This article needs additional citations for verification. (October 2021) |
| Otitis | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Specialty | ENT surgery |
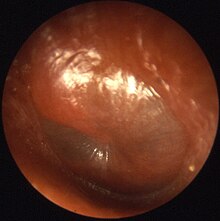
Otitis is a general term for inflammation in ear or ear infection, inner ear infection, middle ear infection of the ear, in both humans and other animals. When infection is present, it may be viral or bacterial.[1][2] When inflammation is present due to fluid build up in the middle ear and infection is not present it is considered Otitis media with effusion.[3] It is subdivided into the following:
- Otitis externa, external otitis, involves inflammation (either infectious or non-infectious) of the external auditory canal, sometimes extending to the pinna or tragus.[4] Otitis externa can be acute or chronic. It can be fungal or bacterial. The most common aetiology of acute otitis externa is bacterial infection,[5] while chronic cases are often associated with underlying skin diseases such as eczema or psoriasis.[6] A third form, malignant otitis externa, or necrotising otitis externa, is a potentially life-threatening, invasive infection of the external auditory canal and skull.[7] Usually associated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection, this form typically occurs in older people with diabetes mellitus, or immunocompromised people.[7] Otomycosis is the fungal form of Otitis Externa that is more common in coastal regions.
- Otitis media, or middle ear infection, involves the middle ear. In otitis media, the ear is infected or clogged with fluid behind the ear drum, in the normally air-filled middle-ear space. This is the most common infection and very common in babies younger than 6 months. This condition sometimes requires a surgical procedure called myringotomy and tube insertion.
- Otitis interna, or labyrinthitis, involves the inner ear. The inner ear includes sensory organs for balance and hearing. When the inner ear is inflamed, vertigo is a common symptom. Other symptoms in adults include pain and drainage from ear or problems with hearing.[8] Symptoms in children can include excessive crying, touching at ears, drainage, and fever.[8]
Treatment can range from increasing fluids and over-the-counter medicine to manage symptoms to antibiotics prescribed by medical providers.[9]
References
[edit]- ^ "Ear Infection (middle ear)". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved November 25, 2021.
- ^ "Otitis". Medlineplus.gov. Retrieved 18 March 2023.
- ^ "Otitis media with effusion". MedlinePlus. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved November 25, 2021.
- ^ Medina-Blasini, Yiraima; Sharman, Tariq (2022), "Otitis Externa", StatPearls, Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing, PMID 32310515, retrieved 2023-01-21
- ^ Schaefer, Paul; Baugh, Reginald F. (2012-12-01). "Acute otitis externa: an update". American Family Physician. 86 (11): 1055–1061. ISSN 1532-0650. PMID 23198673.
- ^ Wiegand, Susanne; Berner, Reinhard; Schneider, Antonius; Lundershausen, Ellen; Dietz, Andreas (2019-03-29). "Otitis Externa". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 116 (13): 224–234. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2019.0224. ISSN 1866-0452. PMC 6522672. PMID 31064650.
- ^ a b Treviño González, José Luis; Reyes Suárez, Laura Lisset; Hernández de León, Jesús Eduardo (2021). "Malignant otitis externa: An updated review". American Journal of Otolaryngology. 42 (2): 102894. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102894. ISSN 1532-818X. PMID 33429178. S2CID 231585754.
- ^ a b "Otitis". Mayo Clinic. Retrieved November 25, 2021.
- ^ "CDC Ear Infection Treatment". CDC. Retrieved November 25, 2021.