 Complex of catalytic domain of human plasmin and streptokinase | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | SK |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Micromedex Detailed Consumer Information |
| Routes of administration | Intravenous |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| CAS Number | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.029.667 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C2100H3278N566O669S4 |
| Molar mass | 47286.86 g·mol−1 |
Streptokinase is a thrombolytic medication activating plasminogen by nonenzymatic mechanism.[1] As a medication it is used to break down clots in some cases of myocardial infarction (heart attack), pulmonary embolism, and arterial thromboembolism.[2] The type of heart attack it is used in is an ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI).[3] It is given by injection into a vein.[2]
Side effects include nausea, bleeding, low blood pressure, and allergic reactions.[2] A second use in a person's lifetime is not recommended.[2] While no harm has been found with use in pregnancy, it has not been well studied in this group.[4] Streptokinase is in the antithrombotic family of medications and works by turning on the fibrinolytic system.[3]
Streptokinase was discovered in 1933 from beta-hemolytic streptococci.[5] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines.[6] It is no longer commercially available in the United States.[7]
Medical uses
[edit]If percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) is not available within 90–120 minutes of first contact, streptokinase is recommended intravenously as soon as possible after the onset of a ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). As streptokinase is a bacterial product, the body has the ability to build up an immunity to it. Therefore, it is recommended that this medication should not be used again after four days from the first administration, as it may not be as effective and can also cause an allergic reaction. For this reason, it is usually given only for a person's first heart attack. Further thrombotic events could be treated with tissue plasminogen activator (tPA). Overdose of streptokinase or tPA can be treated with aminocaproic acid.
Contraindications
[edit]Absolute
[edit]- Any prior intracranial hemorrhage
- Known structural cerebral vascular lesion (e.g., arteriovenous malformation)
- Known cancer inside the skull (primary or metastatic)
- Ischemic stroke more than 4.5 hours and less than 3 months ago
- Suspected aortic dissection
- Active bleeding or bleeding problem other than menstruation
- Significant closed-head or facial trauma within 3 months
- Intracranial or intraspinal surgery within 2 months
- Severe uncontrolled high blood pressure (unresponsive to emergency therapy)
- For streptokinase, prior treatment within the previous 6 months
Relative
[edit]- History of chronic, severe, poorly controlled hypertension
- Significant hypertension on presentation (SBP >180 mm Hg or DBP >110 mm Hg)
- History of prior ischemic stroke more than 3 month ago
- Dementia
- Known intracranial pathology not covered in absolute contraindications
- Traumatic or prolonged (>10 min) CPR
- Major surgery less than three weeks ago
- Recent (within 2 to 4 wk) internal bleeding
- Noncompressible vascular punctures
- Active peptic ulcer
- Oral anticoagulant therapy
Mechanism of action
[edit]| Streptokinase C | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||
| Organism | |||||||
| Symbol | skc | ||||||
| Entrez | 8110746 | ||||||
| PDB | 1BML | ||||||
| UniProt | P00779 | ||||||
| |||||||
| Staphylokinase/Streptokinase family | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
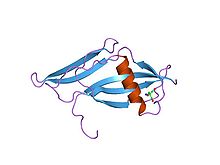 Structure of staphylokinase, a plasminogen activator.[9] | |||||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||||
| Symbol | Staphylokinase | ||||||||||
| Pfam | PF02821 | ||||||||||
| InterPro | IPR004093 | ||||||||||
| SCOP2 | 2sak / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||||
| |||||||||||


Streptokinase belongs to a group of medications known as fibrinolytics, and complexes of streptokinase with human plasminogen can hydrolytically activate other unbound plasminogen by activating through bond cleavage to produce plasmin. There are three domains to streptokinase, denoted α (residues 1–150), β (residues 151–287), and γ (residues 288–414). Each domain binds plasminogen, although none can activate plasminogen independently.[10]
Plasmin is produced in the blood to break down fibrin, the major constituent of blood thrombi, thereby dissolving clots once they have fulfilled their purpose of stopping bleeding. Extra production of plasmin caused by streptokinase breaks down unwanted blood clots, for example, in the lungs (pulmonary embolism). The usual activation of plasminogen is by proteolysis of the Arg561—Val562 bond.[11] The amino group of Val562 then forms a salt-bridge with Asp740, which triggers a conformational change producing the active protease plasmin. When streptokinase is present, it binds to plasminogen to form a complex (streptokinase·plasminogen) that converts substrate plasminogen to plasmin. Residues 1–59 of streptokinase regulate its capacity to induce an active site in bound plasminogen by a nonproteolytic mechanism and to activate substrate plasminogen in a fibrin-independent manner. This complex subsequently rearranges to an active complex although the Arg561–Val562 bond remains intact. Therefore, another residue must substitute for the free amino group of Val562 and provide a counterion for Asp740 in this active complex.[12] Two candidates for this counterion have been suggested: Ile1 of streptokinase and Lys698 of plasminogen. Deletion of Ile1 of streptokinase markedly inhibits its capacity to induce an active site in plasminogen, which supports the hypothesis that establishment of a salt bridge between Ile1 of streptokinase and Asp740 of plasminogen is necessary for streptokinase to induce an active site in plasminogen by a nonproteolytic mechanism.[13] In contrast with the Ile1 substitutions, the Lys698 mutations also decreased the dissociation constant of the streptokinase complex by 15 to 50 fold. These observations suggest that Lys698 is involved in formation of the initial streptokinase·plasminogen complex.[14]
Biology
[edit]Streptokinase is naturally produced by Streptococci spp. bacteria, which use this enzyme to break up blood clots so that they can spread from the initial site of infection. It can also activate fibrin.[15]
It is similar, both in function and in structure, to staphylokinase (Sak) found in Staphylococcus aureus. Staphylokinase is considered a virulence factor,[16] although its presence after the establishment of infection actually decreases disease severity. Both enzymes are carried by phages.[17]
History
[edit]After many years of work along with his student Sol Sherry, William S. Tillett discovered streptokinase in 1933. Initially used in treatment of fibrinous pleural exudates, hemothorax and tuberculous meningitis, its role in acute myocardial infarction was serendipitous.[5]
Research
[edit]Streptokinase may find a use in helping to prevent postoperative adhesions, a common complication of surgery, especially abdominal surgery (appendectomy, gall stones, hysterectomy, etc.) One study using animal models (rats) found that when used with a PHBV membrane drug-delivery system, it was 90 percent effective in preventing adhesions.[18] However, it has not been shown to be effective in humans in a clinical trial.
Marketing
[edit]It is marketed in Chile as Streptase by Alpes Selection, under license of CSL Behring Germany.
Available in Vietnam under the name Mutose. Available in Cuba, Venezuela, Ecuador and other Latin American countries under the trademark Heberkinasa, commercialized by Heber Biotech, Havana, Cuba. Available in India under the name STPase by Cadila Pharmaceuticals, and Myokinase by Biocon Limited.
References
[edit]- ^ Mican J, Toul M, Bednar D, Damborsky J (2019). "Structural Biology and Protein Engineering of Thrombolytics". Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal. 17: 917–938. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2019.06.023. PMC 6637190. PMID 31360331.
- ^ a b c d World Health Organization (2009). Stuart MC, Kouimtzi M, Hill SR (eds.). WHO Model Formulary 2008. World Health Organization. pp. 291–2. hdl:10665/44053. ISBN 9789241547659.
- ^ a b "Streptokinase 1,500,000 iu - Summary of Product Characteristics (SPC) - (eMC)". www.medicines.org.uk. 1 July 2015. Archived from the original on 20 December 2016. Retrieved 14 December 2016.
- ^ "Streptokinase Use During Pregnancy | Drugs.com". www.drugs.com. Archived from the original on 21 December 2016. Retrieved 14 December 2016.
- ^ a b Sikri N, Bardia A (2007). "A history of streptokinase use in acute myocardial infarction". Texas Heart Institute Journal. 34 (3): 318–327. PMC 1995058. PMID 17948083.
- ^ World Health Organization (2019). World Health Organization model list of essential medicines: 21st list 2019. Geneva: World Health Organization. hdl:10665/325771. WHO/MVP/EMP/IAU/2019.06. License: CC BY-NC-SA 3.0 IGO.
- ^ "streptokinase (Intravenous route, Intracoronary route)". Truven Health Analytics. Archived from the original on 8 December 2015. Retrieved 28 November 2015.
- ^ O'Gara PT, Kushner FG, Ascheim DD, Casey DE, Chung MK, de Lemos JA, et al. (January 2013). "2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of ST-elevation myocardial infarction: a report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines". Circulation. 127 (4): e362 – e425. doi:10.1161/CIR.0b013e3182742cf6. PMID 23247304.
- ^ Rabijns A, De Bondt HL, De Ranter C (May 1997). "Three-dimensional structure of staphylokinase, a plasminogen activator with therapeutic potential". Nature Structural Biology. 4 (5): 357–360. doi:10.1038/nsb0597-357. PMID 9145104. S2CID 32914387.
- ^ Mundada LV, Prorok M, DeFord ME, Figuera M, Castellino FJ, Fay WP (July 2003). "Structure-function analysis of the streptokinase amino terminus (residues 1-59)". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 278 (27): 24421–24427. doi:10.1074/jbc.M301825200. PMID 12704199.
- ^ Young KC, Shi GY, Wu DH, Chang LC, Chang BI, Ou CP, Wu HL (January 1998). "Plasminogen activation by streptokinase via a unique mechanism". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 273 (5): 3110–3116. doi:10.1074/jbc.273.5.3110. PMID 9446629.
- ^ Loy JA, Lin X, Schenone M, Castellino FJ, Zhang XC, Tang J (December 2001). "Domain interactions between streptokinase and human plasminogen". Biochemistry. 40 (48): 14686–14695. doi:10.1021/bi011309d. PMID 11724583.
- ^ Wang S, Reed GL, Hedstrom L (April 1999). "Deletion of Ile1 changes the mechanism of streptokinase: evidence for the molecular sexuality hypothesis". Biochemistry. 38 (16): 5232–5240. doi:10.1021/bi981915h. PMID 10213631.
- ^ Wang X, Lin X, Loy JA, Tang J, Zhang XC (September 1998). "Crystal structure of the catalytic domain of human plasmin complexed with streptokinase". Science. 281 (5383): 1662–1665. doi:10.1126/science.281.5383.1662. PMID 9733510.
- ^ Wang H, Lottenberg R, Boyle MD (March 1995). "Analysis of the interaction of group A streptococci with fibrinogen, streptokinase and plasminogen". Microbial Pathogenesis. 18 (3): 153–166. doi:10.1016/S0882-4010(95)90013-6. PMID 7565010.
- ^ Bokarewa MI, Jin T, Tarkowski A (2006). "Staphylococcus aureus: Staphylokinase". The International Journal of Biochemistry & Cell Biology. 38 (4): 504–509. doi:10.1016/j.biocel.2005.07.005. PMID 16111912.
- ^ Kwiecinski J, Jacobsson G, Karlsson M, Zhu X, Wang W, Bremell T, et al. (September 2013). "Staphylokinase promotes the establishment of Staphylococcus aureus skin infections while decreasing disease severity". The Journal of Infectious Diseases. 208 (6): 990–999. doi:10.1093/infdis/jit288. PMID 23801604.
- ^ Yagmurlu A, Barlas M, Gursel I, Gokcora IH (2003). "Reduction of surgery-induced peritoneal adhesions by continuous release of streptokinase from a drug delivery system". European Surgical Research. 35 (1): 46–49. doi:10.1159/000067035. PMID 12566787. S2CID 37453555.
External links
[edit]- "Streptokinase". Drug Information Portal. U.S. National Library of Medicine.