| Progestogen | |
|---|---|
| Drug class | |
 Progesterone, the major progestogen in humans and a widely used medication. | |
| Class identifiers | |
| Synonyms | Progestins; Progestagens; Gestagens, |
| Use | Contraception, menopause, hypogonadism, transgender women, others |
| ATC code | G03D |
| Biological target | Progesterone receptors (PRA, PRB, PRC, mPRs (e.g., mPRα, mPRβ, mPRγ, mPRδ, others)) |
| External links | |
| MeSH | D011372 |
| Legal status | |
| In Wikidata | |
Progestogens, also sometimes written progestins, progestagens or gestagens,[1] are a class of natural or synthetic steroid hormones that bind to and activate the progesterone receptors (PR).[2][3] Progesterone is the major and most important progestogen in the body. The progestogens are named for their function in maintaining pregnancy (i.e., progestational), although they are also present at other phases of the estrous and menstrual cycles.[2][3]
The progestogens are one of three types of sex hormones, the others being estrogens like estradiol and androgens/anabolic steroids like testosterone. In addition, they are one of the five major classes of steroid hormones, the others being the androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, and mineralocorticoids, as well as the neurosteroids. All endogenous progestogens are characterized by their basic 21-carbon skeleton, called a pregnane skeleton (C21). In similar manner, the estrogens possess an estrane skeleton (C18), and androgens, an androstane skeleton (C19).
The terms progesterone, progestogen, and progestin are mistakenly used interchangeably both in the scientific literature and in clinical settings.[1][4][5] Progestins are synthetic progestogens and are used in medicine.[2] Major examples of progestins include the 17α-hydroxyprogesterone derivative medroxyprogesterone acetate and the 19-nortestosterone derivative norethisterone. The progestins are structural analogues of progesterone and have progestogenic activity similarly, but differ from progesterone in their pharmacological properties in various ways.[5]
In addition to their roles as natural hormones, progestogens are used as medications, for instance in menopausal hormone therapy and transgender hormone therapy for transgender women; for information on progestogens as medications, see the progesterone (medication) and progestogen (medication) articles.
Types and examples
[edit]The most important progestogen in the body is progesterone (P4).[6][7] Other endogenous progestogens, with varying degrees of progestogenic activity, include 16α-hydroxyprogesterone (16α-OHP),[8] 17α-hydroxyprogesterone (17α-OHP) (very weak),[9] 20α-dihydroprogesterone (20α-DHP),[10][11] 20β-dihydroprogesterone (20β-DHP),[11] 5α-dihydroprogesterone (5α-DHP),[12] 5β-dihydroprogesterone (5β-DHP) (very weak),[13][14] 3β-dihydroprogesterone (3β-DHP),[15][16] 11-deoxycorticosterone (DOC),[17] and 5α-dihydrodeoxycorticosterone (5α-DHDOC).[18] They are all metabolites of progesterone, lying downstream of progesterone in terms of biosynthesis.
Biological function
[edit]The major tissues affected by progestogens include the uterus, vagina, cervix, breasts, testes, and brain. The main biological role of progestogens in the body is in the female reproductive system, and the male reproductive system,[19] with involvement in regulation of the menstrual cycle, maintenance of pregnancy, and preparation of the mammary glands for lactation and breastfeeding following parturition in women; in men progesterone affects spermiogenesis, sperm capacitation, and testosterone synthesis. Progestogens also have effects in other parts of the body. Unlike estrogens, progestogens have little or no role in feminization.[20]
Biochemistry
[edit]Biosynthesis
[edit]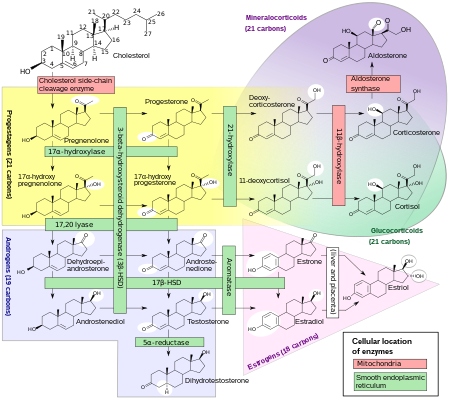
Progesterone is produced from cholesterol with pregnenolone as a metabolic intermediate. In the first step in the steroidogenic pathway, cholesterol is converted into pregnenolone, which serves as the precursor to the progestogens progesterone and 17α-hydroxyprogesterone. These progestogens, along with another steroid, 17α-hydroxypregnenolone, are the precursors of all other endogenous steroids, including the androgens, estrogens, glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, and neurosteroids. Thus, many tissues producing steroids, including the adrenal glands, testes, and ovaries, produce progestogens.
In some tissues, the enzymes required for the final product are not all located in a single cell. For example, in ovarian follicles, cholesterol is converted to androstenedione, an androgen, in the theca cells, which is then further converted into estrogen in the granulosa cells. Fetal adrenal glands also produce pregnenolone in some species, which is converted into progesterone and estrogens by the placenta (see below). In the human, the fetal adrenals produce dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) via the pregnenolone pathway.
| Sex | Sex hormone | Reproductive phase |
Blood production rate |
Gonadal secretion rate |
Metabolic clearance rate |
Reference range (serum levels) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SI units | Non-SI units | ||||||
| Men | Androstenedione | –
|
2.8 mg/day | 1.6 mg/day | 2200 L/day | 2.8–7.3 nmol/L | 80–210 ng/dL |
| Testosterone | –
|
6.5 mg/day | 6.2 mg/day | 950 L/day | 6.9–34.7 nmol/L | 200–1000 ng/dL | |
| Estrone | –
|
150 μg/day | 110 μg/day | 2050 L/day | 37–250 pmol/L | 10–70 pg/mL | |
| Estradiol | –
|
60 μg/day | 50 μg/day | 1600 L/day | <37–210 pmol/L | 10–57 pg/mL | |
| Estrone sulfate | –
|
80 μg/day | Insignificant | 167 L/day | 600–2500 pmol/L | 200–900 pg/mL | |
| Women | Androstenedione | –
|
3.2 mg/day | 2.8 mg/day | 2000 L/day | 3.1–12.2 nmol/L | 89–350 ng/dL |
| Testosterone | –
|
190 μg/day | 60 μg/day | 500 L/day | 0.7–2.8 nmol/L | 20–81 ng/dL | |
| Estrone | Follicular phase | 110 μg/day | 80 μg/day | 2200 L/day | 110–400 pmol/L | 30–110 pg/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 260 μg/day | 150 μg/day | 2200 L/day | 310–660 pmol/L | 80–180 pg/mL | ||
| Postmenopause | 40 μg/day | Insignificant | 1610 L/day | 22–230 pmol/L | 6–60 pg/mL | ||
| Estradiol | Follicular phase | 90 μg/day | 80 μg/day | 1200 L/day | <37–360 pmol/L | 10–98 pg/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 250 μg/day | 240 μg/day | 1200 L/day | 699–1250 pmol/L | 190–341 pg/mL | ||
| Postmenopause | 6 μg/day | Insignificant | 910 L/day | <37–140 pmol/L | 10–38 pg/mL | ||
| Estrone sulfate | Follicular phase | 100 μg/day | Insignificant | 146 L/day | 700–3600 pmol/L | 250–1300 pg/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 180 μg/day | Insignificant | 146 L/day | 1100–7300 pmol/L | 400–2600 pg/mL | ||
| Progesterone | Follicular phase | 2 mg/day | 1.7 mg/day | 2100 L/day | 0.3–3 nmol/L | 0.1–0.9 ng/mL | |
| Luteal phase | 25 mg/day | 24 mg/day | 2100 L/day | 19–45 nmol/L | 6–14 ng/mL | ||
Notes and sources
Notes: "The concentration of a steroid in the circulation is determined by the rate at which it is secreted from glands, the rate of metabolism of precursor or prehormones into the steroid, and the rate at which it is extracted by tissues and metabolized. The secretion rate of a steroid refers to the total secretion of the compound from a gland per unit time. Secretion rates have been assessed by sampling the venous effluent from a gland over time and subtracting out the arterial and peripheral venous hormone concentration. The metabolic clearance rate of a steroid is defined as the volume of blood that has been completely cleared of the hormone per unit time. The production rate of a steroid hormone refers to entry into the blood of the compound from all possible sources, including secretion from glands and conversion of prohormones into the steroid of interest. At steady state, the amount of hormone entering the blood from all sources will be equal to the rate at which it is being cleared (metabolic clearance rate) multiplied by blood concentration (production rate = metabolic clearance rate × concentration). If there is little contribution of prohormone metabolism to the circulating pool of steroid, then the production rate will approximate the secretion rate." Sources: See template. | |||||||
Ovarian production
[edit]Progesterone is the major progestogen produced by the corpus luteum of the ovary in all mammalian species. Luteal cells possess the necessary enzymes to convert cholesterol to pregnenolone, which is subsequently converted into progesterone. Progesterone is highest in the diestrus phase of the estrous cycle.
Placental production
[edit]The role of the placenta in progestogen production varies by species. In the sheep, horse, and human, the placenta takes over the majority of progestogen production, whereas in other species the corpus luteum remains the primary source of progestogens. In the sheep and human, progesterone is the major placental progestogen.
The equine placenta produces a variety of progestogens, primarily 5α-dihydroprogesterone and 5α,20α-tetrahydroprogesterone, beginning on day 60. A complete luteo-placental shift occurs by day 120–150.
Chemistry
[edit]The endogenous progestogens are naturally occurring pregnane steroids with ketone and/or hydroxyl groups at the C3 and C20 positions.
Medical use
[edit]Progestogens, including both progesterone and progestins, are used medically in hormonal birth control, hormone therapy, to treat gynecological disorders, to suppress sex hormone levels for various purposes, and for other indications.
References
[edit]- ^ a b Tekoa L. King; Mary C. Brucker (25 October 2010). Pharmacology for Women's Health. Jones & Bartlett Publishers. p. 373. ISBN 978-1-4496-5800-7.
- ^ a b c Michelle A. Clark; Richard A. Harvey; Richard Finkel; Jose A. Rey; Karen Whalen (15 December 2011). Pharmacology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. p. 322. ISBN 978-1-4511-1314-3.
- ^ a b Bhattacharya (1 January 2003). Pharmacology, 2/e. Elsevier India. p. 378. ISBN 978-81-8147-009-6.
- ^ Tara Parker-Pope (25 March 2008). The Hormone Decision. Simon and Schuster. p. 228. ISBN 978-1-4165-6201-6.
- ^ a b Grant, Ellen (1994). Sexual chemistry: understanding your hormones, the Pill and HRT. Great Britain: Cedar. p. 39. ISBN 978-0749313630.
- ^ D. T. Okpako (22 February 1991). Principles of Pharmacology: A Tropical Approach. Cambridge University Press. pp. 536–. ISBN 978-0-521-34095-3.
- ^ John Laycock; Karim Meeran (1 October 2012). Integrated Endocrinology. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 235–. ISBN 978-1-118-45057-4.
- ^ Storbeck KH, Swart P, Africander D, Conradie R, Louw R, Swart AC (2011). "16α-hydroxyprogesterone: origin, biosynthesis and receptor interaction". Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 336 (1–2): 92–101. doi:10.1016/j.mce.2010.11.016. PMID 21095220. S2CID 5503049.
- ^ Attardi BJ, Zeleznik A, Simhan H, Chiao JP, Mattison DR, Caritis SN (2007). "Comparison of progesterone and glucocorticoid receptor binding and stimulation of gene expression by progesterone, 17-alpha hydroxyprogesterone caproate, and related progestins". Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 197 (6): 599.e1–7. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.05.024. PMC 2278032. PMID 18060946.
- ^ Marianne J. Legato (29 October 2009). Principles of Gender-Specific Medicine. Academic Press. pp. 617–. ISBN 978-0-08-092150-1.
- ^ a b Bertram G. Katzung (30 November 2017). Basic and Clinical Pharmacology 14th Edition. McGraw-Hill Education. p. 728. ISBN 978-1-259-64116-9.
In addition to progesterone, 20α- and 20β-hydroxyprogesterone (20α- and 20β-hydroxy-4-pregnene-3-one) also are found. These compounds have about one-fifth the progestational activity of progesterone in humans and other species.
- ^ Rupprecht R, Reul JM, Trapp T, van Steensel B, Wetzel C, Damm K, Zieglgänsberger W, Holsboer F (1993). "Progesterone receptor-mediated effects of neuroactive steroids". Neuron. 11 (3): 523–30. doi:10.1016/0896-6273(93)90156-l. PMID 8398145. S2CID 11205767.
- ^ Lima-Hernández, Francisco J.; Beyer, Carlos; Gómora-Arrati, Porfirio; García-Juárez, Marcos; Encarnación-Sánchez, José L.; Etgen, Anne M.; González-Flores, Oscar (2012). "Src kinase signaling mediates estrous behavior induced by 5β-reduced progestins, GnRH, prostaglandin E2 and vaginocervical stimulation in estrogen-primed rats". Hormones and Behavior. 62 (5): 579–584. doi:10.1016/j.yhbeh.2012.09.004. ISSN 0018-506X. PMID 23010621. S2CID 40245594.
- ^ Illingworth DV, Elsner C, De Groot K, Flickinger GL, Mikhail G (February 1977). "A specific progesterone receptor of myometrial cytosol from the rhesus monkey". J. Steroid Biochem. 8 (2): 157–60. doi:10.1016/0022-4731(77)90040-1. PMID 405534.
- ^ Junkermann H, Runnebaum B, Lisboa BP (July 1977). "New progesterone metabolites in human myometrium". Steroids. 30 (1): 1–14. doi:10.1016/0039-128X(77)90131-3. PMID 919010. S2CID 28420255.
In the Clauberg bioassay the 3β-hydroxy-4-pregnen-20-one shows about the same potency as progesterone (34). In regard to the biological activity of the 3α epimer no data are available.
- ^ Pincus G, Miyake T, Merrill AP, Longo P (November 1957). "The bioassay of progesterone". Endocrinology. 61 (5): 528–33. doi:10.1210/endo-61-5-528. PMID 13480263.
- ^ The Adrenocortical Hormones: Their Origin · Chemistry, Physiology, and Pharmacology. Springer Science & Business Media. 27 November 2013. pp. 610–. ISBN 978-3-642-88385-9.
- ^ Edwards HE, Vimal S, Burnham WM (2005). "The acute anticonvulsant effects of deoxycorticosterone in developing rats: role of metabolites and mineralocorticoid-receptor responses". Epilepsia. 46 (12): 1888–97. doi:10.1111/j.1528-1167.2005.00295.x. PMID 16393154. S2CID 26030656.
- ^ Oettel, M & Mukhopadhyay, AK (2004). "Progesterone: the forgotten hormone in men?". Aging Male. 7 (3): 236–57. doi:10.1080/13685530400004199. PMID 15669543. S2CID 115377.
- ^ "Progesterone". www.hormone.org. Retrieved 2021-12-11.
- ^ Häggström, Mikael; Richfield, David (2014). "Diagram of the pathways of human steroidogenesis". WikiJournal of Medicine. 1 (1). doi:10.15347/wjm/2014.005. ISSN 2002-4436.
Further reading
[edit]- Utian WH, Shoupe D, Bachmann G, Pinkerton JV, Pickar JH (June 2001). "Relief of vasomotor symptoms and vaginal atrophy with lower doses of conjugated equine estrogens and medroxyprogesterone acetate". Fertil. Steril. 75 (6): 1065–79. doi:10.1016/S0015-0282(01)01791-5. PMID 11384629.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) (the Women's Health, Osteoporosis, Progestin, Estrogen study) - Hulley S, Grady D, Bush T, et al. (August 1998). "Randomized trial of estrogen plus progestin for secondary prevention of coronary heart disease in postmenopausal women. Heart and Estrogen/progestin Replacement Study (HERS) Research Group". JAMA. 280 (7): 605–13. doi:10.1001/jama.280.7.605. PMID 9718051.
External links
[edit]- Progestins at the U.S. National Library of Medicine Medical Subject Headings (MeSH)
- The Nomenclature of Steroids
- The Million Women Study