 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Arixtra |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| License data |
|
| Routes of administration | Subcutaneous |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | N/A |
| Protein binding | 94% |
| Metabolism | renally excreted unchanged |
| Elimination half-life | 17-21 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number |
|
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII |
|
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C31H43N3Na10O49S8 |
| Molar mass | 1728.03 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Fondaparinux (trade name Arixtra) is an anticoagulant medication chemically related to low molecular weight heparins. It is marketed by Viatris. A generic version developed by Alchemia is marketed within the US by Dr. Reddy's Laboratories.
Medical uses
[edit]Clinically, it is used for the prevention of deep vein thrombosis in patients who have had orthopedic surgery[2] as well as for the treatment of deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism.[3]
Fondaparinux is similar to enoxaparin in reducing the risk of ischemic events at nine days, but it substantially reduces major bleeding and improves long-term mortality and morbidity.[4]
It has been investigated for use in conjunction with streptokinase.[5]
Comparison to other agents
[edit]One potential advantage of fondaparinux over LMWH or unfractionated heparin is that the risk for heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT) is substantially lower. Furthermore, there have been case reports of fondaparinux being used to anti-coagulate patients with established HIT as it has no affinity for PF4. However, its renal excretion precludes its use in patients with renal dysfunction.
Unlike direct factor Xa inhibitors, it mediates its effects indirectly through antithrombin III, but unlike heparin, it is selective for factor Xa.[6]
Pharmacology
[edit]Mechanism of action
[edit]Fondaparinux is a synthetic pentasaccharide factor Xa inhibitor. Fondaparinux binds antithrombin and accelerates its inhibition of factor Xa.
Apart from the O-methyl group at the reducing end of the molecule, the identity and sequence of the five monomeric sugar units contained in fondaparinux is identical to a sequence of five monomeric sugar units that can be isolated after either chemical or enzymatic cleavage of the polymeric glycosaminoglycans heparin and heparan sulfate (HS). Within heparin and heparan sulfate this monomeric sequence is thought to form the high-affinity binding site for the anti-coagulant factor antithrombin (AT). Binding of heparin or HS to AT has been shown to increase the anti-coagulant activity of antithrombin 1000 fold. In contrast to heparin, fondaparinux does not inhibit thrombin.
Chemistry
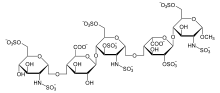
[edit]Abbreviations
[edit]- GlcNS6S = 2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-α-D-glucopyranoside
- GlcA = β-D-glucopyranuronoside
- GlcNS3,6S = 2-deoxy-3,6-di-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-α-D-glucopyranosyl
- IdoA2S = 2-O-sulfo-α-L-idopyranuronoside
- GlcNS6SOMe = methyl-O-2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-α-D-glucopyranoside
Fondaparinux is only accessible by chemical synthesis. Recently, Supriya Dey et al. reported an effective and scalable one-pot synthesis of Fondaparinux.[7]
The sequence of monosaccharides is D-GlcNS6S-α-(1,4)-D-GlcA-β-(1,4)-D-GlcNS3,6S-α-(1,4)-L-IdoA2S-α-(1,4)-D-GlcNS6S-OMe, as shown in the following structure:

References
[edit]- ^ Walenga JM, Jeske WP, Fareed J (2005). "Biochemical and Pharmacologic Rationale for Synthetic Heparin Polysaccharides". Chemistry and Biology of Heparin and Heparan Sulfate. Elsevier. pp. 143–177. doi:10.1016/b978-008044859-6/50006-x. ISBN 978-0-08-044859-6.
The elimination half-life of AT-bound fondaparinux is 17–21 h (171,172). The subcutaneous bioavailability of fondaparinux is nearly 100% and it is distributed mainly in the blood (165,173).
- ^ Fuji T, Fujita S, Ochi T (August 2008). "Fondaparinux prevents venous thromboembolism after joint replacement surgery in Japanese patients". International Orthopaedics. 32 (4): 443–451. doi:10.1007/s00264-007-0360-7. PMC 2532275. PMID 17468868.
- ^ "Arixtra". European Medicines Agency. 2018-09-17. Retrieved 2023-04-03.
- ^ Yusuf S, Mehta SR, Chrolavicius S, Afzal R, Pogue J, Granger CB, et al. (Fifth Organization to Assess Strategies in Acute Ischemic Syndromes Investigators) (April 2006). "Comparison of fondaparinux and enoxaparin in acute coronary syndromes". The New England Journal of Medicine. 354 (14): 1464–1476. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa055443. hdl:2437/113091. PMID 16537663.
- ^ Peters RJ, Joyner C, Bassand JP, Afzal R, Chrolavicius S, Mehta SR, et al. (February 2008). "The role of fondaparinux as an adjunct to thrombolytic therapy in acute myocardial infarction: a subgroup analysis of the OASIS-6 trial". European Heart Journal. 29 (3): 324–331. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehm616. PMID 18245119.
- ^ Comp PC (June 2003). "Selective factor Xa inhibition improves efficacy of venous thromboembolism prophylaxis in orthopedic surgery". Pharmacotherapy. 23 (6): 772–87. doi:10.1592/phco.23.6.772.32190. PMID 12820819. S2CID 19516097.
- ^ Dey S, Lo HJ, Wong CH (June 2020). "Programmable One-Pot Synthesis of Heparin Pentasaccharide Fondaparinux". Organic Letters. 22 (12): 4638–4642. doi:10.1021/acs.orglett.0c01386. PMC 7347301. PMID 32496799.
External links
[edit]- "Fondaparinux". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.