurkanis. Organic Chemistry 4th ed. Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, N. J, 2003 p. 438–439, 452.
- ^ Kiliani, Heinrich (1886-01-01). "Ueber die Constitution der Dextrosecarbonsäure". Berichte der Deutschen Chemischen Gesellschaft. 19 (1): 1128–1130. doi:10.1002/cber.188601901251. ISSN 1099-0682.
- ^ Perlin, A. S.; Purves, C. B. (1953-03-01). "Kiliani's Reduction of Glucose and Fructose Cyanohydrins to the Corresponding Heptanoic Acids and Lactones". Canadian Journal of Chemistry. 31 (3): 227–236. doi:10.1139/v53-033. ISSN 0008-4042.
- ^ Dobmeier, Michael; Herrmann, Josef M; Lenoir, Dieter; König, Burkhard (2012-03-02). "Reduction of benzylic alcohols and α-hydroxycarbonyl compounds by hydriodic acid in a biphasic reaction medium". Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry. 8 (1): 330–336. doi:10.3762/bjoc.8.36. PMC 3302097. PMID 22423302.