| Part of the LGBTQ rights series |
|
|
As of 27 June 2024, 423 municipalities and 30 prefectures in Japan have established a "partnership oath system" (Japanese: パートナーシップ宣誓制度, pātonāshippu sensei seido, pronounced [paːtonaːɕippɯ senseː seːdo]), also known as "partnership certification system" (パートナーシップ証明制度, pātonāshippu shōmei seido), which provides same-sex (and, in some jurisdictions, common-law opposite-sex) couples with some limited benefits.
The couple is issued a special certificate which may be useful in matters such as housing, hospital visitation rights and consenting to surgery for a partner.[1][2] However, the system is not legally binding and there is no legal obligation on landlords or hospitals to honour the couples' rights even if presented with a certificate, though cities have encouraged companies, hospitals and landlords to recognize the certificate.[3] The various benefits provided by the system are also very limited in comparison to those granted to married couples; same-sex couples cannot inherit the estate and property of a deceased partner or attend the funeral of a deceased partner for instance. Partners must meet certain requirements, including living in the municipality or prefecture, being older than 20 years of age, and not having a spouse or another partner. In some jurisdictions, the children and other close relatives of a partnered couple may opt to be recognized in the partnership oath.
Municipal partnership systems
[edit]On April 1, 2015, Shibuya in central Tokyo announced it would offer same-sex couples special "partnership certificates". While these licenses are not legally recognized as marriage certificates, they may be used in civil matters such as hospital visitation rights and housing.[4][5] The Shibuya city office began accepting applications on 28 October 2015.[6] In response to this action by the Shibuya city office, the "Special Committee to Protect Family Ties" (家族の絆を守る特命委員会, kazoku no kizuna wo mamoru tokumei iinkai) of the federal ruling Liberal Democratic Party was formed in March 2015 to discuss the matter. An officer from the Ministry of Justice who was invited to comment stated that the action by Shibuya is legal because the certificate issued is not a marriage certificate and the current Japanese legal code does not prohibit the "partnership" of same-sex couples.[7] In July 2015, Setagaya announced it would be joining Shibuya in issuing partnership certificates from 5 November.[1][8][6] In November 2015, the special city of Takarazuka announced it would issue partnership certificates to same-sex couples beginning on 1 June 2016.[9][10] In December 2015, the city of Iga in Mie Prefecture made a similar announcement, with certificates starting on 1 April 2016,[2][11][12] and on 22 February 2016, Naha, the capital of Okinawa Prefecture, announced it would begin issuing partnership certificates to same-sex couples on 8 July 2016.[13][14]
In April 2016, an LGBT rights group began a campaign for the official recognition of same-sex couples in Sapporo, the capital of Hokkaido Prefecture. The group took its petition to the Sapporo City Government in June 2016.[15] In December 2016, officials announced that Sapporo planned to draw up guidelines by March 2017.[16] In March, the City Government announced that partnership certificates would be issued to couples beginning on 1 June 2017. While the certificates hold no legal meaning, some insurance companies use them to allow same-sex partners to be added as beneficiaries. According to the city, about 1,500 people expressed opinions welcoming the program, while some opposed it.[17][18] Sapporo became the first designated city in Japan to establish a partnership system.[19] On 14 February 2018, the Fukuoka city office announced plans to start issuing partnership certificates to same-sex and different-sex couples from 2 April 2018.[20][21] Osaka followed suit on 9 July 2018,[22] and Chiba on 29 January 2019.[23][24][25] Nakano began offering partnership certificates on 20 August 2018. Couples can receive notarized documentation recognizing a delegation agreement for medical treatment and nursing care, property management and other areas in which married couples share responsibility.[26]
The number of cities which have established a partnership registry has steadily increased in the years since. 21 cities established a same-sex partnership system in 2019, notably Kitakyushu, Kumamoto, Miyazaki,[27] Nagasaki,[28] Sakai, Yokohama,[29] and Yokosuka. 36 more cities followed suit in 2020, including Hamamatsu, Kawasaki, Kyoto, Minato, Nara, Niigata, Okayama, Sagamihara, Saitama, and Takamatsu. 69 more cities followed in 2021, notably Adachi, Chigasaki, Fujisawa, Funabashi, Hiroshima,[30] Kanazawa, Kōchi, Koshigaya, Nishinomiya, and Toyota.[31] 107 cities established a partnership system in 2022, including Akita, Kagoshima, Nagano, Nagoya, and Shizuoka, and 106 cities in 2023, including Kobe, Kashiwa, Morioka, Ōita, Matsudo, Ichikawa, Machida and Fujisawa. On 1 April 2023, Kagawa became the first prefecture in which all municipalities had created their own registries, despite lacking a prefecture-wide registry;[32] Kanagawa became the second by 1 July 2023.
Prefectural partnership systems
[edit]
In January 2019, the Government of Ibaraki Prefecture announced it was considering introducing a partnership system for same-sex couples in April 2019.[33][34][35] In March 2019, Governor Kazuhiko Ōigawa expressed his personal support for the introduction of such a scheme.[36] The Ibaraki Prefectural Assembly began examing legislation to this effect in June 2019.[37] The prefecture has offered partnership certificates since July 1, 2019, which made it the first prefecture to do so.[38][39] Eight days later, Mito, the prefectural capital, announced that couples who are in the possession of the prefecture's certificates would be eligible to move into the municipality's public housing facilities, starting in August 2019.[40]
On 15 January 2020, Osaka Prefecture announced it would start a partnership system on January 22.[41] Governor Hirofumi Yoshimura said in a statement that "we should aim for a society where one can live as themselves". The first couple to receive a certificate were Shuji Yamada and Shigeo Hiruda on 31 January. The certificate allows couples to apply to move into prefectural housing and consent to surgery, among other limited benefits. Five cities in Osaka had already established such a system before it was extended to the entire prefecture.[42] Gunma Prefecture announced on 5 November 2020 that it would introduce a partnership system by the end of the year. The system would provide same-sex couples with some limited recognition, including the right to move into prefectural housing and visit each other in hospitals. Governor Ichita Yamamoto said he hoped the move would "send a positive message" and "promote diversity".[43] On 17 December, Yamamoto announced the system would be established on 21 December.[44] The first certificate was issued to couple Saori Tanaka and Hisanagi Makita in Shibukawa on 24 December.[45]
On 20 November 2020, Governor Eikei Suzuki of Mie Prefecture announced his intention to introduce a partnership system before the end of the year.[46] The system was introduced on 1 September 2021, with the first couple issued a certificate that same day in Tsu.[47][48] Saga Prefecture started its partnership oath system a few days earlier, on 27 August 2021.[49][50] Governor Yoshinori Yamaguchi praised the move.[51] In November 2021, the government of Aomori Prefecture announced its intention to introduce a partnership system on 7 February 2022.[52] A partnership oath system has also been in effect in Akita and Fukuoka prefectures since 1 April 2022.[53][54] On 15 February 2022, Governor Tomikazu Fukuda of Tochigi Prefecture announced he would introduce a partnership system in fall 2022;[55] it was established on 1 September 2022.[56]
On 7 June 2021, the General Affairs Committee of the Tokyo Metropolitan Assembly unanimously accepted a petition, launched by LGBT activists and signed by 18,000 people, to establish a partnership system in Tokyo Metropolis.[57] Governor Yuriko Koike expressed her support for the move, stating it would "respect the human rights of sexual minorities and promote the understanding of Tokyo citizens regarding diversity".[58] The bill was enacted by the Metropolitan Assembly on 15 June 2022. It calls on businesses and other entities to treat same-sex partnerships as equal to married couples, allowing couples to access family-use housing and the right to visit their partners in hospital. At least one partner must be resident in Tokyo or a commuter for work. It came into force on 1 November,[59] with applications being accepted from 10 October,[60] making Tokyo the tenth prefecture to do so.
Governor Hajime Furuta of Gifu Prefecture announced on 10 December 2020 that he was considering establishing a partnership system in the prefecture.[61] Governor Heita Kawakatsu of Shizuoka Prefecture announced on 1 September 2021 that he was also considering it by the end of 2022.[62] The Deputy Governor of Toyama Prefecture voiced the same in December 2021.[63] Both Shizuoka and Toyama prefectures established a partnership system on 1 March 2023.
Overall, the number of prefectures which have established a partnership registry has slowly increased over the years. 1 was established in 2019 (Ibaraki), 2 in 2020 (Osaka, Gunma), 2 in 2021 (Saga, Mie), 5 in 2022 (Aomori, Akita, Fukuoka, Tochigi, Tokyo), 9 in 2023 (Shizuoka, Toyama, Nagano, Gifu, Kagawa, Shimane, Tottori, Fukui, Yamanashi), and 11 in 2024 so far (Yamagata, Wakayama, Aichi, Hyogo, Nara, Oita, Tokushima, Yamaguchi, Shiga, Fukushima, Niigata). The establishment of prefectural systems has often not precluded the subsequent establishments of municipal systems within the same prefecture.
Mutual recognition of certificates
[edit]Between cities
[edit]On October 30, 2019, the cities of Fukuoka and Kumamoto announced they would recognize each other's partnership certificates effective immediately. This marked the first time that two or more jurisdictions in Japan had begun recognizing each other's certificates, easing recognition for same-sex couples. This means that if a same-sex couple with a certificate moves between both cities they need not reapply for a certificate in their new city.[64] Since 1 April 2020, certificates from Kitakyushu and Koga are also recognized between the four cities.[65][66] Certificates from Okayama, Nichinan,[67] and Karatsu are also recognised in Fukuoka.[68]
On December 2, 2019, the mayor of Yokosuka announced his intention to establish a joint recognition scheme with the fellow Kanagawa cities of Zushi and Kamakura, taking effect on 1 April 2020.[69] Hayama joined the scheme on 1 July 2020, and Miura joined on 1 January 2021.[70] In July 2020, Okayama and Sōja agreed to mutually recognize their certificates and eliminate the need for new procedures when couples move between the two cities. Okayama reached a similar agreement with Fukuoka in November 2020 and Hiroshima in January 2021.[67] Hiroshima and Akitakata also mutually recognize their certificates.[71] The cities of Katano and Hirakata decided to recognize each other's certificates in June 2021.[72] Since then, numerous other cities have also established such mutual recognition schemes. On 1 February 2022, a similar agreement took effect between Chigasaki, Fujisawa and Samukawa.[73]
The cities of Chiba and Yokohama made a similar recognition agreement in January 2021, effective on 1 February 2021.[74] In early April 2021, the cities and towns of Amagasaki, Ashiya, Inagawa, Itami, Kawanishi, Nishinomiya, Sanda and Takarazuka, all in Hyōgo Prefecture, agreed to recognize each other's certificates.[75] Likewise, in May 2021, 12 municipalities in Tokyo, Adachi, Bunkyō, Edogawa, Fuchū, Koganei, Kokubunji, Kunitachi, Minato, Nakano, Setagaya, Shibuya and Toshima, agreed to mutually recognize each other's certificates.[76] The cities of Chiba, Funabashi, Ichikawa, Matsudo, Kashiwa, and Narashino, all in Chiba prefecture, signed a mutual recognition agreement on July 11, 2023.[77]
Eighteen cities in Aichi Prefecture signed an agreement to recognize each other's partnership certificates on October 17, 2023.[78] On October 29, 2023, the Kanagawa Prefecture cities of Fujisawa, Yokohama and Isehara signed an agreement.[79]
Between prefectures
[edit]On 18 August 2022, Saga and Ibaraki prefectures announced they would recognize each other's partnership certificates, becoming the first prefectures to do so.[80] Saga Prefecture completed a similar agreement with Fukuoka on 24 November.[81] On 20 December, mutual recognition was established between Ibaraki, Tochigi and Gunma prefectures.[82] On 31 January 2023, Ibaraki signed an agreement with Mie.[83] On September 4, 2023, Ibaraki signed an agreement with Toyama.[84] On February 22, 2024, an agreement was signed between Mie and Gifu prefectures.[85]
Between prefectures and internal municipalities
[edit]In March 2020, Iwate Prefecture passed a law to recognize partnership registries created by municipalities within the prefecture for purpose of benefits, despite not having a prefecture-level registry at the time.[86]
Upon establishing its own partnership registry in November 2022, Tokyo Metropolis mutually recognized all partnership registries in Tokyo's wards and cities.[87]
Between prefectures and external municipalities
[edit]On October 30, 2023, Ibaraki Prefecture and the city of Saitama, Saitama Prefecture signed an agreement to recognize each other's partnership registries.[88]
Partnership System Inter-Municipality Collaboration Network
[edit]On April 1, 2024, the governments of Osaka, Kyoto, and Hyogo prefectures established an Partnership System Inter-Municipality Collaboration Network (Japanese: パートナーシップ制度自治体間連携ネットワーク, romanized: Pātonāshippu seido jichitai-kan renkei nettowāku) as a common mutual agreement through which signatory jurisdictions, including prefectures, cities, towns and villages, may recognize and process each other's partnership registries for purposes of travel or relocation, eliminating the need for returning a certificate to a former jurisdiction of residence, the need to submit documentary proof of non-marriage and the need to repeat the oath.[89] The Network agreement requires those relocating between member jurisdictions to submit a completed Declaration Continuation Form, proof of a certificate from their prior residence, proof of a change of address for both partners and personal identification. On October 23, 2024, 17 prefectures (Aichi, Akita, Aomori, Fukui, Fukuoka, Gifu, Gunma, Ibaraki, Mie, Nara, Niigata, Oita, Saga, Shiga, Toyama, Wakayama and Yamagata) and 150 cities, towns and villages announced their registries' accession to the network agreement effective November 1.[90][91][92][93][94][95][96][97]
The governments of Fukushima, Kagawa, Nagano, Shimane, Shizuoka, Tochigi, Tokushima, Tokyo, Tottori, Yamaguchi and Yamanashi prefectures, all of which have registries, have yet to announce their accession.
List of partnership oath systems
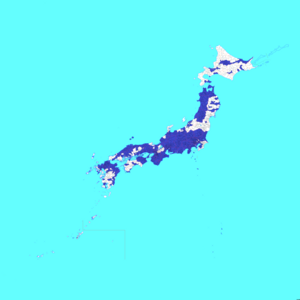
[edit]As of 27 June 2024, the following 423 municipalities and 30 prefectures have established a same-sex partnership oath system, comprising about 84% of the Japanese population. 4 other jurisdictions have policies which have yet to be dated. Prefectures are bolded. An asterisk (*) indicates that familyship registration is also available.
Future partnership systems
[edit]| 2024 | ||
|---|---|---|
| TBD | ||
| TBD |
Measures to allow partnership certificates have been proposed in numerous areas, including the prefectures of Ishikawa,[568] Iwate[569] and Kagoshima;[570] several administrative wards in Tokyo, such as Chiyoda, Chūō, Katsushika, Kōtō,[571] Nerima, Shinjuku, and Taitō; and the cities of Tōgō,[572] Hachinohe,[573] Matsuyama,[574] Fukuyama,[575] Kumano,[575] Onomichi,[575] Saka,[575] Sera,[575] Azumino,[576] Nagayo,[577] Kamo,[578] Sado,[579][580] Tamano,[575] Itoman,[581] Okinawa,[581] Nago,[581] Nanjō,[582] Tomigusuku,[581] Fujieda,[583] Shimada,[584] Higashimurayama,[585] Nichinan, Yonago,[575] Toyama,[586] Hagi,[575] Hirao,[575] Iwakuni[575] and Shimonoseki.[575]
Family registration
[edit]Numerous other municipalities have also established a "partnership familyship system" (パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度, pātonāshippu famirīshippu seido). This system also recognises the children and in-laws of same-sex couples, and allows partners to make medical decisions for their child, and to pick up their children at schools and kindergartens (whereas previously only the biological parent was allowed to pick up the child). The first to establish this system was Akashi, Hyōgo in January 2021 followed by Tokushima in February 2021 and Adachi, Tokyo in April 2021.[587] Tokyo established a partnership system with a similar option in November 2022, becoming the first prefectural government to do so.
List of familyship registries
[edit]List of mutual recognition agreements
[edit]The following is a list of agreements of mutual recognition of partnership oath registries between jurisdictions (Japanese: パートナーシップ制度の相互利用連携, pātonāshippu seido no sōgo riyō renkei).
| 2019 | October 30 | Fukuoka and Kumamoto |
|---|---|---|
| December 2 | Yokosuka, Zushi and Kamakura (Kanagawa) | |
| 2020 | January 1 | Mihara and Hiroshima (Hiroshima) |
| March | Iwate Prefecture with all internal municipalities | |
| March 1 | Yokohama and Sagamihara (Kanagawa) | |
| April 1 | Fuchū (town) and Hiroshima (Hiroshima); Hatsukaichi and Hiroshima (Hiroshima) | |
| July | Okayama and Sōja (Okayama) | |
| July 1 | Yokosuka, Zushi, Kamakura and Hayama (Kanagawa) | |
| November | Okayama, Okayama and Fukuoka, Fukuoka | |
| October 1 | Fuchū (city) and Hiroshima (Hiroshima); Hiroshima and Kaita (Hiroshima) | |
| November 1 | Yokohama and Isehara (Kanagawa), Yokohama and Fujisawa (Kanagawa), | |
| December 1 | Yokohama and Yokosuka (Kanagawa) | |
| 2021 | January | Okayama, Okayama and Hiroshima, Hiroshima |
| January 1 | Yokosuka, Zushi, Kamakura, Hayama and Miura (Kanagawa); Hiroshima and Miyoshi (Hiroshima) | |
| February 1 | Yokohama, Kanagawa and Chiba, Chiba | |
| April | Amagasaki, Ashiya, Inagawa, Itami, Kawanishi, Nishinomiya, Sanda and Takarazuka (Hyogo) | |
| April 1 | Fukuoka, Fukuoka and Hiroshima, Hiroshima; Higashihiroshima and Hiroshima (Hiroshima) | |
| May | Adachi, Bunkyō, Edogawa, Fuchū, Koganei, Kokubunji, Kunitachi, Minato, Nakano, Setagaya, Shibuya and Toshima (Tokyo) | |
| June | Katano and Hirakata (Osaka) | |
| July | Chiba, Funabashi, Ichikawa, Matsudo, Kashiwa, and Narashino (Chiba) | |
| September 27 | Akitakata and Hiroshima (Hiroshima) | |
| 2022 | February 1 | Chigasaki, Fujisawa and Samukawa (Kanagawa) |
| August 18 | Saga Prefecture and Ibaraki Prefecture | |
| November | Tokyo Metropolis with all internal municipalities | |
| November 24 | Saga Prefecture and Fukuoka Prefecture | |
| December 20 | Ibaraki, Tochigi and Gunma prefectures | |
| 2023 | January 31 | Ibaraki Prefecture and Mie Prefecture |
| September 21 | Ibaraki Prefecture and Tochigi Prefecture | |
| October 29 | Fujisawa, Yokohama and Isehara (Kanagawa) | |
| October 30 | Ibaraki Prefecture and Saitama, Saitama | |
| 2024 | February 14 | Yamato, Ebina, Zama, and Ayase (Kanagawa)[605] |
| February 22 | Gifu Prefecture and Mie Prefecture | |
| March 1 | Kasugai, Komaki, Toyoyama (Aichi)[606] | |
| April | Kyoto with Fukuchiyama City, Ayabe City, Kameoka City, Muko City, Nagaokakyo City, Nantan City, Oyamazaki Town (Kyoto); Osaka Prefecture, Osaka City, Sakai City, Ikeda (Osaka); Amagasaki City, Nishinomiya City, Ashiya City, Itami City, Takarazuka City, Kawanishi City, Sanda City, Tamba Sasayama City, Tamba City, Awaji City, Inagawa Town (Hyogo);[607][608] Abashiri, Shari, Kiyosato, Koshimizu, Ōzora, Kushiro, and Muroran (Hokkaido).[609] | |
| September 4 | Okayama City, Soja City, Kasaoka City, Setouchi City, Bizen City, Akaiwa City, Ibara City, Maniwa City, Mimasaka City, Hayashima Town, and Wake Town (Okayama)[610] |
Extension to opposite-sex relationships
[edit]Some jurisdictions extend partnership oath registries to common-law marriages, in which opposite-sex couples enter live-in relationships without civil registration of marriage. Such protections allow for certification of opposite-sex couples who do not wish to be subject to several mandates regarding marriage, including the legal requirement to share the husband's surname. Tokyo became the first prefecture-level jurisdiction to allow common-law couples to enter partnerships. In April 2024, Aichi Prefecture became the first prefecture-level familyship system to be extended to opposite-sex couples.[611]
Statistics
[edit]The first couple to receive a partnership certificate were Koyuki Higashi and Hiroko Masuhara in Shibuya on 5 November 2015. They were personally congratulated by Mayor Ken Hasebe.[6] Later that day, Setagaya issued certificates to seven couples.[6] By April 2017, 17 same-sex partnership certificates had been issued in Shibuya.[612]
319 certificates had been issued in Japan by November 2018.[613][614] This had increased to 617 by October 2019,[615] to 1,052 by June 2020,[616] to 1,301 by November 2020,[617] to 2,018 by July 2021, and to 3,168 by June 2022, with most being issued in Osaka Prefecture followed by Tokyo, Kanagawa and Chiba prefectures.
As of 1 November 2023, residents in 890 total municipalities are eligible to register their partnerships with a municipal or prefecture government's registry, out of 1,719 total municipalities. All 20 designated cities and 28 out of 62 core cities offer municipal partnership registries, while 18 other core cities are covered by existing prefectural registries and 3 others are set to be covered by 2024. 26 of 47 prefectural capitals offer municipal partnership registries, while 11 other prefectural capitals or seats of government are covered by prefectural partnership registries.
| Partnership statistics as of June 2022 |
 |
Private-sector partnerships
[edit]As a private sector response to the lack of national recognition of same-sex partnerships, the Famiee Project created a digital blockchain-secured partnership registry in 2019. In order to receive a Famiee certificate, the couple must apply via a mobile app and will receive a digital certificate to be used as proof of familial status.[618] The Famiee Project received the backing of at least 17 companies who will recognize the digital partnership certificate and treat a couple the same as a different-sex couple for banking and insurance purposes. The partnerships are not currently recognized by the Government of Japan, but aim to create pressure from the private sector for political action to expand LGBT rights in the country.[619]
See also
[edit]- Recognition of same-sex unions in Japan
- Homosexuality in Japan
- Marriage in Japan
- LGBT rights in Japan
- Recognition of same-sex unions in Asia
References
[edit]- ^ a b "Tokyo's Setagaya Ward to begin legally recognizing same-sex partnerships". Rocket News 24. 31 July 2015.
- ^ a b Williams, Joe (December 26, 2015). "Another Japanese city to recognise same-sex relationships". Pink News. Retrieved December 26, 2015.
- ^ "Japanese Court Puts Same-Sex Marriage on the Nation's Agenda". www.cfr.org. 30 March 2021.
- ^ Master Blaster. "Japan government hard at work trying to prevent Shibuya Ward approving same-sex marriages". Rocket News 24.
- ^ "The First Place In East Asia To Welcome Same-Sex Marriage". NPR.org. 11 May 2015. Retrieved 30 June 2015.
- ^ a b c d "Tokyo's Shibuya and Setagaya wards issue first same-sex partnership papers". The Japan Times. 5 November 2015. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ 二階堂, 友紀 (26 March 2015). "渋谷区の「同性婚」条例案、自民内から異論相次ぐ". 朝日新聞社. Archived from the original on 15 May 2019. Retrieved 26 March 2015.
- ^ "Tokyo's Setagaya Ward to begin legally recognizing same-sex partnerships". Japan Today. 31 July 2015. Retrieved 30 September 2015.
- ^ Wee, Darren (December 1, 2015). "Takarazuka first city in Japan's Kansai region to certify gay couples". Gay Star News. Archived from the original on July 30, 2019. Retrieved January 9, 2017.
- ^ "Takarazuka becomes fourth Japanese municipality to recognize same-sex partnerships". RocketNews24. 1 June 2016.
- ^ Masanori, Hiuchi (1 March 2016). "City in Mie Prefecture to recognize same-sex partnerships in April". Asahi Shimbun. Archived from the original on 2016-03-02. Retrieved 2016-03-12.
- ^ "Third Japanese municipality recognizes same-sex unions". The Japan Times. February 17, 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ "Naha starts system to certify same-sex marriages". The Japan Times. 8 July 2016.
- ^ Wilson, Scott (7 July 2016). "Okinawa's capital city Naha officially recognizes same-sex partnerships". RocketNews24.
- ^ Sekine, Kazuhiro (8 April 2016). "Sapporo LGBT activists to take fight for equality to city officials". Asahi Shimbun.
- ^ "Sapporo to join other cities in recognizing same-sex partnerships as marriages". The Japan Times. 22 December 2016. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ "Sapporo to become first major city to recognize LGBT couples in June". The Japan Times. 21 March 2017. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ "Sapporo will be Japan's first major city to recognise same-sex relationships". Gay Times. March 22, 2017. Archived from the original on March 22, 2017. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ "Sapporo first major city in Japan to issue certificates recognizing same-sex couples". The Japan Times. June 2017. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ "Fukuoka city to become Japan's seventh municipality to recognize LGBT couples". The Japan Times. 14 February 2018.
- ^ "Fukuoka begins official recognition of LGBT partnerships". The Japan Times. April 2, 2018.
- ^ "Osaka to start recognizing LGBT couples from July". Kyodo News. 28 June 2018.
- ^ "Chiba to issue nonbinding certificates recognizing same-sex and common-law couples". The Japan Times. 25 August 2018.
- ^ "Chiba 1st Japan city to certify both common-law marriage and LGBT couples". Kyodo News. 29 January 2019.
- ^ 「世間の価値観変えたい」 千葉市パートナーシップ宣誓制度施行 市民や事業者にも理解を (in Japanese). Yahoo! Japan. 30 January 2019.
- ^ "Tokyo's Nakano Ward to offer partnership certificates to same-sex couples this summer". Mainichi Daily News. The Mainichi. 10 May 2018.
- ^ a b "宮崎市6月にも導入 LGBTパートナーシップ". Miyanichi Press. 24 February 2019.
- ^ a b "ートナーシップ宣誓制度」9月2日開始 長崎市、県内初の導入". Nagasaki Shimbun (in Japanese). 20 August 2019.
- ^ a b "パートナーシップ制度 市が年内導入へ". townnews.co.jp (in Japanese). 2 October 2019.
- ^ a b "「パートナー制度」を相互利用 岡山市と広島市、20年度". Tokyo Shimbun (in Japanese). 7 February 2020. Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ a b "三重県パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました" (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 September 2021.
- ^ "香川の全市町、パートナーシップ制度導入完了 「当事者どこにでも」". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-04-02.
- ^ "茨城県がパートナーシップ制度導入を検討 LGBTなど対象 都道府県初" (in Japanese). Mainichi Shimbun. 30 January 2019.
- ^ 茨城県が「パートナーシップ制度」導入めざす 都道府県で初めて、同性カップルの権利後押し (in Japanese). HuffPost Japan. 30 January 2019.
- ^ "Ibaraki to consider LGBT rights bill". The Japan News. 31 January 2019. Archived from the original on 1 February 2019. Retrieved 31 January 2019.
- ^ パートナーシップ導入へ条例改正案可決 茨城県議会. The Sankei News (in Japanese). 25 March 2019. Archived from the original on 30 March 2019. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ "LGBTパートナー制度など報告書案 茨城県の勉強会". Nikkei Asian Review (in Japanese). 6 June 2019.
- ^ Glauert, Rik (24 June 2019). "In a first, entire prefecture in Japan will register same-sex partnerships". Gay Star News. Archived from the original on 30 July 2019. Retrieved 24 June 2019.
- ^ "茨城県が「パートナーシップ宣誓」受け付け開始 都道府県で初". Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 1 July 2019.
- ^ "同性カップル市営住宅OK 水戸市が方針 県の宣誓制度で : 地域". Yomiuri Shimbun (in Japanese). 9 July 2019. Archived from the original on 2019-07-10. Retrieved 2019-07-10.
- ^ "「大阪府パートナーシップ宣誓証明制度」を開始します". 大阪府 (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2020-01-19. Retrieved 2020-01-16.
- ^ "大阪府で同性パートナーシップ証明制度がスタート、第1号のゲイカップル「いつか法的権利を」". OutJapan (in Japanese). 1 February 2020.
- ^ "LGBTカップルに群馬県がパートナーシップ制導入へ 茨城、大阪に続き3例目". Microsoft News (in Japanese). 6 November 2020.
- ^ "「ぐんまパートナーシップ宣誓制度」21日から導入". Yomiuri Shimbun (in Japanese). 18 December 2020. Archived from the original on 18 December 2020. Retrieved 17 December 2020.
- ^ "LGBTを公認 群馬県のパートナーシップ制度で初宣誓、笑顔で「大きな一歩」". Jōmō Shimbun (in Japanese). 25 December 2020.
- ^ "三重県が同性カップルを公的に認める「パートナーシップ制度」導入へ". Chunichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 20 November 2020. Archived from the original on 20 November 2020. Retrieved 21 November 2020.
- ^ "三重県パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました" (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 September 2021.
- ^ "第1号カップル「家族になれて幸せ」 三重で「パートナー制度」開始". Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese). 2 September 2021.
- ^ "佐賀県全体でのパートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 September 2021.
- ^ "佐賀県、パートナー制度開始 性的少数者カップルを婚姻相当と公認 九州初". Yahoo! Japan (in Japanese). 28 August 2021. Archived from the original on 4 September 2021. Retrieved 4 September 2021.
- ^ "佐賀県、性的少数カップルの認定制度 県単位では九州初". Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese). 27 August 2021.
- ^ "青森県パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Aomori Prefecture. 4 February 2022. Retrieved 7 February 2022.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度、福岡県が4月導入の方針 住宅確保の一助へ" (in Japanese). 朝日新聞. 23 January 2022. Retrieved 23 January 2022.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ証明制度」に事実婚含まず"(秋田県)" (in Japanese). YAHOO! Japan. 24 February 2022. Archived from the original on 2 March 2022. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "性的少数者カップルに公的証明書を発行 栃木県が秋に制度導入へ" (in Japanese). 朝日新聞. 16 February 2022. Retrieved 16 February 2022.
- ^ "とちぎパートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Tochigi Prefecture. 1 August 2022. Retrieved 1 September 2022.
- ^ "都議会 パートナーシップ制度創設の請願を全会一致で採択". NHK (in Japanese). 7 June 2021.
- ^ Reynolds, Isabel (7 December 2021). "Tokyo to introduce a same-sex partner system". The Japan Times.
- ^ "Tokyo Assembly Enacts Same-Sex Partnership System". Nippon.com. Tokyo. 15 June 2022.
- ^ "Tokyo adopts 'partnership' status for same-sex couples". Le Monde.fr. 2022-10-10. Retrieved 2022-10-12.
- ^ "同性パートナー制検討 岐阜県、導入時期など議論". Gifu Shimbun (in Japanese). 11 December 2020. Archived from the original on 14 December 2020. Retrieved 13 December 2020.
- ^ "パートナー制度 全県導入方針 静岡県議会一般質問、川勝知事答弁" (in Japanese). Anata no Shizuoka Shinbun. Archived from the original on 2 October 2021. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度導入を検討へ 富山県(北日本放送)". Yahoo!ニュース (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2021-12-04. Retrieved 2021-12-04.
- ^ "LGBTカップルを相互承認 ("LGBT couples mutually approved"". NHK.or.jp (in Japanese). 30 October 2019.
- ^ "北九州市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.kitakyushu.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "北九州市、LGBT制度で連携へ パートナーシップ宣誓 先に導入の福岡・熊本両市と /福岡". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2019-11-13.
- ^ a b "パートナーシップ宣誓制度自治体間相互利用". www.city.okayama.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "これからのMICEを担う学生を応援するスクール開講!!~学生が世界水泳選手権を体験し盛り上げます~(経済観光文化局MICE推進課) (2,356kbyte)" (PDF) (in Japanese). Fukuoka City. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "2019年12月議会・一般質問". hide-fujino.com (in Japanese). 2 December 2019.
- ^ "三浦市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について". www.city.miura.kanagawa.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ a b "安芸高田市パートナーシップ制度はじまります!" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "「パートナー制度」相互利用 枚方・交野市協定". Yomiuri Shimbun (in Japanese). 5 June 2021. Archived from the original on 9 July 2021. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- ^ 藤沢市. "藤沢市は、茅ヶ崎市及び寒川町と「パートナーシップ宣誓制度に係る自治体間連携に関する協定」を締結しました". 藤沢市 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2021-12-22.
- ^ "他の自治体との都市間連携". City of Yokohama (in Japanese).
- ^ "同性カップルの「パートナーシップ制度」、転居時の手続き簡単に 阪神間7市1町が連携". Kobe Shimbun (in Japanese). 6 April 2021.
- ^ "府中市はじめ都内12区市で「同性パートナーシップ制度」を導入している自治体の交流組織を結成website=go2senkyo.com" (in Japanese). 20 May 2021.
- ^ 日本放送協会. "パートナーシップ制度で連携へ 千葉県内の6つの市が協定|NHK 千葉県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB. Retrieved 2023-07-26.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度、愛知18市町が連携へ 転居時の手続き簡素化". gooニュース (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-10-27.
- ^ "藤沢市、横浜市、伊勢原市「パートナーシップ宣誓制度に係る自治体間連携に関する協定」締結 | 湘南人". 湘南人 | 湘南エリアの最新ニュース・グルメ・イベント穴場情報満載! (in Japanese). 2023-10-29. Retrieved 2023-10-30.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」 茨城と佐賀が情報連携" (in Japanese). 日本経済新聞. 19 August 2022. Retrieved 19 August 2022.
- ^ "佐賀県とパートナーシップ宣誓制度に関する協定を締結します! - 福岡県庁ホームページ". www.pref.fukuoka.lg.jp. Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ^ "「いばらきパートナーシップ宣誓制度」の北関東3県自治体間連携の締結について|古河市公式ホームページ". www.city.ibaraki-koga.lg.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-01-30.
- ^ "三重県と茨城県が協定 パートナーシップ宣誓制度(伊勢新聞)". Yahoo!ニュース (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-02-04.
- ^ "茨城県と富山県の間で「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」の連携協定が締結されました - 種部恭子(タネベキョウコ) | 選挙ドットコム". 選挙ドットコム (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-09-21.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」相互連携など、取り組み確認 三重、岐阜両県知事の懇談会:中日新聞Web". 中日新聞Web (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-02-22.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度について". 岩手県 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ "都パートナーシップ宣誓制度 16区市と連携|東京都". www.metro.tokyo.lg.jp. Retrieved 2023-01-29.
- ^ "茨城県、パートナーシップ宣誓制度でさいたま市と連携". 日本経済新聞 (in Japanese). 2023-10-30. Retrieved 2023-10-30.
- ^ 大阪府. "パートナーシップ宣誓証明制度 自治体間連携について". 大阪府 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度自治体間連携ネットワークへ加入します - 愛知県". www.pref.aichi.jp. Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ 富山県. "パートナーシップ制度自治体間連携ネットワークへの参加について". 富山県 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度自治体間連携ネットワークへの加入及び青森県パートナーシップ宣誓制度の拡充します". 青森県庁ホームページ (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ "奈良県パートナーシップ制度/奈良県公式ホームページ". www.pref.nara.jp. Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度に関する連携を拡大します!~11月1日、全国169自治体と新たに連携開始~ - 福岡県庁ホームページ". www.pref.fukuoka.lg.jp. Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ "福井県パートナーシップ宣誓制度を実施しています。 | 福井県ホームページ". www.pref.fukui.lg.jp. Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ 山形県. "パートナーシップ宣誓証明制度の自治体間連携への参加について". 山形県 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ "滋賀県パートナーシップ宣誓制度 自治体間連携を開始します!|滋賀県ホームページ". 滋賀県ホームページ (in Japanese). 2024-10-23. Retrieved 2024-10-28.
- ^ Kita-Kantou (December 27, 2018). "LGBTパートナー認定、群馬・大泉町が来月導入" (in Japanese). Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ 同性パートナーシップ制度 江戸川区も導入. 日テレNEWS24 (in Japanese). 15 March 2019.
- ^ "府中市、LGBTパートナー認定 来年4月に" (in Japanese). November 29, 2018. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ 定例記者会見(平成31年2月). Hirakata-shi homepage (in Japanese). 1 March 2019.
- ^ "熊本市がパートナー公認へ LGBT、来年4月導入" (in Japanese). December 4, 2018. Archived from the original on April 2, 2019. Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ パートナーシップ制度、小田原市が4月導入 県内2例目. カナロコ (Kanaloco) (in Japanese). 22 February 2019. Archived from the original on 23 February 2019. Retrieved 23 February 2019.
- ^ 性的少数者カップル公認 横須賀市、小田原市が制度導入へ. カナロコ (Kanaloco) (in Japanese). 31 March 2019.
- ^ 堺市パートナーシップ宣誓制度. Sakai-shi homepage (in Japanese). 12 March 2019.
- ^ "LGBT「パートナー宣誓制度」創設へ 大阪府堺市で4月から". HuffPost Japan (in Japanese). 2 February 2019. Archived from the original on 7 February 2019. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- ^ 堺市も同性パートナー 4月導入、事実婚は含めず /大阪. Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 31 January 2019.
- ^ 同性カップル認定へ パートナーシップ制度、26日に条例案 /岡山. Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 20 February 2019.
- ^ 東京・豊島区がパートナー制度 条例制定、渋谷に続き全国2例目 (in Japanese). The Sankei News. 22 March 2019. Archived from the original on 3 April 2019. Retrieved 25 March 2019.
- ^ 性的少数者や事実婚、横須賀市も4月からパートナー制度. Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese). 14 February 2019.
- ^ Jimbun, Mainichi (September 19, 2018). "LGBTなど 豊島区も「パートナーシップ制度」導入へ" (in Japanese). Retrieved March 20, 2021.
- ^ 同性カップル、夫婦同等に 鹿沼市、県内初の宣誓制度 6月導入. Sankei Shimbun (in Japanese). 23 April 2019.
- ^ "Kitakyushu City starts partnership system from July 1st. "I would like to change from the administration first"". HuffPost. 11 June 2019.
- ^ 7月からパートナーシップ制度導入. Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 21 February 2019.
- ^ 西尾市パートナーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関する要綱 Archived 2019-09-06 at the Wayback Machine. city.nishio.aichi,jp
- ^ "同姓カップル認定 都市部から 長崎市「パートナーシップ制度」導入". Nishinippon Shinbun (in Japanese). 2 September 2019.
- ^ "三田市が同性カップル認定 制度導入は県内2例目". 神戸新聞NEXT (in Japanese). 13 October 2019.
- ^ "交野市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を実施". city.katano.osaka.jp. 22 November 2019.
- ^ "横浜市、パートナーシップ制度導入 LGBTや事実婚で". Nihon Keizai Shinbun (in Japanese). 13 November 2019.
- ^ "【11月19日発表】「大東市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」スタート!". city.daito.lg.jp (in Japanese). 19 November 2019. Archived from the original on 23 November 2019. Retrieved 23 November 2019.
- ^ "神奈川・鎌倉市、パートナーシップ制度を導入". 日本経済新聞 電子版 (in Japanese). 4 December 2019. Retrieved 2019-12-04.
- ^ "鎌倉市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.kamakura.kanagawa.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "三豊市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入します!". www.city.mitoyo.lg.jp (in Japanese). 2 December 2019.
- ^ "神戸新聞NEXT|阪神|性的少数者のパートナー制度 尼崎市、1組目の受領証交付". www.kobe-np.co.jp (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2020-01-12. Retrieved 2020-01-13.
- ^ "文京区パートナーシップ宣誓の取扱いについて" (PDF). city.bunkyo.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "LGBTカップル公認制度 浜松市、4月施行". Shizuoka Shimbun (in Japanese). 6 February 2020. Archived from the original on 12 February 2020. Retrieved 12 February 2020.
- ^ "LGBTカップル公認へ 浜松市、要綱制定を検討". Shizuoka Shimbun (in Japanese). 6 June 2019. Archived from the original on 10 June 2019. Retrieved 25 June 2019.
- ^ "LGBTパートナーシップ宣誓制度 木城町導入へMiyanichi" (in Japanese). 23 March 2020.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度、古賀市が来月導入 性的少数者カップル支援 /福岡". Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 3 March 2020.
- ^ "みなとマリアージュ制度をスタートします(制度の概要)". city.minato.tokyo.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "奈良市で「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」を導入". PR Times (in Japanese). 14 February 2020.
- ^ "新潟市で4月1日から同性パートナーシップ宣誓制度導入、北信越で初". OutJapan (in Japanese). 12 March 2020.
- ^ "「パートナー制度」4月導入". TownNews.com (in Japanese). 18 March 2020.
- ^ "LGBT「パートナーシップ制度」 さいたま市、4月1日開始". tokyo-np-co-jp (in Japanese). 20 December 2019. Archived from the original on 22 December 2019. Retrieved 22 December 2019.
- ^ "高松市が同性パートナーシップ証明制度導入を決定、三豊市でも年明けから". www.outjapan.co.jp (in Japanese). 4 December 2019.
- ^ "徳島市が4月から同性パートナーシップ証明制度を導入". OutJapan (in Japanese). 1 March 2020.
- ^ "性的少数者カップル公認へ 制度の概要など解説/大和郡山市が「市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」". 47NEWS (in Japanese). 23 March 2020.
- ^ "逗子市 「パートナー制度」導入 来月から 鎌倉、横須賀市と連携も". Tokyo Shimbun (in Japanese). 24 March 2020. Archived from the original on 25 March 2020. Retrieved 26 March 2020.
- ^ "川越市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". city.kawagoe.saitama.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度について". city.toyoake.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "同性パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.itami.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "同性カップルに証明書 「婚姻に準ずる」と認定へ". Kobe Shimbun (in Japanese). 13 May 2020.
- ^ "芦屋市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". city.ashiya.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "令和2年7月1日からパートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります!". town.hayama.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度 葉山町も20年度導入目指す". kanaloco.jp (in Japanese). 14 November 2019.
- ^ "いなべ市がパートナーシップ宣誓制度 条例案提出へ". Chunichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 27 May 2020.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度、川崎市が7月1日導入へ". Kanaloco (in Japanese). 16 June 2020.
- ^ "市民・企業から意見募集パートナーシップ宣誓制度案発表". TownNews.com (in Japanese). 17 April 2020.
- ^ "Okayama to join other Japan cities issuing certificates for same-sex partnetships". Japan News. Okayama. 1 June 2020.
- ^ "富田林市パートナーシップ宣誓証明制度について". www.city.tondabayashi.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 川西市が来月導入 /兵庫". Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 16 July 2020.
- ^ "川西市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について". www.city.kawanishi.hyogo.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度". city.kaizuka.lg.jp (in Japanese). 28 August 2020.
- ^ "京都市パートナーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関する要綱" (PDF). Kyoto City (in Japanese). Retrieved 8 November 2022.
- ^ "Kyoto begins offering partnership oaths to publicly recognize city's LGBTQ couples". Mainichi Daily News. 2 September 2020.
- ^ "坂戸市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.sakado.lg.jp (in Japanese). 15 September 2020.
- ^ "小金井市パートナーシップ宣誓制度の実施について 令和2年10月2日報道発表". www.city.koganei.lg.jp (in Japanese). 2 October 2020.
- ^ "北本市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.kitamoto.saitama.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "同性カップルを"結婚相当関係"". NHK (in Japanese). 1 November 2020.
- ^ "令和2年11月1日から「栃木市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」を始めました。". www.city.tochigi.lg.jp (in Japanese). 1 November 2020.
- ^ "栃木市が「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」創設 鹿沼に続く". The Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese). 7 October 2020.
- ^ "国分寺市パートナーシップ制度". www.city.kokubunji.tokyo.jp (in Japanese). 16 November 2020.
- ^ "鴻巣市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.konosu.saitama.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "青森県弘前市が同性パートナーシップ証明制度導入へ、東北初". Out Japan (in Japanese). 28 August 2020.
- ^ "弘前市パートナーシップ宣誓制度10日に施行". www.toonippo.co.jp (in Japanese). 4 December 2020.
- ^ "渋川市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.shibukawa.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度、東かがわ市で始まる!。". go2senkyo.com (in Japanese). 27 November 2020.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度開始". TownNews.com (in Japanese). 26 June 2020.
- ^ "三浦市 パートナー制度導入へ". Town News (in Japanese). 23 October 2020.
- ^ "パートナー制度1月導入 広島市方針". www.chugoku-np.co.jp (in Japanese). 24 September 2020.
- ^ "明石市も「パートナー制」 性的少数者対象 来年度にも導入 /兵庫". Mainichi Shimbun (in Japanese). 19 September 2019.
- ^ "明石市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度". www.city.akashi.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "高知市で「パートナーシップ登録制度」が始まり、初日に3組のカップルが登録申請しました". Out Japan (in Japanese). 2 February 2021.
- ^ "高知市に同性パートナー制導入を 県内NPOが署名提出". Kochi Shimbun (in Japanese). 14 February 2020.
- ^ "桶川市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.okegawa.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "多様な性のLGBTQ+のカップルを公認 京都・亀岡市がパートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始". Kyoto Shimbun (in Japanese). 2 March 2021.
- ^ "伊奈町パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します". www.town.saitama-ina.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "上尾市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します". www.city.ageo.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "足立区が同性パートナーシップ証明制度を来年度から導入することを発表しました". Out Japan (in Japanese). 24 November 2020.
- ^ "足立区パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度を令和3年4月1日から開始します". www.city.adachi.tokyo.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "多様性ある群馬へ、一歩 LGBTカップルを公認 パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.tokyo-np.co.jp (in Japanese). 14 November 2020.
- ^ "安中市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について". www.city.annaka.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "茅ヶ崎市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.chigasaki.kanagawa.jp (in Japanese). 20 November 2020.
- ^ "「パートナー制度」導入へ". Town News (in Japanese). 27 November 2020.
- ^ "富士市パートナーシップ宣誓制度 県内2例目の導入へ". fuji-news.net (in Japanese).
- ^ "富士市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.fuji.shizuoka.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "藤沢市が導入検討へ". TownNews.com (in Japanese). 13 March 2020.
- ^ "藤沢市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.fujisawa.kanagawa.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "行田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります". www.city.gyoda.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "本庄市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します。". www.city.honjo.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "指宿市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.ibusuki.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "生駒市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.ikoma.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "臼杵市、西宮市、延岡市、生駒市などでも同性パートナーシップ証明制度導入へ". OutJapan (in Japanese). 26 March 2021.
- ^ "北島町が「同性カップル」公認 パートナーシップ宣誓制度導入". Tokushima Shimbun (in Japanese). 3 April 2021.
- ^ "越谷市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.koshigaya.saitama.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "くにたちパートナーシップ制度". www.city.kunitachi.tokyo.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "松本市が中核市に パートナーシップ宣誓制度も県内初導入". matsumoto.keizai.biz (in Japanese). 1 April 2021.
- ^ "三芳町もパートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入へ". honnahiroshi.blog.fc2.com (in Japanese). 29 October 2020.
- ^ "「日南市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」が始まります。". www.city.nichinan.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 西宮市も来春導入へ". kobe-np.co.jp (in Japanese). 15 September 2020. Archived from the original on 26 October 2020. Retrieved 25 September 2020.
- ^ "西宮市パートナーシップ宣誓証明制度". www.nishi.or.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ a b "小豆島の2町 パートナーシップ制度導入へ". www.news24.jp (in Japanese). 19 March 2021.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.town.shodoshima.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "多度津町パートナーシップ宣誓制度について". www.town.tadotsu.kagawa.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "天理市パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました". www.city.tenri.nara.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "豊橋市パートナーシップ制度". www.city.toyohashi.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "臼杵市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.usuki.oita.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "大和市パートナーシップ宣誓制度の運用を開始します". www.city.yamato.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "延岡市パートナーシップ宣誓制度 令和3年4月26日(月曜)スタート!". www.city.nobeoka.miyazaki.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "浦安市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.urayasu.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "千代田町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Chiyoda Town. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
- ^ "長岡京市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.nagaokakyo.lg.jp (in Japanese). 15 May 2024.
- ^ "東松山市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.migashimatsuyama.lg.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ ""結婚相当の関係"と公的に認定…『パートナーシップ制度』金沢市長が導入を前向きに検討する意向". Yahoo! Japan (in Japanese). 10 December 2020. Archived from the original on 10 December 2020. Retrieved 10 December 2020.
- ^ "石川県金沢市パートナーシップ宣誓制度開始 "第1号"のカップルが会見で思い語る". Yahoo! Japan (in Japanese). 1 July 2021. Archived from the original on 1 July 2021. Retrieved 3 July 2021.
- ^ a b "パートナー宣誓制度 南足柄と大井で施行へ". Town News (in Japanese). 13 March 2021.
- ^ "三好市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度". www.miyoshi.i-tokushima.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました!". www.city.iruma.saitama.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 September 2021.
- ^ "新富町が「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」導入 県内で5番目". Miyazaki Prefecture News (in Japanese). 15 September 2021.
- ^ "宇部市がパートナーシップ制度を導入 山口県内で初". www.news.livedoor.com (in Japanese). 19 February 2021.
- ^ "宇部市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.ube.yamaguchi.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "LGBTカップル 婚姻相当に認定 備前市 パートナー制度10月導入" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 県内初、きょうから導入 手続きで受領証カード交付 彦根 /滋賀". Mainichi (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ "唐津市パートナーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関する要綱" (PDF) (in Japanese). City of Karatsu. Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "川島町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を始めました" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 久喜市で1組手続き 今月導入 /埼玉" (in Japanese). Mainichi. Retrieved 3 October 2021.
- ^ "「松田町パートナーシップ宣誓制度」" (in Japanese). Matsuda Town Website. Retrieved 8 October 2021.
- ^ "毛呂山町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "熊本県菊池郡大津町で、本日10月1日よりパートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました" (in Japanese). Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "浦添市「性の多様性条例」が施行 パートナーシップ宣誓証明を1組申請". Okinawa Times (in Japanese). Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "向日市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 October 2021.
- ^ "狭山市パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります" (in Japanese). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "那賀町パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Naka Village. 1 November 2021. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "開始しました『えびの市パートナーシップ宣誓制度』" (in Japanese). Ebino City. 2 December 2021. Retrieved 3 December 2021.
- ^ "甲州市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kōshū City. 1 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "「倉敷市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」" (in Japanese). Kurashiki City. 1 December 2021. Retrieved 2 December 2021.
- ^ "2人の間柄は"婚姻関係"と同じ…「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」開始 県内自治体では初【岡山・真庭市】" (in Japanese). 1 December 2021. Archived from the original on 2 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました" (in Japanese). Town of Tokigawa. 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "善通寺市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Zentsūji City. 1 December 2021. Retrieved 1 December 2021.
- ^ "白山市で「パートナーシップ制度」" (in Japanese). NHK News. 10 December 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "【12月1日(水曜日)予約開始】ふなばしパートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Funabashi City. 16 December 2021. Retrieved 16 November 2021.
- ^ "草加市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します【予約受付は、12月13日(月曜日)から】" (in Japanese). Sōka City. 8 December 2021. Archived from the original on 13 December 2021. Retrieved 20 December 2021.
- ^ "飯能市がパートナーシップ制度 同性カップルの関係を公認 来年1月1日導入". Bunka Shinbun (in Japanese). 17 November 2021. Retrieved 4 December 2021.
- ^ "日高市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Hidaka City. 27 December 2021. Retrieved 28 December 2021.
- ^ "鹿児島市で「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」がスタート" (in Japanese). NHK News Web. 4 January 2022. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ^ "三原市がパートナー制 22年1月導入、手続きに個室も" (in Japanese). 25 October 2021. Retrieved 26 October 2021.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度を開始します!" (in Japanese). 28 December 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- ^ "蒲郡市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Gamagōri City. 12 December 2021. Retrieved 4 January 2022.
- ^ "綾瀬市パートナーシップ宣誓制度(2022年(令和4年)2月1日開始)" (in Japanese). Ayase City. 1 February 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2022.
- ^ "パートナー・ファミリーシップ制度開始、4組が届け出 市川市" (in Japanese). Goo News. 2 February 2022. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Samukawa Town. 2 January 2021. Retrieved 2 January 2021.
- ^ "多摩市パートナーシップ制度について" (in Japanese). Tama City. 19 January 2022. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "吉川市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Yoshikawa City. 1 February 2022. Retrieved 2 February 2022.
- ^ "江別市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Ebetsu City. 25 February 2022. Retrieved 1 March 2022.
- ^ "上峰町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kamimine Town. 3 March 2022. Retrieved 26 March 2022.
- ^ "美馬市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Mima City. 1 March 2022. Retrieved 1 March 2022.
- ^ "深谷市パートナーシップ宣誓制度 令和4年3月23日スタート" (in Japanese). Fukaya City. 23 March 2022. Retrieved 23 March 2022.
- ^ "愛川町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Aikawa. Retrieved 2 May 2022.
- ^ "秋田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Akita City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "阿南市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Anan City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "広報あつぎ2022年3月1日号(第1370号)" (PDF). Atsugi City (in Japanese). Retrieved 28 February 2021.
- ^ a b c d e "パートナーシップ宣誓制度導入市町について" (in Japanese). Kagawa Prefecture. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "『豊後大野市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度』4月1日スタート!" (in Japanese). Bungo-Ōno City. 2 March 2022. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 海老名市が4月から導入へ" (in Japanese). カナロコ. 6 March 2022. Retrieved 6 March 2022.
- ^ "府中町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Fuchū Town. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "富士見市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Fujimi City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "多様な性を認め合おう 市がパートナーシップ制度の運用開始" (in Japanese). 両丹日日新聞. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 5 April 2022.
- ^ "福津市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度の導入についての市民意見公募結果" (in Japanese). Fukutsu City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ制度」函館も導入 4月から、道内4自治体目". Hokkaido Shimbun (in Japanese). 25 February 2021. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "鳩山町パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Hatoyama Town. 24 March 2022. Retrieved 24 March 2022.
- ^ "廿日市市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Hatsukaichi City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "姫路市パートナー制度導入「待ちわびていた」 市長が1組目に宣誓受領証渡して祝福" (in Japanese). 神戸新聞. 2 April 2022. Retrieved 3 April 2021.
- ^ "平塚市パートナーシップ宣誓制度(令和4年4月1日開始)" (in Japanese). Hiratsuka City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "門川町パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります" (in Japanese). Kadogawa Town. Retrieved 2 April 2022.
- ^ a b c "開成、中井、山北町でパートナー制度 足柄上で相互利用へ" (in Japanese). カナロコ. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ a b c "パートナー制度で連携 本庄市、美里町、神川町、上里町 「性的マイノリティーの理解深まれば」" (in Japanese). 東京新聞. 25 February 2022. Retrieved 2 March 2022.
- ^ "観音寺市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "令和4年4月から笠岡市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度が始まります" (in Japanese). Kasaoka City. 31 March 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "粕屋町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Kasuya Town. 31 March 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ "北区パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kita Ward. 18 March 2022. Retrieved 18 March 2022.
- ^ "北見市、パートナー制度制定 6月から宣誓受け付け" (in Japanese). 北海道新聞. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 5 April 2022.
- ^ "駒ヶ根市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Komagane City. Retrieved 11 December 2023.
- ^ "子どもも家族」は静岡県内初 静岡、湖西市パートナー制度運用開始" (in Japanese). あなたの静岡新聞. 5 April 2022. Retrieved 5 April 2022.
- ^ "熊谷市パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります" (in Japanese). Kumagaya City. 3 March 2022. Retrieved 3 March 2022.
- ^ "宮代町がパートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度を4月から" (in Japanese). 朝日新聞. 15 February 2022. Retrieved 17 March 2022.
- ^ "武蔵野市パートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Musashino City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "二宮町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Ninomiya Town. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "野木町パートナーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関する要綱を次のように定め、令和4年4月1日から適用する" (PDF) (in Japanese). Nogi Town. 11 March 2022. Retrieved 8 June 2022.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Ōiso Town. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 14 April 2022.
- ^ "県内初の条例による「パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度」を開始します。" (in Japanese). Okazaki City. 30 March 2022. Retrieved 31 March 2022.
- ^ "「西都市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」を導入しました" (in Japanese). Saito City. 1 April 2022. Retrieved 6 April 2022.
- ^ "関市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (PDF) (in Japanese). Seki City. 9 February 2022. Retrieved 9 February 2022.
- ^ "パートナー宣誓来月開始" (in Japanese). 東日新聞. 9 March 2022. Retrieved 9 March 2022.
- ^ "静岡市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Shizuoka City. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "田原市パートナーシップ制度を導入します" (PDF) (in Japanese). Tahara City. 24 March 2022. Retrieved 2 April 2022.
- ^ "高浜市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Takahama City. 30 March 2022. Retrieved 2 April 2022.
- ^ "竹田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度』が 2022年(令和4年)4月1日からスタートします" (PDF) (in Japanese). Taketa City. Retrieved 6 January 2022.
- ^ "同性カップル、結婚相当と認定 たつの市「パートナー制度」4月導入へ 市営住宅入居可能に" (in Japanese). 神戸新聞NEXT. 15 February 2022. Retrieved 17 February 2022.
- ^ "八潮市パートナーシップ宣誓制度をスタート" (PDF) (in Japanese). Yashio City. 24 February 2022. Retrieved 28 February 2022.
- ^ "横瀬町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Yokoze Town. 31 March 2022. Retrieved 1 April 2022.
- ^ "吉見町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Yoshimi Town. 25 March 2022. Retrieved 30 March 2022.
- ^ "吉岡町パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Yoshioka Town. 6 June 2022. Retrieved 2 July 2022.
- ^ "荒川区同性パートナーシップ制度を開始します!" (in Japanese). Arakawa City. 21 April 2022. Retrieved 8 May 2022.
- ^ "春日井市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度 案内チラシ" (PDF) (in Japanese). Kasugai City. Retrieved 6 May 2022.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度の開始について" (in Japanese). Hyūga City. 31 May 2022. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- ^ "習志野市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度が始まりました". Narashino City (in Japanese). 1 June 2022. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- ^ "鳴門市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Naruto City. 1 June 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ "坂出市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Sakaide City. 1 June 2022. Retrieved 4 June 2022.
- ^ "土佐清水市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ登録制度" (in Japanese). Tosashimizu City. Retrieved 1 June 2022.
- ^ "ふじみ野市パートナーシップ宣誓制度(令和4年7月1日開始)" (in Japanese). Fujimino City. Retrieved 1 July 2022.
- ^ "茨木市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Ibaraki City. 1 July 2022. Retrieved 2 July 2022.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 清川村も導入" (in Japanese). Town News. 15 July 2022. Retrieved 16 July 2022.
- ^ "山陰初導入へ「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」 鳥取県境港市" (in Japanese). Sakaiminato City. Retrieved 1 July 2022.
- ^ "豊川市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Toyokawa City. 28 June 2022. Retrieved 2 July 2022.
- ^ "菊池市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入しました" (in Japanese). Kikuchi City. 29 July 2022. Retrieved 3 August 2022.
- ^ "一宮市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を開始します!" (in Japanese). Ichinomiya City. 5 September 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2022.
- ^ "9月1日からパートナーシップ宣誓制度がはじまります。" (in Japanese). Miki Town. 31 August 2022. Retrieved 4 September 2022.
- ^ "三郷市パートナーシップ 宣誓制度のご案内" (PDF) (in Japanese). Misato City. Retrieved 1 September 2022.
- ^ "令和4年8月24日(水曜日)臨時市長記者会見" (in Japanese). Sanjō City. 24 August 2022. Retrieved 1 September 2022.
- ^ "佐野市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を実施しています" (in Japanese). Sano Town. 1 September 2022. Retrieved 2 September 2022.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度」について" (in Japanese). Toyoyama Town. 7 September 2022. Retrieved 11 September 2022.
- ^ "阿波市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を開始しました。" (in Japanese). Awa City. 1 October 2022. Retrieved 22 November 2022.
- ^ "パートナー制度きょう導入 越前市、5組宣誓予定" (in Japanese). 中日新聞. 1 October 2022. Retrieved 1 October 2022.
- ^ "10月1日から「橋本市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」が始まります" (in Japanese). Hashimoto City. 15 September 2022. Retrieved 1 October 2022.
- ^ "海田町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kaita Town. 22 September 2022. Retrieved 1 October 2022.
- ^ "令和4年10月1日より黒潮町パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります" (in Japanese). Kuroshio Town. 20 September 2022. Retrieved 25 September 2022.
- ^ "美作市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度/美作市ホームページ" (in Japanese). Mimasaka City. Retrieved 23 March 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Miyoshi City. 4 October 2022. Retrieved 17 November 2022.
- ^ "なすしおばらパートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (PDF) (in Japanese). Nasushiobara Town. Retrieved 25 September 2022.
- ^ "とちぎパートナーシップ宣誓書受領カード等の利用先について" (PDF) (in Japanese). Tochigi Prefecture. 1 October 2022. Retrieved 3 October 2022.
- ^ "広報せとうち令和4(2022)年10月号(第215号)" (PDF) (in Japanese). Setouchi City. 22 September 2022. Retrieved 4 October 2022.
- ^ "座間市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始" (PDF) (Press release) (in Japanese). Zama: Zama City. 30 September 2022. Retrieved 2 October 2022.
- ^ "戸田市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度について" (in Japanese). Toda City. 1 October 2022. Retrieved 11 October 2022.
- ^ "Tokyo Partnership Oath System User Guide" (PDF). Tokyo Metropolitan Government. April 2023. Retrieved 25 May 2023.
- ^ "池田市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Ikeda City. 25 October 2022. Retrieved 1 November 2022.
- ^ "令和4年11月から南国市パートナーシップ登録制度が始まります!" (1 November 2022) (in Japanese). Nankoku City. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Asakuchi City. 1 December 2022. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- ^ "長野市「パートナーシップ宣言制度」 カップルが申請に訪れる". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 1 December 2022. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- ^ "報道資料 令和4年11月7日発表 「名古屋市ファミリーシップ制度」の受付を開始します" (in Japanese). Nagoya City. 30 November 2022. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- ^ "第1号カップル「認められうれしい」 パートナーシップ制度 帯広で初の登録". 十勝毎日新聞電子版 (in Japanese). 1 December 2022. Retrieved 1 December 2022.
- ^ "「人権啓発映画会」ならびに「パートナーシップ宣誓書受領証交付式」の開催について" (PDF) (Press release) (in Japanese). Nonoichi City. 1 December 2022. Retrieved 6 December 2022.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度、きょう施行 一関市、県内で初の導入". IWATE NIPPO 岩手日報 (in Japanese). 23 December 2022. Retrieved 23 December 2022.
- ^ "日田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Hita City. Retrieved 1 January 2023.
- ^ "丸亀市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Marugame City. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始しました | 小鹿野町" (in Japanese). Ogano Town. Retrieved 10 March 2023.
- ^ "白岡市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します。" (in Japanese). Shiraoka City. 27 December 2022. Retrieved 1 January 2023.
- ^ "苫小牧市でパートナーシップ制度開始 道内自治体で6例目 |NHK 北海道のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 4 January 2023. Retrieved 4 January 2023.
- ^ "広島県三次市 三次市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Miyoshi City. Retrieved 5 January 2023.
- ^ "和光市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度" (in Japanese). Wakō City. Retrieved 12 January 2023.
- ^ "岩見沢市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Iwamizawa City. 1 February 2023. Retrieved 1 February 2023.
- ^ "小牧市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を開始します(令和5年2月1日~)" (in Japanese). Komaki City. 31 January 2022. Retrieved 1 February 2023.
- ^ "誰もが暮らしやすく、新潟長岡市でパートナーシップ制度開始 性的少数者のカップルを証明、ファミリーシップ制度も". 新潟日報デジタルプラス (in Japanese). 2 February 2023. Retrieved 2 February 2023.
- ^ "静岡県パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります" (in Japanese). Shizuoka Prefecture. 1 March 2023. Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ^ 杉山, 加奈 (1 March 2023). "富山県でパートナーシップ宣誓制度開始". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 March 2023.
- ^ "菊陽町パートナーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関する要綱" (PDF) (in Japanese). Kikuyō Town. 8 March 2023. Retrieved 11 March 2023.
- ^ "香南市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kōnan City. 23 February 2023. Retrieved 23 February 2023.
- ^ "日進市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Nisshin City. 9 February 2023. Retrieved 9 March 2023.
- ^ "嵐山町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を始めました" (in Japanese). Ranzan Town. 1 March 2023. Retrieved 10 March 2023.
- ^ "調布市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Chōfu City. 5 March 2023. Retrieved 15 March 2023.
- ^ "柏市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度を施行" (in Japanese). Kashiwa City. 13 March 2023. Retrieved 15 March 2023.
- ^ "加須市パートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Kazo City. 16 March 2023. Retrieved 22 March 2023.
- ^ "朝霞市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度" (PDF) (in Japanese). Asaka City. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "阿蘇 広報あそ 2023年4月号" (PDF) (in Japanese). Aso City. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "令和5年度からパートナーシップ制度を導入" (PDF) (in Japanese). Ayabe City. 28 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "令和5年4月から「豊後高田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」がスタートします!" (in Japanese). Bungotakada City. 30 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "知立市がパートナーシップ制度 4月から導入". 中日新聞Web (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "五條市パートナーシップ宣誓手続き" (in Japanese). Gojō City. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」を創設しました。" (in Japanese). Hakone Town. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ "半田市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Handa City. 27 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "蓮田市/4月1日から蓮田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Hasuda City. 17 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "東広島市パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります!~すべての人が自分らしく生きることができるまち~" (in Japanese). Higashihiroshima City. 23 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "日野市パートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Hino City. 12 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "市営住宅の入居資格の見直しについて - 北斗市" (in Japanese). Hokuto City. 3 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "井原市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度について(令和5年4月開始)" (in Japanese). Ibara City. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "性的少数者向け、パートナー制度 斑鳩町、4月創設 /奈良". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). 28 February 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "今治市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Imabari City. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "海津市ファミリーシップの宣誓に関する要綱" (PDF). Kaizu City (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "苅田町公式 パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kanda Town. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "春日部市パートナーシップ・ ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を開始します。" (PDF) (Press release) (in Japanese). Kasukabe City. 16 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入します" (in Japanese). Katsuyama City. 22 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "木更津市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kisarazu City. 27 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "「小林市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」が導入されました。" (in Japanese). Kobayashi City. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 4 April 2023.
- ^ "合志市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度の運用を開始しました" (in Japanese). Kōshi City. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "町田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Machida City. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "米原市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Maibara City. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "「松伏町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度」(素案)について" (in Japanese). Matsubushi Town. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "同性カップル(LGBTQ+)などに証明書 明和町が三重県内初 子供も家族認定(夕刊三重)". Yahoo!ニュース (in Japanese). Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "- 和歌山県 那智勝浦町 -那智勝浦町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度を導入しました" (in Japanese). Nachikatsuura Town. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "埼玉 広がるパートナーシップ 63市町村中54が導入:朝日新聞デジタル". 朝日新聞デジタル (in Japanese). 26 March 2023. Retrieved 27 March 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 全17市町に拡大 /香川". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "那須烏山市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Nasukarasuyama City. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- ^ "新座市パートナーシップ・ ファミリーシップ届出制度 利用の手引き" (PDF) (in Japanese). Niiza City. p. 1. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "「直方市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」が始まります" (in Japanese). Nōgata City. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "小川町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度の開始" (in Japanese). Ogawa Town. 3 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "『パートナーシップ制度』 大村市が新年度導入 対象者に証明書を交付". 長崎新聞社 (in Japanese). 2 March 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "令和5年4月1日から「小山市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」をはじめます" (in Japanese). Oyama City. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "大洲市 パートナーシップ制度で意見募集". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 8 January 2023. Retrieved 18 January 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度 新たに勝山市と鯖江市が4月から導入へ|NHK 福井県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "酒田市パートナーシップ宣誓制度". www.city.sakata.lg.jp (in Japanese). 31 March 2023. Retrieved 31 March 2023.
- ^ "幸手市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Satte City. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "志木市パートナーシップ及びファミリーシップ届出制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Shiki City. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "杉戸町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Sugito Town. 15 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "吹田市パートナーシップ宣誓証明制度" (in Japanese). Suita City. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "墨田区パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Sumida City. 1 April 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "高砂市「多様な性」に関する取組方針" (in Japanese). Takasago City. 3 April 2023. Retrieved 3 April 2023.
- ^ "丹波市 パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Tamba City. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "令和5年4月1日 丹波篠山市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Tamba-Sasayama City. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度の導入|東海市公式ウェブサイト" (in Japanese). Tōkai City. 29 March 2023. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "鶴ヶ島市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Tsurugashima City. Retrieved 1 April 2023.
- ^ "和気町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Wake Town. 3 April 2023. Retrieved 5 April 2023.
- ^ "湯河原町パートナーシップ宣誓制度(令和5年4月1日開始)" (in Japanese). Yugawara Town. 31 March 2023. Retrieved 2 April 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Suginami City. 24 April 2023. Retrieved 26 April 2023.
- ^ "松原市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Matsubara City. 28 April 2023. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "盛岡市がパートナーシップ制度導入 1日から申請受け付け". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 1 May 2023. Retrieved 1 May 2023.
- ^ "田川市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Tagawa City. 16 May 2023. Retrieved 16 May 2023.
- ^ "安芸市パートナーシップ登録制度" (in Japanese). Aki City. 1 June 2023. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ "あわら市パートナーシップ宣誓制度(2023年6月1日施行)" (in Japanese). Awara City. 25 May 2023. Retrieved 1 June 2023.
- ^ "東秩父村パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度の開始" (in Japanese). Higashichichibu Village. 1 June 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- ^ "長久手市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Nagakute City. 1 June 2023. Retrieved 31 May 2023.
- ^ "大山崎町パートナーシップ宣誓制度について(令和5年6月1日掲載)" (in Japanese). Ōyamazaki Town. 1 June 2023. Retrieved 5 June 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度の自治体間連携について" (in Japanese). Hadano City. 7 July 2023. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ "7月1日 - 伊勢原市" (PDF) (in Japanese). Isehara City. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ "加古川市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度" (in Japanese). Kakogawa City. 26 June 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- ^ "【令和5年7月1日から開始】刈谷市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Kariya City. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ "香春町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kawara Town. 29 June 2023. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ "幸田町パートナーシップ宣誓制度 - 幸田町公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Kōta Town. 1 July 2023. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ "真鶴町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Manazuru Town. 30 June 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- ^ "大府市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップの宣誓に関 する要綱" (PDF) (in Japanese). Ōbu City. Retrieved 2 July 2023.
- ^ "近江八幡市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Ōmihachiman City. 23 June 2023. Retrieved 1 July 2023.
- ^ "蕨市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度について" (in Japanese). Warabi City. 5 July 2023. Retrieved 6 July 2023.
- ^ "長野県パートナーシップ届出制度のご案内" (in Japanese). Nagano Prefecture. 23 June 2023. Retrieved 27 June 2023.
- ^ "「瀬戸市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度」を開始します". www.city.seto.aichi.jp. Retrieved 2023-08-01.
- ^ "須坂市パートナーシップ届出制度を制定しました" (in Japanese). Suzaka City. 26 June 2023. Retrieved 14 September 2023.
- ^ "「2人の関係、県が認めてくれるのは心強い」 岐阜県「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」開始 第1号カップルを認定". 岐阜新聞Web (in Japanese). 1 September 2023. Retrieved 3 September 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 大分市で運用始まる 県内6例目". OBSニュース (in Japanese). 1 September 2023. Retrieved 3 September 2023.
- ^ "岩手県宮古市 9月28日から宮古市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度をはじめます" (in Japanese). Miyako City. 26 September 2023. Retrieved 27 September 2023.
- ^ "「香川県パートナーシップ制度」について" (in Japanese). Kagawa Prefecture. 1 October 2023. Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- ^ "島根県パートナーシップ宣誓制度(令和5年10月1日開始)" (in Japanese). Shimane Prefecture. Retrieved 1 October 2023.
- ^ "とっとり安心ファミリーシップ制度/とりネット/鳥取県公式サイト" (in Japanese). Tottori Prefecture. Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度についてそ 愛知県知多市" (in Japanese). Chita City. Retrieved 25 October 2023.
- ^ "府中市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Fuchū City, Hiroshima. Retrieved 2 October 2023.
- ^ "日置市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Hioki City. 5 October 2023. Retrieved 8 October 2023.
- ^ "くらよし安心ファミリーシップ制度のご案内" (in Japanese). Kurayoshi City. Retrieved 12 January 2024.
- ^ "和歌山県新宮市 新宮市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度が始まります!" (in Japanese). Shingū City. 29 September 2023. Retrieved 1 October 2023.
- ^ "津幡町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Tsubata Town. Retrieved 8 October 2023.
- ^ "矢巾町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました" (in Japanese). Yahaba Town. 2 October 2023. Retrieved 7 October 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度について" (in Japanese). Nirasaki City. 2 October 2023. Retrieved 8 October 2023.
- ^ "福井県パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Fukui Prefecture. 1 November 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Yamanashi Prefecture. 1 November 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ "令和4年11月1日、東京都パートナーシップ宣誓制度が導入されました|板橋区公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Itabashi Ward. 1 November 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Minano Town. 8 November 2023. Retrieved 9 November 2023.
- ^ "小浜市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入します" (in Japanese). Obama City. 25 October 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ "坂井市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Sakai City. 24 October 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ "敦賀市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Tsuruga City. 26 October 2023. Retrieved 1 November 2023.
- ^ a b "寄居町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度について" (in Japanese). Yorii Town. 1 November 2023. Retrieved 21 November 2023.
- ^ "永平寺町パートナーシップ宣誓制度(2023年11月27日施行)" (in Japanese). Eiheiji Town. 27 November 2023. Retrieved 27 November 2023.
- ^ a b "早島町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Hayashima Town. 30 November 2023. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入します" (in Japanese). Kai City. 1 December 2023. Retrieved 13 December 2023.
- ^ "かほく市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kahoku City. 11 December 2023. Retrieved 12 December 2023.
- ^ "「神戸市ライフパートナー制度」が始まります" (in Japanese). Kobe City. 11 December 2023. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ^ "淡路市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入します" (in Japanese). Awaji City. Retrieved 27 November 2023.
- ^ "大山町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度が始まりました。" (in Japanese). Daisen Town. Retrieved 28 January 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度、24年1月1日導入 福井市方針". 中日新聞Web (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-10-31.
- ^ "泉佐野市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Izumisano City. Retrieved 26 December 2023.
- ^ "三朝町安心ファミリーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Misasa Town. 16 January 2024. Retrieved 18 January 2024.
- ^ "小樽市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Otaru City. 1 January 2024. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ "高知県大月町で2024年からパートナーシップ制度を導入・初めての届け出が役場に提出される【高知】|RKC NEWS NNN". 日テレNEWS NNN (in Japanese). 10 January 2024. Retrieved 10 January 2024.
- ^ "性的少数者や事実婚のカップル公認で「生きづらさの解消に」 志布志市がパートナーシップ宣誓制度を開始 鹿児島で4自治体目(お試し)". 鹿児島のニュース - 南日本新聞 (in Japanese). 10 January 2023. Retrieved 11 January 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度に関するお知らせ" (in Japanese). Soeda Town. 1 January 2024. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ "令和6年1月1日から「玉村町パートナーシップ届出制度」を開始します" (in Japanese). Tamamura Town. 1 December 2023. Retrieved 5 December 2023.
- ^ "滝川市 パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (PDF) (in Japanese). Takikawa City. Retrieved 25 December 2023.
- ^ "滝川市パートナー制度、1日開始 市営住宅入居可能に". 北海道新聞 (in Japanese). 29 December 2023. Retrieved 31 December 2023.
- ^ "ファミリーシップ制度を開始します - 八頭町公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Yazu Town. 1 January 2024. Retrieved 2 March 2024.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」山形県で2024年1月4日から開始". TBS News Dig (in Japanese). 27 December 2023. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- ^ "伊達市、24年1月から「パートナーシップ制度」 福島県で初". 福島民友新聞社 (in Japanese). 15 September 2023. Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ^ "千葉県市原市 パートナーシップ制度 2024年1月から導入". チバテレ+プラス (in Japanese). 4 December 2023. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "旭川市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (PDF) (in Japanese). Asahikawa City. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- ^ "ホーム>組織から探す>和歌山県パートナーシップ宣誓制度について(令和6年2月1日施行) 音声読み上げ 和歌山県パートナーシップ宣誓制度について(令和6年2月1日施行)" (in Japanese). Wakayama Prefecture. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ "秩父市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度に関する要綱" (PDF) (in Japanese). Chichibu City. Retrieved 2 February 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Izumi City. 25 January 2023. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を導入 来年2月1日から 上越市". 上越タイムス社 - "上越地域のことが一番詳しく載っている"地域日刊紙を発行しています (in Japanese). 26 December 2023. Retrieved 27 December 2023.
- ^ "江南市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kōnan City. 18 January 2024. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ "流山市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップの届出制度が始まります(令和6年2月1日施行)" (in Japanese). Nagareyama City. 11 January 2024. Retrieved 1 February 2024.
- ^ "深川市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Fukagawa City. 26 February 2024. Retrieved 27 February 2024.
- ^ "羽生市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Hanyū City. 1 March 2024. Retrieved 2 March 2024.
- ^ "新潟村上市が「パートナーシップ制度」を3月1日から導入、新潟県内市町村で5例目 ファミリーシップ制度も実施". 新潟日報デジタルプラス (in Japanese). 15 February 2024. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ "尾張旭市ファミリーシップ制度について - 尾張旭市公式ホームページ(多様性推進課)" (in Japanese). Owariasahi City. 4 March 2024. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ "越生町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関 する要綱" (PDF) (in Japanese). Ogose Town. Retrieved 10 April 2024.
- ^ "愛知県ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について - 愛知県" (in Japanese). Aichi Prefecture. 18 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "兵庫県パートナーシップ制度" (PDF) (in Japanese). Hyōgo Prefecture. Retrieved 21 March 2024.
- ^ "奈良県パートナーシップ制度/奈良県公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Nara Prefecture. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "大分県パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります!" (in Japanese). Oita Prefecture. 26 March 2024. Retrieved 26 March 2024.
- ^ "県のパートナーシップ宣誓制度、24年4月1日スタート". 徳島新聞デジタル (in Japanese). 28 November 2023. Retrieved 28 November 2023.
- ^ "網走市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Abashiri City. 22 March 2024. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- ^ 山野, 拓郎; 大室, 一也 (1 April 2024). "パートナーシップ宣誓制度、山口市で第1号カップル:朝日新聞デジタル". 朝日新聞デジタル (in Japanese). Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- ^ "赤磐市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関する要綱" (PDF) (in Japanese). Akaiwa City. p. 5. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "安城市 パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓届出制度 利用の手引き" (PDF) (in Japanese). Anjo City. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "扶桑町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度(令和6年4月1日開始)" (in Japanese). Fusō City. 25 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "平群町パートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Heguri Town. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "東浦町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Higashiura. 27 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d "「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」県が来月導入 オンライン申請も". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 26 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "「平泉町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度」について" (in Japanese). Hiraizumi Town. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "いの町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Ino Town. Retrieved 8 April 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度|犬山市" (in Japanese). Inuyama City. 25 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "上川町パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Kamikawa Town. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "加西市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度に関する規則" (PDF). Kasai City (in Japanese). Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓証明制度を開始します" (in Japanese). Katakami City. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 4 April 2024.
- ^ "川西町パートナーシップ宣誓制度 (令和6年4月1日~)" (in Japanese). Kawanishi Town. 3 April 2024. Retrieved 22 April 2024.
- ^ "君津市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度(令和6年4月施行) - 君津市公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Kimitsu City. 1 March 2024. Retrieved 2 March 2024.
- ^ "北広島町パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kitahiroshima Town. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "北上市パートナーシップ宣誓制度が始まります!" (in Japanese). Kitakami City. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ a b c "パートナー制度4月1日開始 網走市と近隣4町 対象者や条件統一、公営住宅入居申請など可能に:北海道新聞デジタル". 北海道新聞デジタル (in Japanese). 28 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "清須市ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kiyosu City. 29 March 2024. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "小松島市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Komatsushima City. 25 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "小清水町パートナーシップの宣誓の取扱いに関する要綱(案)" (PDF) (in Japanese). Koshimizu Town. Retrieved 24 March 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度導入に係るパブリックコメントにおける実施結果の公表について" (in Japanese). Kuji City. 29 January 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "草津市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入します". www.city.kusatsu.shiga.jp (in Japanese). 28 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "串本町パートナーシップ・フアミリーシップ制度について(令和6年4月1日施行)" (in Japanese). Kushimoto Town. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度 釧路市が宣誓予約開始". 北海道新聞デジタル (in Japanese). 15 March 2024. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ "三木市パートナーシップ制度を導入" (PDF) (in Japanese). Miki City. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "南あわじ市パートナーシップ宣誓制度を導入します" (in Japanese). Minamiawaji City. 29 March 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "三鷹市 |三鷹市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Mitaka City. 8 April 2024. Retrieved 22 April 2024.
- ^ "室蘭市パートナーシップ宣誓制度(令和6年4月1日開始)" (in Japanese). Muroran City. Retrieved 22 February 2024.
- ^ "長浜市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Nagahama City. 27 March 2024. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "令和6年4月1日から「長瀞町パートナーシップ宣誓制度」を開始しました!" (in Japanese). Nagatoro Town. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 10 April 2024.
- ^ "京都府南丹市が「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」 LGBTQのカップル公認|社会|地域のニュース|京都新聞". 京都新聞 (in Japanese). 2024-02-15. Retrieved 2024-02-14.
- ^ a b 日本放送協会 (9 January 2024). "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 陸前高田市と大船渡市も導入方針|NHK 岩手県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ^ "大口町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度/大口町" (in Japanese). Oguchi Town. Retrieved 29 March 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 大野市 1日に導入:日刊県民福井Web". 中日新聞Web (in Japanese). 27 March 2024. Retrieved 27 March 2024.
- ^ "陸前高田市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Rikuzentakata City. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ "「宍粟市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度」が始まります" (in Japanese). Shisō City. 14 February 2024. Retrieved 15 February 2024.
- ^ "紫波町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度(令和6年4月1日開始)|【企画課】男女共同参画|企画総務部|組織から探す|紫波町役場" (in Japanese). Shiwa Town. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "パートナー制度、庄原市が導入へ 4月、県内10例目 /広島". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). 18 February 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ届出制度を開始します - 袖ケ浦市公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Sodegaura City. Retrieved 8 April 2024.
- ^ "洲本市パートナーシップ宣誓制度の導入について" (in Japanese). Sumoto City. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 3 May 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Takachiho Town. Retrieved 22 April 2024.
- ^ "武豊町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度|武豊町公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Taketoyo. 25 March 2024. Retrieved 28 March 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について - 内子町ホームページ" (in Japanese). Uchiko Town. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "山口市パートナーシップ宣誓制度 - 山口市ウェブサイト" (in Japanese). Yamaguchi City. 16 February 2024. Retrieved 18 February 2024.
- ^ "播磨町パートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Harima Town. Retrieved 9 June 2024.
- ^ "5月13日より南相馬市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度を導入します" (in Japanese). Minamisoma. 13 May 2024. Retrieved 13 May 2024.
- ^ "南知多町パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度|南知多町公式ウェブサイト" (in Japanese). Minamichita Town. 10 June 2024. Retrieved 20 June 2024.
- ^ "甲賀市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップの宣誓制度に関する要綱" (PDF) (in Japanese). Kōka City. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "甲賀市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kōka City. Retrieved 12 June 2024.
- ^ "福島市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Fukushima City. 27 June 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ "「桜井市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」を導入します。" (in Japanese). Sakurai City. 1 July 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ "新発田市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Shibata City. 1 July 2024. Retrieved 1 July 2024.
- ^ "木津川市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kizugawa City. Retrieved 26 September 2024.
- ^ "「国富町パートナーシップ宣誓制度」について - 宮崎県国富町ホームページ" (in Japanese). Kunitomi Town. Retrieved 26 September 2024.
- ^ "「山口県パートナーシップ宣誓制度実施要綱」について - 山口県ホームページ". Yamaguchi Prefecture. Retrieved 2024-09-03.
- ^ "福島県 「パートナーシップ制度」の運用はじまる|NHK 福島県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 2 September 2024. Retrieved 8 September 2024.
- ^ "新潟県「パートナーシップ制度」スタート!性的少数者カップルの関係を公的証明、初日は届け出予約1組 第四北越銀行もサービス開始". 新潟日報デジタルプラス (in Japanese). 3 September 2024. Retrieved 8 September 2024.
- ^ "滋賀県パートナーシップ宣誓制度について|滋賀県ホームページ" (in Japanese). Shiga Prefecture. 4 September 2024. Retrieved 8 September 2024.
- ^ "本宮市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度 - 本宮市公式ホームページ" (in Japanese). Motomiya City. 2 September 2024. Retrieved 26 September 2024.
- ^ "胎内市/パートナーシップ制度" (in Japanese). Tainai City. 27 September 2024. Retrieved 2 October 2024.
- ^ "富津市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Futtsu City. 30 September 2024. Retrieved 2 October 2024.
- ^ "鹿屋市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kanoya City. 5 September 2024. Retrieved 2 October 2024.
- ^ "北広島市パートナーシップ宣誓制度" (in Japanese). Kitahiroshima City. 25 September 2024. Retrieved 2 October 2024.
- ^ "津山市パートナーシップ宣誓制度について" (in Japanese). Tsuyama City. Retrieved 26 September 2024.
- ^ 長崎新聞 (2024-12-03). "パートナーシップ宣誓制度 長崎・時津町も導入、県内3例目 | 長崎新聞". 長崎新聞 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-12-03.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ制度」仙台市 来年度中に導入へ(ミヤギテレビ)". Yahoo!ニュース (in Japanese). 20 September 2023. Retrieved 21 September 2023.
- ^ "仙台市、パートナー宣誓制度を導入 10日から". 日本経済新聞 (in Japanese). 2024-12-03. Retrieved 2024-12-03.
- ^ "宮城・栗原市がパートナーシップ制度導入へ 2024年度から". 河北新報オンライン (in Japanese). 16 December 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度 来年度中の運用を予定 幕別一般質問(十勝毎日新聞)". 十勝毎日新聞電子版 (in Japanese). 17 September 2023. Retrieved 16 September 2023.
- ^ "「パートナーシップ制度」23年度導入へ 富岡町、福島県内で初". gooニュース (in Japanese). 15 December 2022. Retrieved 15 December 2022.
- ^ パートナーシップ制度を延期 飛だ市、議会から「拙速」. Asahi Shimbun (in Japanese). 20 March 2019.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度も…LGBTQへの理解進める条例案 馳知事が9月の議会提出目指す考え(石川テレビ)". Yahoo!ニュース (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-02-25.
- ^ "岩手:パートナー制「岩手モデル」 県指針策定へ 認定要件など検討:地域ニュース". 読売新聞オンライン (in Japanese). 6 December 2022. Retrieved 16 December 2022.
- ^ "鹿児島県知事選挙 「鹿児島県としてパートナーシップ宣誓制度を」 てのくち里花さん 鹿児島県知事... - 井上かつひろ(イノウエカツヒロ) | 選挙ドットコム". 選挙ドットコム (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-06-20.
- ^ "江東区パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度(素案)に関するご意見". 江東区 (in Japanese). Kōtō Ward. Retrieved 2 November 2023.
- ^ "パートナーシップ、ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について" (PDF) (in Japanese). Tōgō Town. Retrieved 24 March 2023.
- ^ "令和3年12月八戸市議会定例会一般質問日程表" (PDF). Hachinohe City (in Japanese). Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ "松山市がファミリーシップ制度導入検討 24年度末までの運用開始目指す". 愛媛新聞社 (in Japanese). 1 December 2023. Retrieved 4 December 2023.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k "パートナー制度、中国地方自治体の25%が検討 広島市は4日開始". 中国新聞 (in Japanese). 2 January 2021. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "パートナーシップ宣誓制度、安曇野市も検討 性的少数者カップルの公的証明". 信濃毎日新聞 (in Japanese). 3 September 2022. Retrieved 5 September 2020.
- ^ "1番 八 木 亮 三 議員" (PDF) (in Japanese). Nagayo Town. Retrieved 10 December 2021.
- ^ "令和5年度施政方針 新しい可能性を育て「笑顔あふれるまち」へ - 新潟県加茂市" (in Japanese). Kamo City. Retrieved 22 March 2023.
- ^ "令和3年第5回(9月)佐渡市議会定例会会議録" (PDF) (in Japanese). Sado City. Retrieved 29 November 2021.
- ^ "佐渡市がパートナーシップ制度導入を検討 市長「できるだけ早い形で」". 新潟日報 (in Japanese). 17 September 2022. Retrieved 21 September 2022.
- ^ a b c d "県内5市が同性・パートナーシップ制度を検討 県は検討せず|NHK 沖縄県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 21 November 2022. Retrieved 24 November 2022.
- ^ "沖縄・南城市長選/平和求めSDGs推進/チョービン市長が政策発表". www.jcp.or.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2021-12-22.
- ^ "性の多様性セミナーを開催します!!" (in Japanese). Retrieved 11 October 2021.
- ^ "LGBTカップル公認へ 静岡市、2022年4月に制度導入方針". Anata no Shizuoka Shinbun (in Japanese). Retrieved 2 October 2021.
- ^ "一般質問一覧表(令和4年3月定例会)". www.city.higashimurayama.tokyo.jp. Retrieved 2022-02-21.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度 富山市が導入を検討(北日本放送)". Yahoo!ニュース (in Japanese). Archived from the original on 2021-12-23. Retrieved 2021-12-23.
- ^ "リスト:同性パートナーシップ証明制度を導入している/導入予定の自治体". outjapan.co.jp (in Japanese).
- ^ "LGBTQカップルの親や子どもも家族「ファミリーシップ制度」導入 三田市 市住入居など可能に". 神戸新聞NEXT (in Japanese). 2023-08-03. Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ "事実婚や近親者も対象 宮古市パートナーシップ制度9月導入". 河北新報オンライン (in Japanese). 2023-07-29. Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ "高松市が「ファミリーシップ宣誓制度」を9月に導入へ 香川県の自治体で4例目". KSB (in Japanese). 2023-08-22. Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ 日本放送協会. "鳥取県「とっとり安心ファミリーシップ制度」10月から導入|NHK 鳥取県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB. Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ 日本放送協会. "橋本市 ファミリーシップ制度 10月から導入へ|NHK 和歌山県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB. Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ "性的少数者カップルらの子や親も「家族」 山梨・韮崎市が認定制度". 毎日新聞 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ 日本放送協会. "新宮市 パートナーシップ制度など2つの制度10月から導入へ|NHK 和歌山県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB. Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ "新潟市 家族に相当と認める制度「ファミリーシップ」導入へ". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 21 December 2023. Retrieved 21 December 2023.
- ^ "性的少数者カップルの子どもらも支援、宝塚市が「ファミリーシップ宣誓制度」導入". gooニュース (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-01-30.
- ^ "都道府県初、パートナーや子を「家族」に 愛知県、ファミリーシップ制度導入へ:中日新聞Web". 中日新聞Web (in Japanese). Retrieved 2023-11-01.
- ^ "川越市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度/川越市" (in Japanese). Kawagoe City. Retrieved 10 April 2024.
- ^ "田原市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度について|田原市ホームページ" (in Japanese). Tahara City. 1 April 2024. Retrieved 1 April 2024.
- ^ "天理市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度が始まりました" (in Japanese). Tenri City. Retrieved 3 April 2024.
- ^ "東海市で4月から「ファミリーシップ宣誓制」 LGBTQカップルの子も家族に:中日新聞Web". 中日新聞Web (in Japanese). 13 March 2024. Retrieved 16 March 2024.
- ^ "パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ制度について/豊橋市" (in Japanese). Toyohashi City. Retrieved 30 March 2024.
- ^ "善通寺市 性的マイノリティー 来月から子どもや親も家族認定|NHK 香川県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB (in Japanese). 17 March 2024. Retrieved 31 March 2024.
- ^ "豊川市 令和6年7月1日から「豊川市パートナーシップ宣誓制度」を「豊川市パートナーシップ・ファミリーシップ宣誓制度」に拡充します" (Press release) (in Japanese). Toyokawa City. 28 June 2024. Retrieved 29 June 2024.
- ^ "大和、海老名、座間、綾瀬の4市でパートナーシップ制度 3月から共同運用". カナロコ by 神奈川新聞 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-02-15.
- ^ "春日井市・小牧市・豊山町パートナーシップ制度で連携 転居した場合の手続き簡単に". 中日新聞Web (in Japanese). 6 March 2024. Retrieved 22 March 2024.
- ^ 日本放送協会. "京都市 「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」で30自治体と連携へ|NHK 京都府のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB. Retrieved 2024-02-22.
- ^ "京都市:大阪・兵庫とパートナーシップ宣誓制度の都市間連携を開始し、31自治体に拡充します!". 京都市情報館 (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-02-22.
- ^ "パートナーシップ制度で網走など5市町 釧路、室蘭市とも連携:北海道新聞デジタル". 北海道新聞デジタル (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-05-12.
- ^ 日本放送協会. "「パートナーシップ宣誓制度」導入の県内11自治体が連携協定|NHK 岡山県のニュース". NHK NEWS WEB. Retrieved 2024-09-04.
- ^ "【同性パートナーシップ証明制度】愛知県が4月から「ファミリーシップ宣誓制度」を導入". www.outjapan.co.jp (in Japanese). Retrieved 2024-04-01.
- ^ Kikuchi, Daisuke (May 8, 2017). "Tokyo Rainbow Pride participants march for 'change' in LGBT recognition". The Japan Times.
- ^ 自治体のパートナーシップ制度 (in Japanese).
- ^ "319 Couples Using Partnership Systems Across Japan". Archived from the original on 2019-03-28. Retrieved 2018-12-04.
- ^ 自治体のパートナーシップ制度 (in Japanese). 8 October 2019. Archived from the original on 16 December 2019. Retrieved 16 December 2019.
- ^ "地方自治体の同性パートナー認知件数 (2020年6月30日時点)". Nijiiro Diversity (in Japanese). 14 July 2020. Archived from the original on 1 October 2020. Retrieved 3 September 2020.
- ^ "全国で1301組の同性カップルに証明書 : パートナーシップ制度スタートから5年". nippon.com (in Japanese). 9 November 2020.
- ^ "Famiee Project". Famiee Project. 2020. Retrieved 29 September 2020.
- ^ Beh, Lih Yi (29 April 2020). "Japan firms back same-sex partnership certificate campaign in gay rights push". Openly. Thomson Reuters Foundation. Retrieved 29 September 2020.