 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
Cadmium acetate
| |
| Other names
Cadmium diacetate
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.008.049 |
| EC Number |
|
PubChem CID
|
|
| RTECS number |
|
| UNII |
|
| UN number | 2570 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| Cd(CH3COO)2 (anhydrous) Cd(CH3COO)2·2H2O (dihydrate) | |
| Molar mass | 230.500 g/mol (anhydrous) 266.529 g/mol (dihydrate) |
| Appearance | colorless crystals (anhydrous) white crystals (dihydrate) |
| Odor | acetic acid |
| Density | 2.341 g/cm3 (anhydrous) 2.01 g/cm3 (dihydrate) |
| Melting point | 255 °C (491 °F; 528 K) (anhydrous) dihydrate decomposes at 130°C [1] |
| soluble (anhydrous), very soluble (dihydrate) | |
| Solubility | soluble in methanol, ethanol (anhydrous) soluble in ethanol (dihydrate) |
| -83.7·10−6 cm3/mol | |
| Structure | |
| monoclinic | |
| Hazards | |
| GHS labelling: | |
  
| |
| Warning | |
| H302, H312, H332, H410 | |
| P261, P264, P270, P271, P273, P280, P301+P312, P302+P352, P304+P312, P304+P340, P312, P322, P330, P363, P391, P501 | |
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |
| NIOSH (US health exposure limits): | |
PEL (Permissible)
|
[1910.1027] TWA 0.005 mg/m3 (as Cd)[2] |
REL (Recommended)
|
Ca[2] |
IDLH (Immediate danger)
|
Ca [9 mg/m3 (as Cd)][2] |
| Related compounds | |
Other anions
|
Cadmium fluoride Cadmium chloride Cadmium bromide Cadmium iodide |
Other cations
|
Zinc acetate Mercury(II) acetate Silver acetate |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
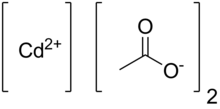
Cadmium acetate is the chemical compound with the formula Cd(O2CCH3)2(H2O)2. The compound is marketed both as the anhydrous form and as a dihydrate, both of which are white or colorless. Only the dihydrate has been verified by X-ray crystallography.
Preparation, reactions, and uses
[edit]It forms by treating cadmium oxide with acetic acid:[3][4]
- CdO + 2 CH3CO2H + H2O → Cd(O2CCH3)2(H2O)2
It can also be prepared by treating cadmium nitrate with acetic anhydride.[5]
Cadmium acetate has few applications. By reaction with trioctylphosphine selenide, it has often been used as a precursor to cadmium selenide and related semiconductors.[6]
Structure of the dihydrate
[edit]
Unlike the coordination geometry of zinc in zinc diacetate dihydrate, cadmium is seven coordinate in Cd(O2CCH3)2(H2O)2.[7] It is a coordination polymer, featuring acetate ligands interconnecting cadmium centers.
Safety
[edit]Cadmium compounds are considered Group 1 carcinogens by the IARC.
References
[edit]- ^ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. p. 447. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ a b c NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards. "#0087". National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ Gangolli, S. (1999). The Dictionary of Substances and Their Effects. London: Royal Society of Chemistry. pp. 12–13. ISBN 9780854048137. Retrieved 2009-03-29.
- ^ Patnaik, Pradyot (2003). Handbook of Inorganic Chemical Compounds. McGraw-Hill Professional. pp. 143–144. ISBN 0-07-049439-8. Retrieved 2009-03-29.
- ^ F. Wagenknecht; R. Juza (1963). "Cadmium acetate". In G. Brauer (ed.). Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry, 2nd Ed. Vol. 2. NY, NY: Academic Press. p. 1105.
- ^ García-Rodríguez, Raúl; Hendricks, Mark P.; Cossairt, Brandi M.; Liu, Haitao; Owen, Jonathan S. (2013). "Conversion Reactions of Cadmium Chalcogenide Nanocrystal Precursors". Chemistry of Materials. 25 (8): 1233–1249. doi:10.1021/cm3035642.
- ^ Harrison, W.; Trotter, J. (1972). "Crystal and molecular structure of cadmium diacetate dihydrate". Journal of the Chemical Society, Dalton Transactions (8–9): 956. doi:10.1039/dt9720000956.
